ADHD medications play a significant role in managing Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These medications work by altering brain chemistry, primarily focusing on neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are crucial for attention, focus, and behavior regulation.
Understanding the different types of ADHD medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ADHD medications, covering various aspects, including stimulant and non-stimulant options, dosage considerations, long-term effects, and alternative treatment approaches.
Introduction to ADHD Medications
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by difficulties with attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. While ADHD is a lifelong condition, medications can be a valuable tool in managing its symptoms and improving quality of life.
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of ADHD medications, exploring their different types, mechanisms of action, side effects, and considerations for choosing the right treatment.
Types of ADHD Medications
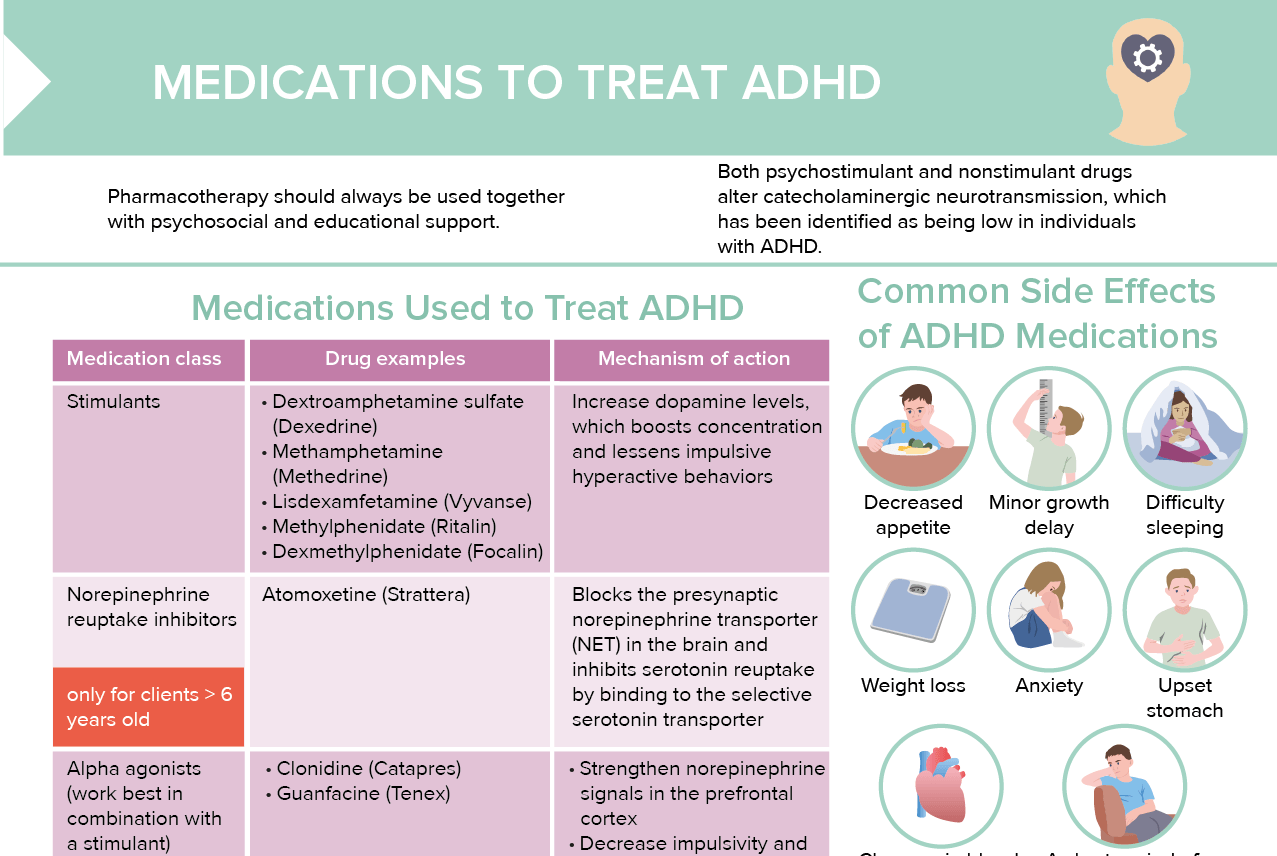
ADHD medications fall into two main categories: stimulants and non-stimulants.
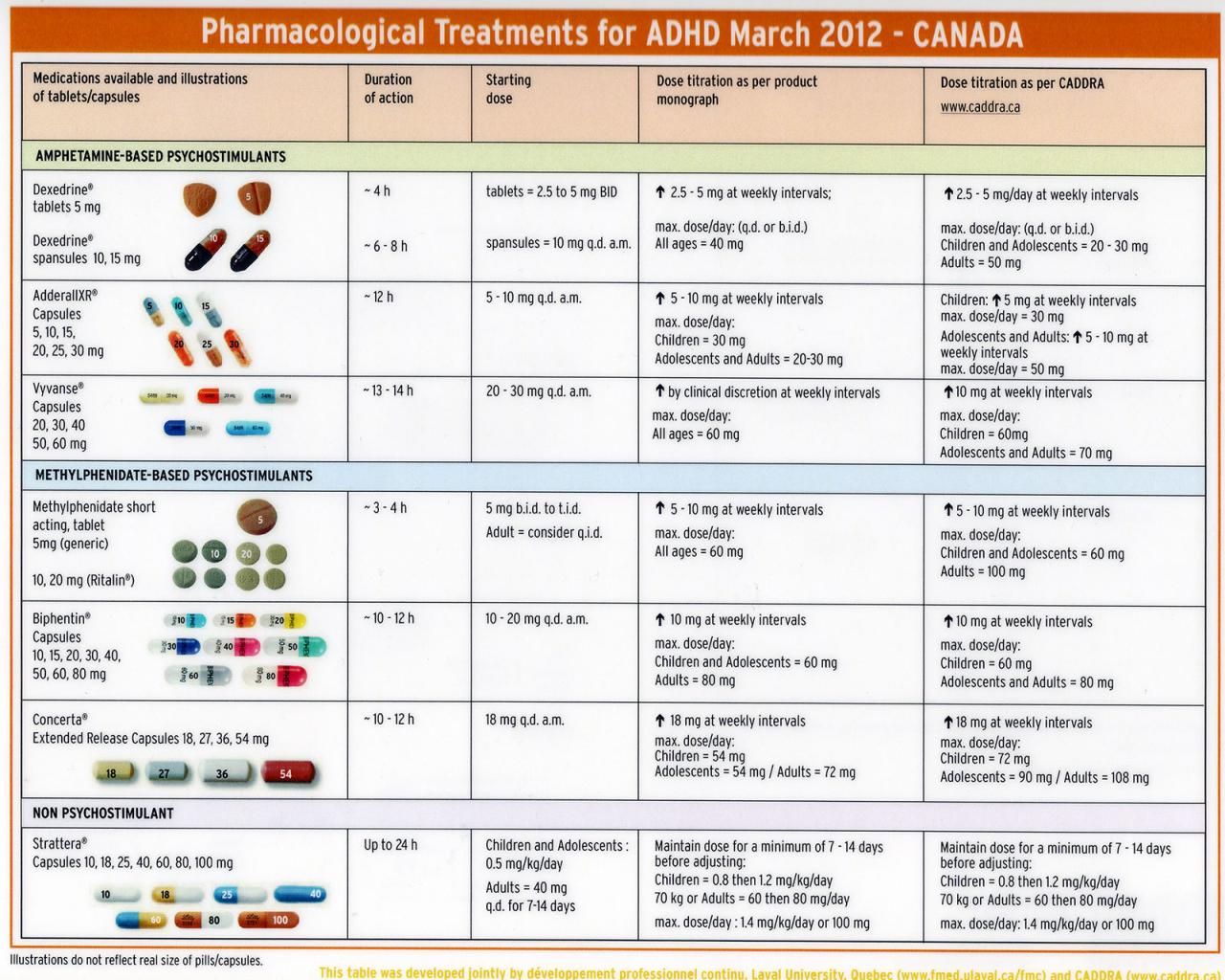
- Stimulantswork by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in regulating attention, focus, and behavior. Common stimulant medications include methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and amphetamines (Adderall, Vyvanse).
- Non-stimulants, on the other hand, work through different mechanisms in the brain. They do not directly increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels but rather influence other neurochemical pathways that affect attention and behavior. Examples of non-stimulant medications include atomoxetine (Strattera) and guanfacine (Intuniv).
How ADHD Medications Work in the Brain
The exact mechanisms by which ADHD medications work in the brain are still being researched. However, current understanding suggests that both stimulants and non-stimulants target specific brain regions involved in attention, focus, and impulse control.
- Stimulantsare believed to increase the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the prefrontal cortex, a brain region responsible for executive functions, including planning, decision-making, and working memory.
- Non-stimulants, like atomoxetine, are thought to work by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine, thereby increasing its availability in the brain. Guanfacine, another non-stimulant, affects the activity of a neurotransmitter called norepinephrine, which plays a role in regulating attention and impulse control.
Common Side Effects of ADHD Medications
Like all medications, ADHD medications can cause side effects. The severity and type of side effects can vary depending on the individual, the specific medication, and the dosage. Some common side effects include:
- Stimulants:Decreased appetite, insomnia, headache, anxiety, and stomach upset.
- Non-stimulants:Nausea, fatigue, drowsiness, and dry mouth.
Stimulant Medications
Stimulant medications are often the first-line treatment for ADHD. They are generally effective in improving attention, focus, and behavior. Here’s a closer look at different types of stimulant medications:
Types of Stimulant Medications
- Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta):Methylphenidate is a stimulant medication that is available in both short-acting and long-acting formulations. Short-acting methylphenidate needs to be taken multiple times a day, while long-acting formulations provide a more sustained effect.
- Amphetamines (Adderall, Vyvanse):Amphetamines are another type of stimulant medication used for ADHD. Like methylphenidate, they are available in both short-acting and long-acting formulations. Adderall is a combination of amphetamine salts, while Vyvanse is a prodrug that converts into amphetamine in the body.
Dosage Ranges and Administration Methods
The dosage of stimulant medication is determined by the doctor based on the individual’s age, weight, and severity of symptoms.
- Methylphenidate:Typical starting dosages for children range from 5 to 10 mg per day, while adults may start with 10 to 20 mg per day. Methylphenidate is usually taken orally in tablet or capsule form.
- Amphetamines:The starting dosage for Adderall is typically 5 to 10 mg per day, while Vyvanse dosages range from 10 to 70 mg per day. These medications are also taken orally in tablet or capsule form.
Benefits and Risks of Stimulant Medications
Stimulant medications can provide significant benefits for individuals with ADHD. However, it’s important to weigh these benefits against potential risks.
- Benefits:Improved attention, focus, concentration, and behavior. Increased productivity and academic performance. Reduced impulsivity and hyperactivity.
- Risks:Insomnia, decreased appetite, headache, anxiety, stomach upset, potential for abuse and dependence, cardiovascular problems (rare).
Non-Stimulant Medications: Adhd Medications
Non-stimulant medications offer an alternative treatment option for ADHD, particularly for individuals who experience side effects or have contraindications to stimulants.
Types of Non-Stimulant Medications, Adhd medications
- Atomoxetine (Strattera):Atomoxetine is a non-stimulant medication that works by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine in the brain. It is available in capsule form and is typically taken once a day.
- Guanfacine (Intuniv):Guanfacine is another non-stimulant medication that affects the activity of norepinephrine. It is available in tablet form and is typically taken once a day.
Mechanisms of Action for Non-Stimulant Medications
- Atomoxetine:By blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine, atomoxetine increases its levels in the brain, which helps improve attention, focus, and behavior.
- Guanfacine:Guanfacine works by activating a specific type of receptor in the brain called the alpha-2A adrenergic receptor. This activation helps regulate the release of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters, contributing to improved attention and behavior.
Side Effects and Effectiveness
Non-stimulant medications generally have a different profile of side effects compared to stimulants.
- Atomoxetine:Common side effects include nausea, fatigue, drowsiness, and dry mouth. It may take several weeks to see the full effects of atomoxetine.
- Guanfacine:Common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, and low blood pressure. Guanfacine may also cause dizziness and lightheadedness.
The effectiveness of non-stimulant medications varies among individuals. They may be less effective than stimulants for some people with ADHD, but they can be a good option for those who experience significant side effects from stimulants or have contraindications to their use.
Choosing the Right Medication
Choosing the right ADHD medication is a collaborative process between the individual and their doctor. Several factors are considered when making this decision, including:
Factors Considered by Doctors
- Age:The age of the individual is a crucial factor, as different medications may be more appropriate for different age groups.
- Severity of Symptoms:The severity of ADHD symptoms, including the specific areas of difficulty, can influence the choice of medication.
- Medical History:The individual’s medical history, including any existing conditions or medications they are taking, is important to consider.
- Family History:A family history of ADHD or other mental health conditions can also be relevant.
- Preferences and Goals:The individual’s preferences, goals, and lifestyle can influence the choice of medication and dosage.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Before starting ADHD medication, it’s essential to have a conversation with your doctor and ask them questions. Here are some important questions to consider:
- What type of medication do you recommend for me, and why?
- What are the potential benefits and risks of this medication?
- How long will it take to see the effects of the medication?
- What are the possible side effects, and how can they be managed?
- How often will I need to follow up with you to monitor my progress?
- Are there any alternative treatments that I could consider?
Summary of ADHD Medications
Here is a table summarizing different types of ADHD medications, their typical dosages, and potential side effects:
| Medication Type | Medication Name | Typical Dosage Range | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulant | Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) | Children: 5-10 mg/day, Adults: 10-20 mg/day | Decreased appetite, insomnia, headache, anxiety, stomach upset |
| Stimulant | Amphetamines (Adderall, Vyvanse) | Adderall: 5-10 mg/day, Vyvanse: 10-70 mg/day | Insomnia, decreased appetite, headache, anxiety, stomach upset |
| Non-Stimulant | Atomoxetine (Strattera) | Variable, typically 40-80 mg/day | Nausea, fatigue, drowsiness, dry mouth |
| Non-Stimulant | Guanfacine (Intuniv) | Variable, typically 1-4 mg/day | Drowsiness, fatigue, low blood pressure, dizziness |
Managing Side Effects
While ADHD medications can be effective, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and strategies for managing them.
Common Side Effects and Strategies
- Decreased Appetite:Encourage healthy eating habits, offer nutritious snacks throughout the day, and consider taking medication after meals.
- Insomnia:Avoid taking medication late in the day, establish a regular sleep schedule, and create a relaxing bedtime routine.
- Headache:Over-the-counter pain relievers can be helpful, and staying hydrated is important.
- Anxiety:Discuss anxiety concerns with your doctor, consider relaxation techniques, and engage in activities that reduce stress.
- Stomach Upset:Taking medication with food can minimize stomach upset.
- Drowsiness:Avoid driving or operating machinery if feeling drowsy, and adjust dosage or timing of medication as needed.
- Fatigue:Get enough sleep, engage in regular physical activity, and consider adjusting the dosage or timing of medication.
- Dry Mouth:Drink plenty of water, chew sugar-free gum, and use a mouthwash to keep your mouth moist.
Side Effects and Possible Solutions
| Side Effect | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Decreased Appetite | Encourage healthy eating habits, offer nutritious snacks, take medication after meals. |
| Insomnia | Avoid medication late in the day, establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine. |
| Headache | Over-the-counter pain relievers, stay hydrated. |
| Anxiety | Discuss concerns with your doctor, relaxation techniques, stress-reducing activities. |
| Stomach Upset | Take medication with food. |
| Drowsiness | Avoid driving or operating machinery, adjust dosage or timing. |
| Fatigue | Get enough sleep, engage in regular physical activity, adjust dosage or timing. |
| Dry Mouth | Drink plenty of water, chew sugar-free gum, use mouthwash. |
Long-Term Use and Potential Risks
Long-term use of ADHD medications is generally safe for most individuals. However, it’s important to be aware of potential risks and to monitor for any changes in health or behavior.
Potential Long-Term Effects
- Tolerance:Over time, some individuals may develop tolerance to the effects of ADHD medications, requiring dosage adjustments.
- Dependence:While ADHD medications are not addictive in the same way as illicit drugs, some individuals may experience dependence, meaning they rely on the medication to function normally. This is more common with stimulant medications.
- Cardiovascular Effects:Long-term use of stimulant medications may increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure and heart rate. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a doctor are essential.
- Growth and Development:In children, long-term use of stimulant medications may slightly affect growth and development. However, this is usually temporary, and growth typically catches up once the medication is discontinued.
Importance of Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a doctor are crucial for individuals taking ADHD medications, especially for long-term use. This allows the doctor to assess the medication’s effectiveness, monitor for side effects, and adjust dosage as needed.
Potential Risks Associated with Long-Term Use
- Increased risk of cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure and heart rate.
- Potential for tolerance and dependence, especially with stimulant medications.
- Possible impact on growth and development in children.
- Risk of misuse and abuse, especially with stimulant medications.
Alternative Treatments for ADHD
While medications can be an effective part of ADHD management, they are not the only option. Non-medication approaches, such as therapy and behavioral interventions, can also play a significant role in improving symptoms and quality of life.
Therapy and Behavioral Interventions
Therapy, particularly cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly beneficial for individuals with ADHD. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to ADHD symptoms. Therapists can teach coping skills, strategies for managing impulsivity and distractibility, and techniques for improving organization and time management.
If you’re struggling with heartburn and acid reflux, you might be dealing with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Fortunately, there are a variety of gastroesophageal reflux disease medications available to help manage your symptoms. These medications work in different ways, either by reducing stomach acid production or by strengthening the lower esophageal sphincter.
It’s important to talk to your doctor to find the right medication for you and to understand potential side effects.
Examples of Alternative Treatments
- Mindfulness:Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help individuals with ADHD develop greater awareness of their thoughts and feelings, improve focus, and manage stress.
- Exercise:Regular physical activity can have a positive impact on ADHD symptoms, improving attention, focus, and mood.
- Dietary Changes:Some individuals with ADHD report improvements in symptoms by making dietary changes, such as reducing sugar intake and increasing consumption of omega-3 fatty acids. However, more research is needed to confirm these effects.
- Educational Support:Children with ADHD may benefit from educational support, such as individualized learning plans, accommodations, and extra help in specific areas.
Effectiveness of Medication and Non-Medication Approaches
The most effective approach to managing ADHD often involves a combination of medication and non-medication strategies. Medication can provide immediate relief from symptoms, while therapy and behavioral interventions can help individuals develop long-term coping skills and strategies for managing their condition.
The specific combination of treatments will vary depending on the individual’s needs, preferences, and severity of symptoms.
If you’re struggling with heartburn and acid reflux, you’re not alone. Millions of people experience these symptoms, which can be caused by gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Fortunately, there are effective treatments available, including gastroesophageal reflux disease medication. These medications can help to reduce acid production in your stomach, allowing your esophagus to heal and providing relief from uncomfortable symptoms.
Final Wrap-Up
While ADHD medications can be effective in managing symptoms and improving quality of life, it’s crucial to remember that they are not a cure-all. A holistic approach involving medication, therapy, behavioral interventions, and lifestyle modifications often yields the best results.
Choosing the right treatment plan requires careful consideration of individual needs, preferences, and potential risks and benefits. By working closely with a qualified healthcare professional, individuals with ADHD can find strategies that effectively manage their symptoms and live fulfilling lives.