Chlamydia medication is essential for treating this common sexually transmitted infection. While chlamydia often goes unnoticed due to its subtle symptoms, it can have serious long-term health consequences if left untreated. Understanding the various treatment options, prevention strategies, and potential risks is crucial for managing chlamydia effectively.
This guide explores the different types of medications used to treat chlamydia, how they work, and their potential side effects. We’ll also discuss the importance of completing the full course of medication as prescribed, and how to access treatment safely and responsibly.
Chlamydia: An Overview
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteriumChlamydia trachomatis*. It can affect both men and women, and is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people don’t know they have it.
Symptoms of Chlamydia
While many people with chlamydia don’t experience any symptoms, some may notice:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge in women
- Burning sensation during urination in both men and women
- Pain during intercourse in women
- Pain or swelling in the testicles in men
Long-Term Health Consequences
If left untreated, chlamydia can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women
- Infertility in both men and women
- Ectopic pregnancy in women
- Chronic pain in both men and women
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of chlamydia are crucial to prevent these complications. Regular testing is recommended for sexually active individuals, especially those who have multiple partners or engage in unprotected sex.
Chlamydia Medication: Treatment Options
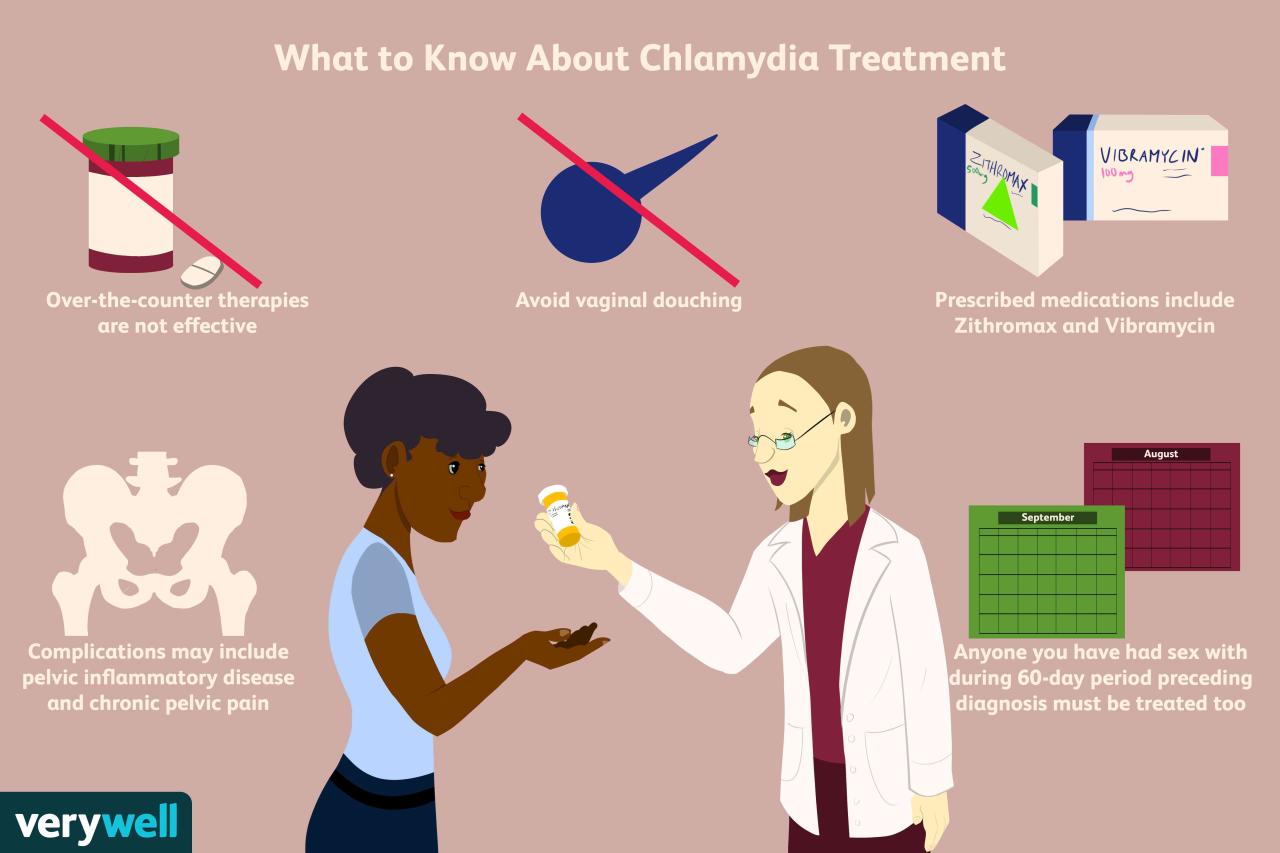
Chlamydia is typically treated with antibiotics, which effectively kill the bacteria causing the infection.
Common Medications
The most common medications used to treat chlamydia include:
- Azithromycin: A single dose of this antibiotic is usually effective in treating chlamydia. It is taken orally.
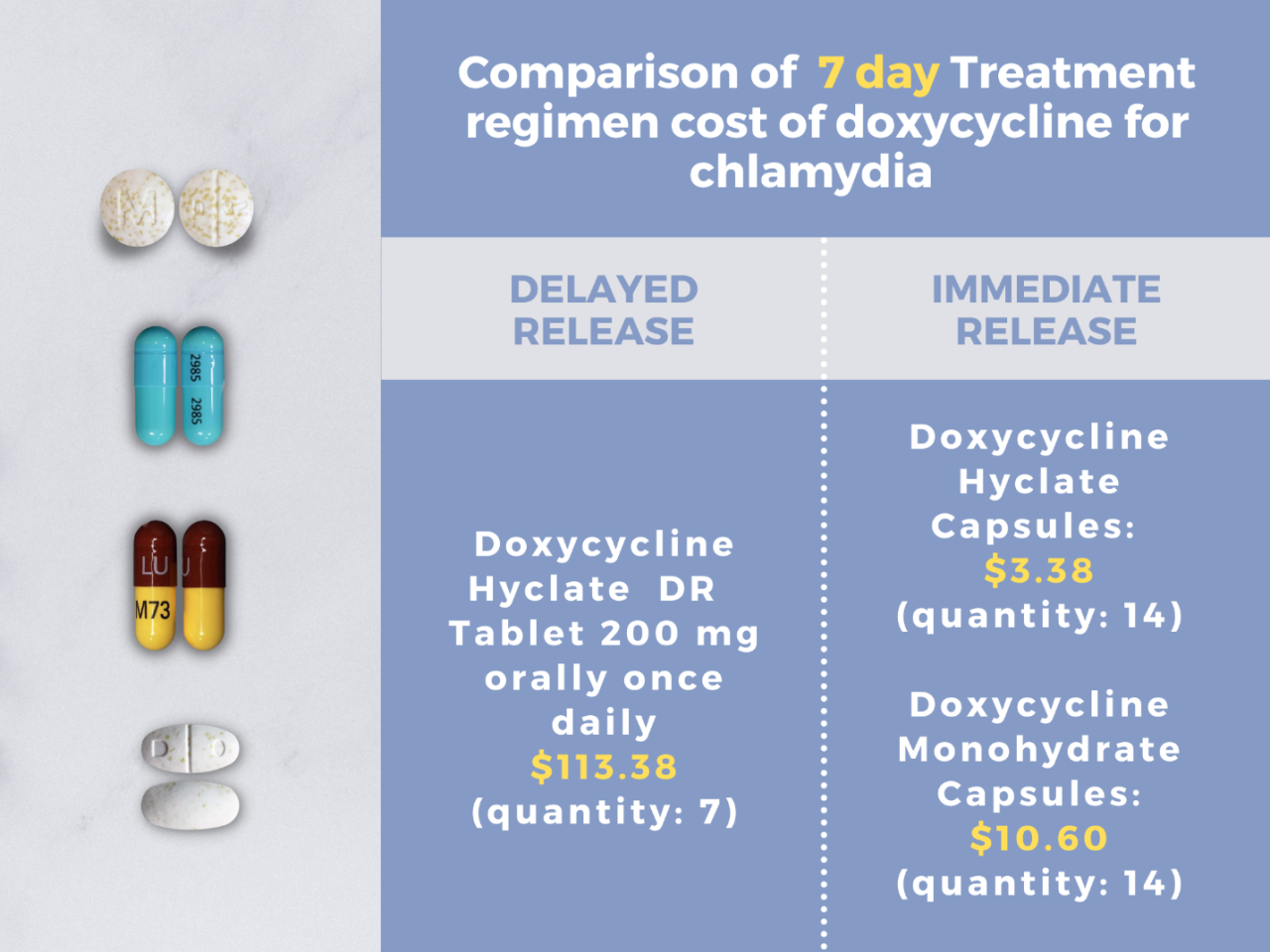
- Doxycycline: This antibiotic is taken twice a day for a week. It is also taken orally.
Mechanism of Action
Both azithromycin and doxycycline work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. They target the bacterial ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis. By blocking this process, the antibiotics effectively kill the bacteria.
Effectiveness and Side Effects
Both azithromycin and doxycycline are highly effective in treating chlamydia. However, they can cause some side effects, such as:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Headache
Importance of Completing the Full Course, Chlamydia medication
It is crucial to complete the full course of medication as prescribed by your doctor, even if you start feeling better. This ensures that all the bacteria are killed and prevents the infection from returning.
Obtaining Chlamydia Medication
To get chlamydia medication, you need to be diagnosed with the infection by a healthcare professional.
Diagnosis
Chlamydia is typically diagnosed through a urine test or a swab taken from the cervix in women or the urethra in men.
Obtaining Medication
Once diagnosed, you can obtain chlamydia medication through:
- Doctor’s Prescription: Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate medication and provide instructions on how to take it.
- Online Pharmacies: Some online pharmacies offer chlamydia medication, but it is important to ensure that they are licensed and reputable. You should also consult with your doctor before ordering medication online.
Seeking Treatment from a Qualified Healthcare Professional
It is essential to seek treatment from a qualified healthcare professional for chlamydia. They can provide accurate diagnosis, prescribe the appropriate medication, and monitor your progress.
Safe and Responsible Medication Use
Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when taking chlamydia medication. Do not share your medication with anyone else, and dispose of unused medication properly.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Chlamydia is primarily spread through sexual contact.
Modes of Transmission
Chlamydia can be transmitted through:
- Vaginal sex
- Anal sex
- Oral sex
Prevention Strategies
You can reduce your risk of chlamydia infection by:
- Practicing safe sex: Use condoms consistently and correctly during all sexual activities.
- Getting tested regularly: If you are sexually active, it is important to get tested for chlamydia regularly, especially if you have multiple partners or engage in unprotected sex.
- Talking to your partner: Be open and honest with your partner about your sexual health and get tested together.
Role of Safe Sex Practices
Safe sex practices, such as using condoms, are essential for preventing the spread of chlamydia and other STIs. Condoms create a barrier that prevents the exchange of bodily fluids, which can carry the bacteria that cause chlamydia.
Chlamydia and Pregnancy
Chlamydia infection during pregnancy can pose risks to both the mother and the baby.
Potential Risks
Chlamydia can cause:
- Premature birth: Chlamydia infection can trigger inflammation in the cervix, which can lead to premature labor.
- Low birth weight: Babies born to mothers with chlamydia are more likely to have low birth weight.
- Pneumonia and conjunctivitis in newborns: Chlamydia can be passed to the baby during childbirth, causing pneumonia or conjunctivitis.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of chlamydia during pregnancy are essential to prevent these complications. Pregnant women should be tested for chlamydia during their first prenatal visit and again in the third trimester.
Resources and Support
If you are pregnant and have chlamydia, your doctor can provide you with information and support. They can also prescribe the appropriate medication to treat the infection.
Ending Remarks: Chlamydia Medication
Chlamydia is a treatable infection, and early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications. By understanding the risks, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your sexual health and protect yourself and your partners. Remember, regular testing and safe sex practices are crucial for preventing chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections.