Depression medication plays a crucial role in managing this common mental health condition. These medications work by influencing brain chemistry, targeting neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. While there are various types of depression medication, each works differently and carries its own set of benefits and risks.
Understanding the different categories, how they work, and potential side effects is essential for making informed decisions about treatment. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action based on individual needs and medical history.
Types of Depression Medication
Depression is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. While lifestyle changes, therapy, and support groups can be helpful, sometimes medication is necessary to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
There are several different types of depression medication, each working in different ways to target specific brain chemicals.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are the most commonly prescribed type of antidepressant. They work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other functions. SSRIs are generally well-tolerated and have fewer side effects than older antidepressants.
- Examples:Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Paroxetine (Paxil), Citalopram (Celexa), Escitalopram (Lexapro)
- Common Uses:Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Side Effects:Nausea, headache, sexual dysfunction, weight gain, insomnia, and anxiety.
- Potential Interactions:SSRIs can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Norepinephrine is another neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood, attention, and energy levels. SNRIs are often effective for people who have not responded well to SSRIs.
- Examples:Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta), Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq)
- Common Uses:Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and fibromyalgia.
- Side Effects:Nausea, headache, sweating, increased blood pressure, and insomnia.
- Potential Interactions:SNRIs can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
TCAs are older antidepressants that have been used for decades. They work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. TCAs can be effective for depression, but they are often associated with more side effects than SSRIs and SNRIs.
- Examples:Amitriptyline (Elavil), Imipramine (Tofranil), Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Common Uses:Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and sleep disorders.
- Side Effects:Drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction.
- Potential Interactions:TCAs can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs), Depression medication
MAOIs are a class of antidepressants that work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. MAOIs are generally reserved for people who have not responded to other types of antidepressants.
- Examples:Phenelzine (Nardil), Tranylcypromine (Parnate), Isocarboxazid (Marplan)
- Common Uses:Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and atypical depression.
- Side Effects:Dizziness, headache, drowsiness, insomnia, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction.
- Potential Interactions:MAOIs can interact with a wide range of medications, foods, and supplements. It is crucial to follow a strict diet and avoid certain substances while taking MAOIs.
Atypical Antidepressants
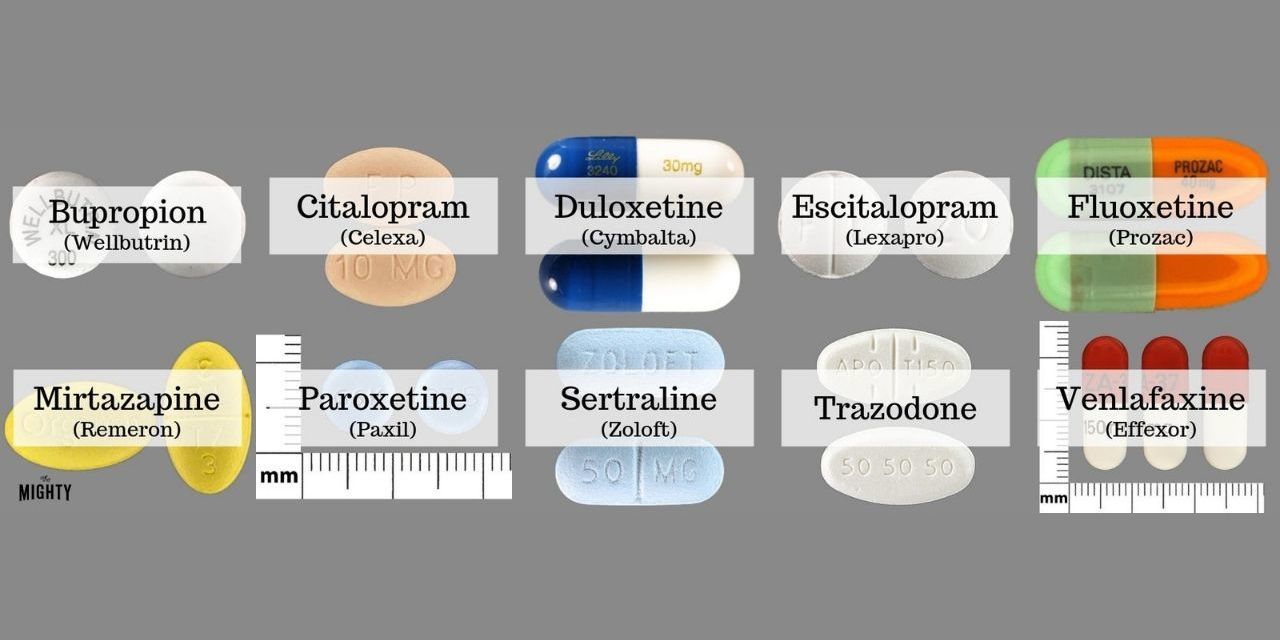
Atypical antidepressants are a group of medications that do not fit neatly into any of the other categories. They work by affecting different neurotransmitters and brain pathways.
- Examples:Bupropion (Wellbutrin), Mirtazapine (Remeron), Trazodone (Desyrel), Vilazodone (Viibryd)
- Common Uses:Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and smoking cessation.
- Side Effects:Dry mouth, constipation, weight gain, insomnia, and anxiety.
- Potential Interactions:Atypical antidepressants can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications, supplements, and herbal remedies.
How Depression Medication Works
Depression medication works by influencing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, particularly serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other functions. By altering the balance of these chemicals, depression medication can help alleviate symptoms of depression.
For example, SSRIs and SNRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, respectively, leading to an increase in their levels in the brain. This increase in neurotransmitter levels helps to improve mood, reduce anxiety, and enhance overall well-being.
MAOIs work by inhibiting the enzyme that breaks down these neurotransmitters, leading to a similar effect. Atypical antidepressants have more complex mechanisms of action, often affecting multiple neurotransmitter systems.
It’s important to note that depression medication doesn’t “cure” depression; it helps manage symptoms. While some people may experience a significant improvement in their symptoms with medication, others may need to combine medication with therapy or lifestyle changes to achieve optimal results.
Benefits of Depression Medication
Depression medication can provide significant benefits for individuals struggling with depression. These benefits can include:
- Symptom Relief:Medication can help reduce or eliminate symptoms of depression, such as sadness, hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in activities.
- Improved Mood:Medication can help elevate mood and promote feelings of happiness and well-being.
- Increased Energy Levels:Depression medication can help combat fatigue and increase energy levels, making it easier to engage in daily activities.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function:Some medications can improve concentration, focus, and memory, which can be helpful for individuals struggling with cognitive impairments related to depression.
- Improved Quality of Life:By alleviating symptoms and improving mood, depression medication can help individuals lead more fulfilling and productive lives.
It’s important to remember that the effectiveness of depression medication can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience significant relief from their symptoms with medication, while others may need to combine medication with therapy or lifestyle changes to achieve optimal results.
Risks and Side Effects
Like all medications, depression medication can have potential risks and side effects. These side effects can vary depending on the type of medication and the individual’s sensitivity. Some common side effects include:
- Nausea:This is a common side effect of many antidepressants, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs.
- Weight Gain:Some antidepressants, such as TCAs and SNRIs, can cause weight gain.
- Sexual Dysfunction:This is a common side effect of many antidepressants, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs. It can include decreased libido, difficulty achieving orgasm, and erectile dysfunction.
- Insomnia:Some antidepressants can cause insomnia, especially when taken in the evening.
- Drowsiness:TCAs and MAOIs can cause drowsiness.
- Anxiety:Some antidepressants, particularly SSRIs, can initially worsen anxiety symptoms.
It’s important to discuss any potential side effects with your healthcare provider. They can help you manage any side effects and determine if the benefits of medication outweigh the risks.
It’s also crucial to monitor for any unusual or severe side effects. If you experience any serious or concerning side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Interactions and Contraindications
Depression medication can interact with other medications, supplements, and substances. These interactions can potentially increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of the medication. It’s crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, including over-the-counter medications.
There are also contraindications for specific medications. For example, some antidepressants are not recommended for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, or individuals with certain pre-existing medical conditions. It’s essential to discuss your medical history and any potential contraindications with your healthcare provider before starting any depression medication.
Choosing the Right Medication
Choosing the right depression medication is a collaborative process that involves your healthcare provider and you. Your healthcare provider will consider factors such as your individual needs, symptoms, medical history, and potential interactions with other medications. They will also discuss your preferences and concerns regarding medication options.
The process of selecting the right medication may involve trial and error. Your healthcare provider may start with a low dose of medication and gradually increase it until you experience symptom relief. They may also monitor your progress and adjust the medication or dosage as needed.
It’s important to be patient and communicate openly with your healthcare provider about your experiences with medication. It may take some time to find the right medication and dosage that works best for you.
Using Depression Medication Safely and Effectively
To use depression medication safely and effectively, it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully. This includes taking the medication as prescribed, at the right time, and for the recommended duration. It’s also important to refill your medication on time to avoid running out.
If you experience any side effects, discuss them with your healthcare provider. They may be able to adjust your dosage or recommend strategies for managing side effects. It’s also important to keep track of your symptoms and progress to ensure the medication is working effectively.
Remember, depression medication is a tool to help manage symptoms and improve your well-being. It’s not a quick fix, and it’s important to be patient and consistent with your treatment plan.
Therapy and Medication
Therapy and medication can be used together to effectively treat depression. Therapy can help you understand your depression, develop coping skills, and address underlying issues that may be contributing to your symptoms. Medication can help alleviate symptoms and improve your mood, making it easier to engage in therapy and benefit from its effects.
While medication can address the biological aspects of depression, therapy can address the psychological and social factors that may be contributing to your condition. Combining therapy and medication can provide a comprehensive approach to treatment and improve long-term outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes and Depression Medication
Lifestyle changes can complement depression medication and enhance its effectiveness. These changes can include:
- Regular Exercise:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Healthy Diet:Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve mood and energy levels.
- Stress Management Techniques:Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can worsen depression symptoms.
- Adequate Sleep:Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Social Connection:Spending time with loved ones and engaging in social activities can improve mood and reduce feelings of isolation.
Making these lifestyle changes can enhance the effectiveness of depression medication and promote overall well-being.
Alternatives to Medication
There are alternative treatments for depression that do not involve medication. These alternatives can be effective for some individuals, but they may not be suitable for everyone.
- Psychotherapy:Therapy can help you understand your depression, develop coping skills, and address underlying issues that may be contributing to your symptoms. Different types of therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT), have been shown to be effective for depression.
- Exercise:Exercise releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Mindfulness Practices:Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can worsen depression symptoms.
- Light Therapy:Light therapy can be helpful for seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression that occurs during the winter months.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT):ECT is a more invasive treatment option that involves inducing a brief seizure under general anesthesia. It is typically reserved for individuals with severe depression who have not responded to other treatments.
It’s important to discuss alternative treatment options with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your individual needs.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are struggling with depression, it’s crucial to seek professional help from a qualified healthcare professional. They can diagnose your condition, recommend appropriate treatment options, and provide ongoing support.
There are many resources available for individuals seeking support and treatment for depression. These resources include:
- Primary Care Physicians:Your primary care physician can provide initial assessment and referral to a mental health professional.
- Psychiatrists:Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of mental health conditions. They can prescribe medication and provide therapy.
- Psychologists:Psychologists are mental health professionals who provide therapy but cannot prescribe medication.
- Therapists:Therapists are mental health professionals who provide therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT).
- Support Groups:Support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to connect with others who understand their experiences.
- Online Resources:Many online resources provide information about depression, treatment options, and support groups.
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness. Don’t hesitate to reach out for professional support if you are struggling with depression.
Ultimate Conclusion
Depression medication can be a valuable tool for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. However, it’s important to remember that medication is often most effective when combined with therapy and lifestyle changes. By working closely with a healthcare professional, individuals can create a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and promotes long-term well-being.