What is RTI in Education? It’s a revolutionary approach to supporting students’ academic and behavioral needs, shifting the focus from reactive intervention to proactive prevention. RTI, or Response to Intervention, acts as a framework for identifying students who are struggling early on and providing them with the necessary support to thrive.
Imagine a classroom where every student has the chance to reach their full potential. This is the vision behind RTI, a multi-tiered system that utilizes data-driven strategies to address individual needs and foster student growth. By implementing universal screening, targeted interventions, and continuous progress monitoring, RTI empowers educators to provide personalized support and guide students towards success.
What is RTI in Education?
RTI, or Response to Intervention, is a framework that aims to support students’ academic and behavioral needs by providing early intervention and tailored support. This framework focuses on identifying students who are struggling early on and providing them with the appropriate interventions to help them succeed.
Definition of RTI in Education
RTI is a multi-tiered system of support (MTSS) that uses a data-driven approach to identify students who are struggling and provide them with the appropriate interventions. The core principles of RTI include:
- Early identification and intervention:RTI emphasizes identifying students at risk for academic or behavioral difficulties as early as possible. This allows for timely intervention and prevents problems from escalating.
- Data-driven decision-making:RTI relies on data collection and analysis to monitor student progress and make informed decisions about interventions. This ensures that interventions are effective and tailored to individual student needs.
- Tiered interventions:RTI utilizes a tiered system of interventions, with increasing intensity and support provided as needed. This allows for individualized support based on student needs and progress.
- Collaboration and communication:RTI requires collaboration among teachers, administrators, parents, and specialists to ensure that students receive the best possible support. Open communication and shared decision-making are essential for successful RTI implementation.
The key components of RTI include:
- Universal screening:This involves administering assessments to all students to identify those who may be at risk for academic or behavioral difficulties. Universal screening helps to cast a wide net and ensure that no student falls through the cracks.
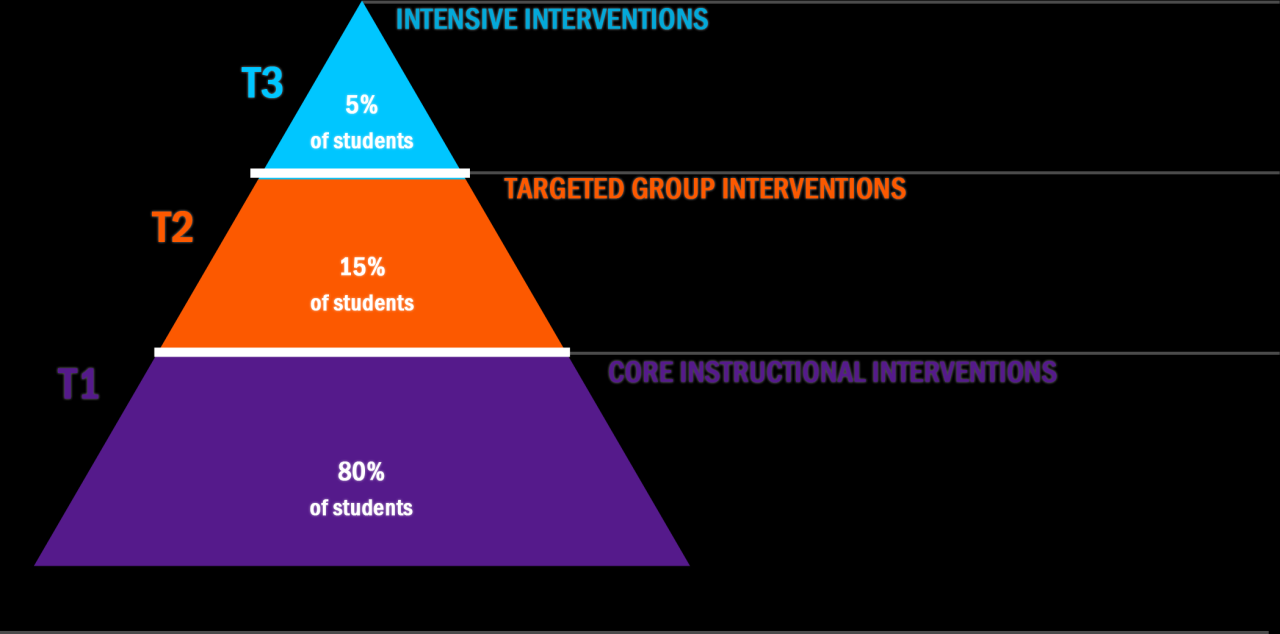
- Tiered interventions:RTI uses a tiered system of interventions to provide increasingly intensive support to students who need it. The three tiers of intervention are:
- Tier 1:This tier provides high-quality instruction and support to all students. This includes evidence-based practices and strategies that are designed to meet the needs of the majority of students.
- Tier 2:This tier provides targeted interventions to students who are not making adequate progress in Tier 1. These interventions are typically more intensive and focused on specific areas of need.
- Tier 3:This tier provides the most intensive and individualized support to students who have not responded to interventions in Tiers 1 and 2. Students in Tier 3 may require specialized instruction, therapy, or other services.
- Progress monitoring:This involves regularly assessing student progress to determine the effectiveness of interventions and adjust them as needed. Progress monitoring data helps to ensure that interventions are working and that students are making progress toward their goals.
Purpose of RTI in Education
The primary goal of RTI is to improve educational outcomes for all students by providing early intervention and support to those who need it. RTI aims to:
- Identify students at risk early:By using universal screening and progress monitoring, RTI can identify students who are struggling before their difficulties become more severe. This allows for early intervention and prevents academic failure.
- Provide appropriate interventions:RTI uses a tiered system of interventions to provide individualized support based on student needs and progress. This ensures that students receive the interventions that are most likely to help them succeed.
- Prevent academic failure:By providing early intervention and support, RTI can help to prevent students from falling behind academically. This can lead to improved student achievement and a more positive learning experience.
- Promote student success:RTI aims to create a school environment that supports the success of all students. By providing early intervention and tailored support, RTI can help students to reach their full potential.
Tiers of Intervention in RTI
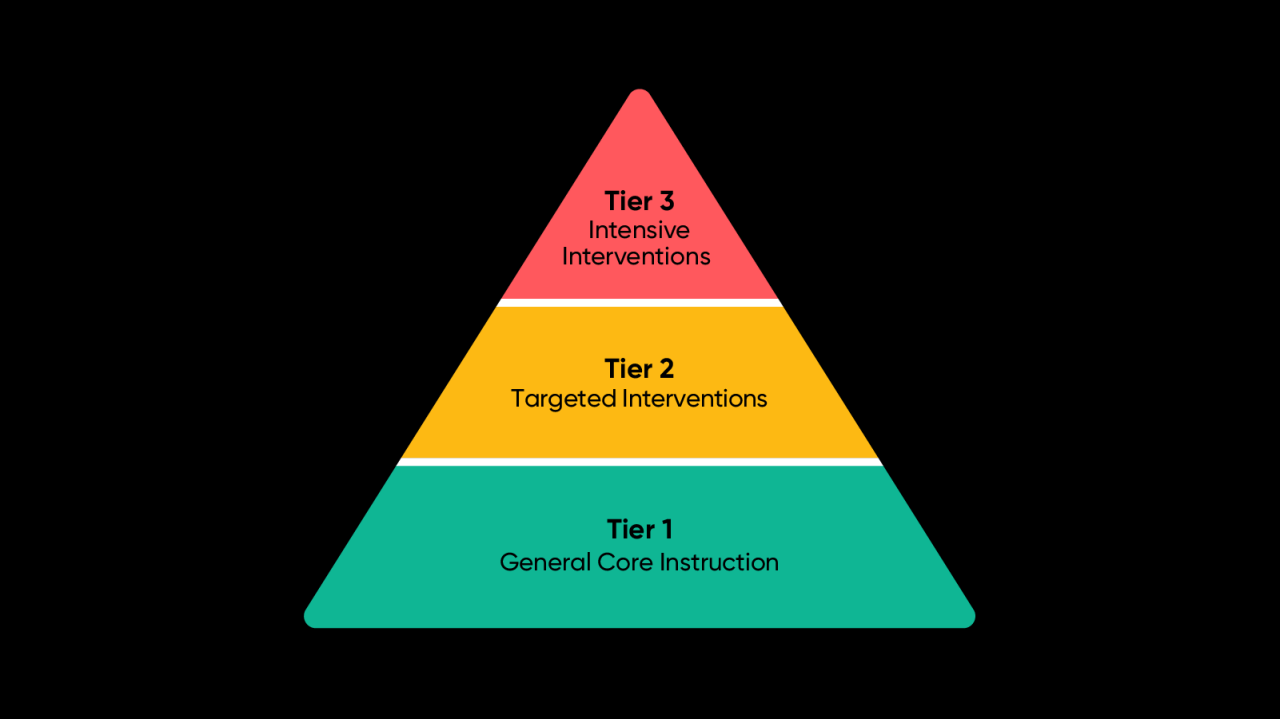
RTI utilizes a three-tiered system of interventions to provide increasingly intensive support to students who need it. Each tier has specific characteristics and purposes:
- Tier 1:This tier provides high-quality instruction and support to all students. It is the foundation of RTI and aims to meet the needs of the majority of students. Tier 1 interventions include:
- Evidence-based instructional practices: Teachers use research-supported methods to deliver instruction, such as explicit instruction, differentiated instruction, and cooperative learning.
- Universal screening: All students are assessed regularly to identify those who may be at risk for academic or behavioral difficulties. This helps to ensure that no student falls through the cracks.
- Positive classroom management: Teachers create a supportive and structured classroom environment that promotes student engagement and learning. This includes clear expectations, consistent routines, and positive reinforcement.
- Tier 2:This tier provides targeted interventions to students who are not making adequate progress in Tier
1. These interventions are more intensive and focused on specific areas of need. Tier 2 interventions include
- Small group instruction: Students receive additional support in small groups, focusing on specific skills or concepts that they are struggling with.
- Targeted strategies: Teachers use specific strategies to address individual student needs, such as graphic organizers, mnemonic devices, or peer tutoring.
- Increased frequency of progress monitoring: Students are assessed more frequently to monitor their progress and adjust interventions as needed.
- Tier 3:This tier provides the most intensive and individualized support to students who have not responded to interventions in Tiers 1 and
2. Tier 3 interventions include
- Individualized instruction: Students receive one-on-one or small group instruction tailored to their specific needs. This may involve specialized instruction, therapy, or other services.
- Intensive progress monitoring: Students are assessed very frequently to monitor their progress and make adjustments to interventions as needed.
- Collaboration with specialists: Teachers work closely with specialists, such as school psychologists or special education teachers, to develop and implement individualized interventions.
The intensity and duration of interventions vary across the tiers. Tier 1 interventions are the least intensive and are provided to all students. Tier 2 interventions are more intensive and are provided to a smaller group of students who need additional support.
Tier 3 interventions are the most intensive and are provided to a very small group of students who have not responded to interventions in the other tiers.
Role of Data in RTI
Data collection and analysis are essential components of RTI. Data is used to:
- Identify students at risk:Universal screening results provide valuable information about students who may be struggling academically or behaviorally. This data helps to identify students who need additional support.
- Monitor student progress:Progress monitoring data helps to track student growth over time and determine the effectiveness of interventions. This data allows teachers to adjust interventions as needed to ensure that students are making progress.
- Make informed decisions:Data helps to inform decision-making about interventions, student placement, and other aspects of RTI implementation. This ensures that decisions are based on evidence and not on assumptions.
Different types of data are used in RTI, including:
- Universal screening results:These results provide a snapshot of student performance at a particular point in time and help to identify students who may be at risk.
- Progress monitoring data:This data tracks student progress over time and provides information about the effectiveness of interventions.
- Student performance information:This includes data from classroom assessments, standardized tests, and other sources that provide information about student learning and achievement.
| Data Collection Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Universal screening | Identify students at risk for academic or behavioral difficulties |
| Progress monitoring | Track student progress over time and determine the effectiveness of interventions |
| Classroom assessments | Gather information about student learning and achievement in specific areas |
| Standardized tests | Compare student performance to national norms and identify areas of strength and weakness |
| Observations | Gather information about student behavior and engagement in the classroom |
| Teacher-made assessments | Assess student understanding of specific concepts or skills |
Benefits of RTI in Education
Implementing RTI in schools can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Improved student achievement:RTI can lead to improved student achievement by providing early intervention and tailored support to students who need it. This can help to close achievement gaps and ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed.
- Reduced need for special education services:RTI can help to reduce the need for special education services by providing early intervention and support to students who are struggling. This can help to keep students in the general education setting and provide them with the support they need to succeed.
- Enhanced student engagement:RTI can help to enhance student engagement by providing a more individualized and supportive learning environment. This can lead to increased motivation and a more positive learning experience for students.
- More equitable access to education:RTI can help to ensure that all students have equitable access to a high-quality education, regardless of their background or learning needs. This can help to close achievement gaps and create a more equitable learning environment for all students.
There are many real-world examples of schools successfully using RTI and achieving positive outcomes. For example, a study by the National Center for Learning Disabilities found that schools using RTI saw significant improvements in student achievement, particularly among students with learning disabilities.
Another study by the University of Oregon found that RTI implementation led to a decrease in the number of students referred for special education services.
Challenges of RTI Implementation
While RTI offers numerous benefits, implementing it effectively can present challenges for schools. These challenges may include:
- Lack of resources:Implementing RTI effectively requires resources, such as trained staff, time for professional development, and appropriate assessments. Schools may face challenges in securing these resources, especially in underfunded districts.
- Staff training:Teachers need to be trained on how to implement RTI effectively, including how to use data to make decisions about interventions, how to provide effective interventions, and how to collaborate with other stakeholders. This can require significant time and resources.
- Buy-in from stakeholders:RTI requires buy-in from all stakeholders, including teachers, administrators, parents, and students. This can be challenging to achieve, especially if stakeholders are unfamiliar with RTI or have concerns about its implementation.
- Time commitment:RTI requires a significant time commitment from teachers and administrators. This can be challenging in schools with limited resources and time constraints.
- Data management:Managing data effectively is crucial for RTI implementation. Schools may face challenges in collecting, analyzing, and using data to make informed decisions about interventions.
To overcome these challenges and ensure effective RTI implementation, schools can take several steps, including:
- Securing adequate resources:Schools need to secure adequate resources to support RTI implementation, including funding for staff training, assessments, and other materials. This may involve advocating for increased funding or finding creative ways to leverage existing resources.
- Providing ongoing professional development:Teachers need ongoing professional development to stay up-to-date on best practices for RTI implementation. This can include workshops, online courses, and peer coaching.
- Building stakeholder buy-in:Schools need to build buy-in from all stakeholders by providing clear communication about the benefits of RTI, involving stakeholders in the implementation process, and addressing their concerns.
- Prioritizing time for RTI:Schools need to prioritize time for RTI activities, such as data analysis, intervention planning, and collaboration. This may involve adjusting schedules or finding creative ways to make time for RTI.
- Implementing data management systems:Schools need to implement data management systems that are user-friendly and efficient. This can help to ensure that data is collected, analyzed, and used effectively to inform decision-making.
RTI and Special Education
RTI is closely related to special education. RTI can be used to identify students who may need special education services. If a student does not respond to interventions in Tiers 1 and 2, they may be referred for a special education evaluation.
The special education evaluation process determines whether the student meets the criteria for special education services.
RTI can help to ensure that students receive the appropriate support they need, whether in the general education setting or in special education. RTI can also help to reduce the number of students who are unnecessarily referred for special education evaluations.
RTI and Differentiated Instruction, What is rti in education
RTI and differentiated instruction are closely related. Differentiated instruction is a teaching approach that involves tailoring instruction to meet the needs of individual students. RTI principles can inform differentiated instruction practices by providing a framework for identifying student needs and providing appropriate interventions.
RTI data can be used to inform differentiated instruction. For example, if a student is struggling with reading comprehension, the teacher can use RTI data to determine the specific area of need and provide differentiated instruction that addresses that need.
This might involve providing the student with graphic organizers, reading strategies, or additional support in small groups.
RTI and Collaboration
Collaboration is essential for successful RTI implementation. Different stakeholders play important roles in RTI, including:
- Teachers:Teachers are responsible for providing high-quality instruction, implementing interventions, and monitoring student progress.
- Administrators:Administrators provide leadership and support for RTI implementation, including ensuring that resources are available, providing professional development, and monitoring progress.
- Parents:Parents are involved in the RTI process by being informed about their child’s progress and collaborating with teachers to develop interventions.
- Specialists:Specialists, such as school psychologists, special education teachers, and speech-language pathologists, provide expertise and support for students who need more intensive interventions.
Collaboration among stakeholders is essential for ensuring that students receive the appropriate support they need. This collaboration can take many forms, such as:
- Team meetings:Teachers, administrators, parents, and specialists meet regularly to discuss student progress, develop interventions, and coordinate services.
- Data sharing:Stakeholders share data about student performance and progress to inform decision-making.
- Communication:Stakeholders communicate regularly with each other to ensure that everyone is informed about student progress and needs.
The collaborative process involved in RTI implementation can be illustrated by the following flowchart:
[Insert flowchart here]
Final Wrap-Up
RTI is more than just a system; it’s a philosophy that emphasizes collaboration, data-driven decision-making, and a commitment to providing every student with the opportunity to succeed. By implementing RTI effectively, schools can create a culture of support, reduce the need for special education services, and empower students to reach their full potential.