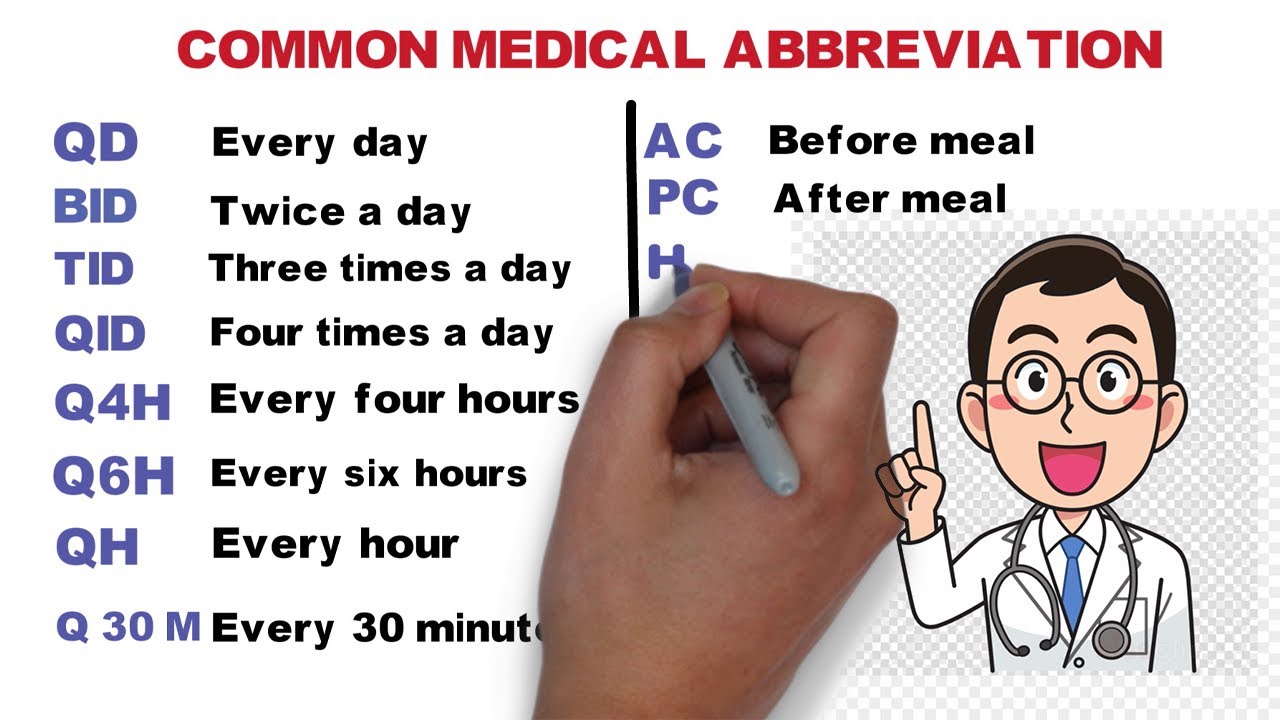
Medical assistants are the backbone of many healthcare settings, playing a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient patient care. From welcoming patients and managing schedules to assisting with examinations and administering medications, these professionals are essential to the day-to-day operations of hospitals, clinics, and private practices.
Their responsibilities encompass a wide range of administrative and clinical tasks, requiring a unique blend of skills, including strong communication, empathy, and technical proficiency. This combination allows medical assistants to effectively bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers, fostering a positive and supportive environment for all.
The Role of a Medical Assistant
Medical assistants play a crucial role in the healthcare system, providing essential support to physicians and other healthcare professionals. They perform a wide range of administrative and clinical tasks, ensuring the smooth operation of medical practices and the delivery of quality patient care.
Administrative Responsibilities
Medical assistants handle various administrative duties that contribute to the efficient functioning of a medical office. These tasks include:
- Scheduling appointments: Coordinating patient appointments, managing schedules, and ensuring timely access to healthcare services.
- Managing patient records: Maintaining accurate and confidential patient files, including medical history, insurance information, and treatment records.
- Answering phones and handling correspondence: Responding to patient inquiries, scheduling appointments, and relaying messages to healthcare providers.
- Billing and insurance processing: Assisting with insurance claims, verifying patient coverage, and managing billing procedures.
Clinical Responsibilities
Medical assistants also perform a variety of clinical tasks under the supervision of physicians and nurses. These responsibilities include:
- Taking vital signs: Measuring blood pressure, temperature, pulse, and respiration rates to assess patient health.
- Assisting with examinations: Preparing patients for examinations, assisting with procedures, and providing comfort and support.
- Administering medication: Preparing and administering medications, following proper protocols and ensuring patient safety.
- Collecting and processing specimens: Drawing blood, collecting urine samples, and preparing specimens for laboratory analysis.
Education and Training Requirements

Aspiring medical assistants can pursue various educational pathways to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills for this profession. These pathways typically involve a combination of classroom instruction and hands-on training.
Educational Pathways
The most common educational options for medical assistants include:
- Associate degree programs: Two-year programs that provide a comprehensive understanding of medical assisting principles and practices.
- Certificate programs: Shorter programs that focus on specific aspects of medical assisting, such as administrative or clinical tasks.
Essential Skills and Knowledge
During their training, medical assistants acquire a wide range of skills and knowledge, including:
- Medical terminology: Understanding the language used in healthcare settings, including anatomical terms, medical procedures, and diagnoses.
- Patient care techniques: Learning how to provide basic patient care, including taking vital signs, assisting with examinations, and administering medications.
- Administrative procedures: Mastering the skills necessary for managing patient records, scheduling appointments, and handling insurance claims.
- Medical software and equipment: Gaining proficiency in using electronic health records (EHRs), medical billing software, and common medical equipment.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Medical assistants are encouraged to pursue continuing education and professional development opportunities to stay up-to-date with advancements in healthcare and maintain their skills. This may include:
- Attending conferences and workshops: Learning about new technologies, procedures, and best practices in medical assisting.
- Taking continuing education courses: Enhancing their knowledge and skills in specific areas of medical assisting.
- Pursuing certifications: Obtaining professional certifications, such as the Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) credential, to demonstrate their expertise and enhance their career prospects.
Essential Skills and Qualities
To succeed as a medical assistant, individuals need a combination of soft skills, technical skills, and ethical considerations. These qualities are essential for providing effective patient care and contributing to a positive healthcare environment.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are interpersonal qualities that enable medical assistants to interact effectively with patients, colleagues, and other healthcare professionals. These skills include:
- Communication: Clearly and concisely communicating with patients, physicians, and other healthcare team members, both verbally and in writing.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with other healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive patient care.
- Empathy: Understanding and responding to the emotional needs of patients, providing compassion and support.
- Problem-solving: Identifying and resolving issues that may arise in the medical office or during patient care.
Technical Skills, Medical assistant
Technical skills are essential for performing the clinical and administrative tasks required of a medical assistant. These skills include:
- Proficiency in medical software: Using electronic health records (EHRs), medical billing software, and other healthcare applications.
- Knowledge of medical equipment: Operating common medical equipment, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) machines, blood pressure monitors, and thermometers.
- Clinical procedures: Performing basic clinical procedures, such as taking vital signs, administering medications, and collecting specimens.
Ethical Considerations

Medical assistants must adhere to strict ethical guidelines and maintain patient confidentiality. Key ethical considerations include:
- Patient privacy: Protecting patient information and ensuring confidentiality in all interactions.
- Professionalism: Maintaining a professional demeanor and ethical conduct in all interactions with patients and colleagues.
- Honesty and integrity: Acting with honesty and integrity in all aspects of their work, upholding the highest ethical standards.
Career Opportunities and Job Outlook
Medical assistants are in high demand across a wide range of healthcare settings. They work in hospitals, clinics, private practices, and other healthcare facilities, providing essential support to physicians and other healthcare professionals.
Healthcare Settings
Medical assistants find employment in various healthcare settings, including:
- Hospitals: Assisting physicians and nurses in inpatient and outpatient settings.
- Clinics: Providing administrative and clinical support in primary care, specialty, and urgent care settings.
- Private practices: Working in physician offices, providing a wide range of administrative and clinical support.
- Other healthcare facilities: Working in nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and other healthcare organizations.
Job Market Trends and Growth
The demand for medical assistants is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by factors such as an aging population, increasing healthcare needs, and the expansion of healthcare services. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects a 15% growth in medical assistant employment from 2020 to 2030, significantly faster than the average for all occupations.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Medical assistants have various career paths and advancement opportunities. With experience and continued education, they can progress to roles such as:
- Office manager: Managing the administrative operations of a medical office.
- Medical billing specialist: Specializing in medical billing and insurance processing.
- Clinical coordinator: Coordinating patient care and managing clinical operations.
- Healthcare administrator: Managing the administrative and financial aspects of healthcare organizations.
The Impact of Technology on the Medical Assistant Role
Technology has significantly transformed the medical assistant role, integrating electronic health records (EHRs) and other technologies into medical practices. This has led to changes in the tasks and responsibilities of medical assistants, creating both benefits and challenges.
Integration of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The adoption of EHRs has revolutionized patient record management, allowing medical assistants to access and update patient information electronically. This has streamlined administrative tasks, improved patient care coordination, and reduced the risk of errors.
Transformation of Tasks and Responsibilities
Technology has transformed the tasks and responsibilities of medical assistants, leading to:
- Increased focus on patient care: Medical assistants are able to spend more time interacting with patients and providing direct care, as administrative tasks are automated.
- Enhanced data analysis: EHRs provide medical assistants with access to comprehensive patient data, enabling them to analyze trends and identify potential health risks.
- Greater efficiency: Technology has increased efficiency in scheduling appointments, managing patient records, and processing insurance claims.
Potential Benefits and Challenges
While technology has brought significant benefits to the medical assistant profession, it has also presented some challenges:
- Technological literacy: Medical assistants need to be technologically proficient to navigate EHRs and other healthcare applications effectively.
- Cybersecurity concerns: EHRs contain sensitive patient information, requiring medical assistants to be aware of cybersecurity risks and implement appropriate safeguards.
- Potential for job displacement: Automation of certain tasks may lead to job displacement in some areas of medical assisting.
Professional Organizations and Resources
Professional organizations and resources play a vital role in supporting medical assistants by providing continuing education opportunities, networking events, and advocacy for the profession. These organizations offer valuable resources for medical assistants throughout their careers.
Key Professional Organizations
Some key professional organizations for medical assistants include:
- American Association of Medical Assistants (AAMA): The largest professional association for medical assistants, offering certification, continuing education, and advocacy.
- American Medical Technologists (AMT): Another major professional organization for medical assistants, offering certification, education, and career resources.
- National Healthcareer Association (NHA): A leading provider of certification examinations for medical assistants, offering a range of credentials and resources.
Available Resources
These organizations provide a variety of resources for medical assistants, including:
- Continuing education opportunities: Workshops, conferences, and online courses to enhance skills and stay up-to-date with industry trends.
- Networking events: Opportunities to connect with other medical assistants, healthcare professionals, and employers.
- Career resources: Job boards, career advice, and professional development resources to support career advancement.
- Advocacy: Representing the interests of medical assistants and advocating for policies that support the profession.
Importance of Professional Membership and Involvement
Professional membership and involvement offer numerous benefits for medical assistants, including:
- Access to resources: Membership provides access to valuable resources, such as continuing education, networking opportunities, and career support.
- Professional development: Organizations offer opportunities for professional development, enhancing skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Professional membership can enhance career prospects by demonstrating commitment to the profession and providing access to networking opportunities.
- Advocacy: Membership allows medical assistants to participate in advocacy efforts, shaping the future of the profession.
Final Wrap-Up
The demand for medical assistants continues to grow, making it a rewarding and stable career path. With the increasing complexity of the healthcare system and the rising emphasis on patient-centered care, the role of the medical assistant is becoming even more vital.
By embracing technology, continuing their professional development, and upholding the highest ethical standards, medical assistants will continue to play a critical role in shaping the future of healthcare.