Gastroenteritis medication sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a world where stomach bugs and intestinal woes are tackled head-on. From over-the-counter remedies to prescription options, this exploration delves into the various ways to manage the discomfort and inconvenience of gastroenteritis.
We’ll uncover the secrets behind effective home remedies, explore preventative measures, and navigate the complexities of managing gastroenteritis in different populations, including children, the elderly, and pregnant women. Join us as we embark on this journey to understand and conquer this common ailment.
Gastroenteritis, also known as the stomach flu, is a common illness that affects millions of people each year. It’s characterized by a range of unpleasant symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and fever. The causes of gastroenteritis are varied, encompassing viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections.
Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach, as well as preventing future infections.
It’s important to remember that everyone’s journey with depression is unique. If you’re struggling, know that you’re not alone and there are resources available to help. One option to consider is depression medication , which can be a valuable tool in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
However, it’s crucial to discuss treatment options with a mental health professional to determine the best course of action for your individual needs.
Understanding Gastroenteritis: Gastroenteritis Medication
Gastroenteritis, commonly known as the stomach flu, is a common illness that affects the digestive system. It’s characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines, leading to a range of unpleasant symptoms. While the term “stomach flu” is often used, it’s important to note that gastroenteritis is not caused by the influenza virus.
Instead, it’s usually caused by viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections.
Causes of Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is primarily caused by infections. The most common culprits are:
- Viruses:Rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus, and astrovirus are among the most frequent viral causes of gastroenteritis. These viruses are highly contagious and spread easily through contaminated food, water, or contact with infected individuals.
- Bacteria:Bacteria like Salmonella, Campylobacter, E. coli, and Shigella can cause bacterial gastroenteritis. These bacteria often contaminate food and water, leading to infection.
- Parasites:Parasites like Giardia and Cryptosporidium can also cause gastroenteritis. These parasites are typically found in contaminated water sources.
Symptoms of Gastroenteritis
The symptoms of gastroenteritis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual’s health. However, the most common symptoms include:
- Diarrhea:Loose, watery stools, sometimes accompanied by abdominal cramps.
- Vomiting:Forceful expulsion of stomach contents.
- Nausea:Feeling sick to your stomach.
- Abdominal cramps:Pain or discomfort in the stomach area.
- Fever:Elevated body temperature.
- Dehydration:Loss of fluids due to vomiting and diarrhea, leading to symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and dry mouth.
Types of Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis can be classified into different types based on the causative agent:
- Viral Gastroenteritis:This is the most common type, often caused by norovirus and rotavirus. Symptoms usually include vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
- Bacterial Gastroenteritis:Caused by bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli. Symptoms can be more severe and may include fever, bloody diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Parasitic Gastroenteritis:Caused by parasites like Giardia and Cryptosporidium. Symptoms can include diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and bloating.
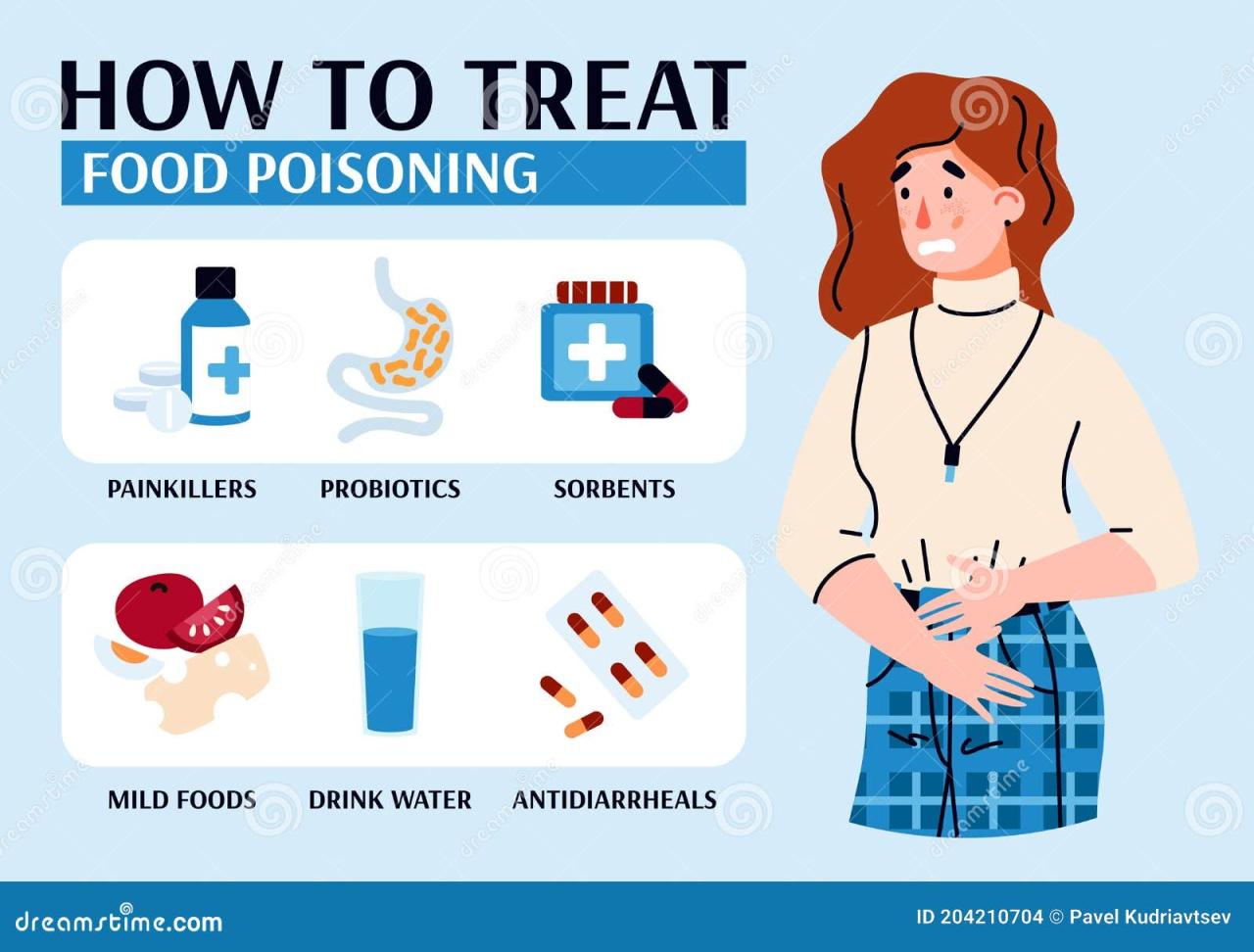
Gastroenteritis Medication: Over-the-Counter Options
For mild to moderate cases of gastroenteritis, over-the-counter (OTC) medications can help manage symptoms. These medications are generally safe for most adults and children, but it’s always best to consult with a doctor or pharmacist before using them, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Common OTC Medications for Gastroenteritis
- Antidiarrheals:These medications help slow down bowel movements and reduce diarrhea. Examples include loperamide (Imodium) and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol).
- Anti-nausea Medications:These medications can help reduce nausea and vomiting. Examples include ondansetron (Zofran) and promethazine (Phenergan).
- Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS):These solutions are essential for replacing lost fluids and electrolytes due to dehydration. They are available in powder form and can be mixed with water.
- Antacids:These medications can help neutralize stomach acid and reduce heartburn. Examples include Tums and Rolaids.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Action
- Loperamide (Imodium):This medication works by slowing down the movement of the muscles in the intestines, allowing the body more time to absorb fluids and reduce diarrhea.
- Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol):This medication has antidiarrheal and anti-inflammatory properties. It helps coat the stomach lining and reduce irritation.
- Ondansetron (Zofran):This medication blocks the action of serotonin in the brain, reducing nausea and vomiting.
- Promethazine (Phenergan):This medication has antihistamine and anticholinergic properties, helping to reduce nausea and vomiting.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions, Gastroenteritis medication
While OTC medications are generally safe, they can have potential side effects and interactions. It’s important to read the medication labels carefully and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
If you’re struggling with depression, know that you’re not alone. There are effective treatments available, including depression medication , which can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the best treatment options for you, and remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
- Loperamide (Imodium):Side effects may include constipation, abdominal pain, and dizziness.
- Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol):Side effects may include dark stools, constipation, and ringing in the ears.
- Ondansetron (Zofran):Side effects may include headache, dizziness, and constipation.
- Promethazine (Phenergan):Side effects may include drowsiness, dry mouth, and blurred vision.
Gastroenteritis Medication: Prescription Options
In severe cases of gastroenteritis, prescription medications may be necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications. These medications are typically used when OTC medications are not effective or when there are underlying health concerns.
Prescription Medications for Gastroenteritis
- Antibiotics:Antibiotics are only effective for bacterial gastroenteritis. They are not effective against viral or parasitic infections. Examples include ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and azithromycin (Zithromax).
- Anti-emetics:These medications are stronger than OTC anti-nausea medications and can help manage severe vomiting. Examples include prochlorperazine (Compazine) and metoclopramide (Reglan).
- Intravenous Fluids:In cases of severe dehydration, intravenous fluids may be necessary to replenish lost fluids and electrolytes.
Indications for Using Prescription Medications
Prescription medications for gastroenteritis are typically used in the following scenarios:
- Severe dehydration:When OTC oral rehydration solutions are not sufficient to manage dehydration.
- Persistent vomiting:When OTC anti-nausea medications are not effective.
- Bloody diarrhea:This may indicate a bacterial infection that requires antibiotic treatment.
- Underlying health conditions:Individuals with underlying health conditions like diabetes or kidney disease may require prescription medications to manage gastroenteritis.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Prescription medications for gastroenteritis can be beneficial in managing symptoms and preventing complications. However, they also carry potential risks.
- Antibiotics:While effective against bacterial infections, antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, potentially leading to side effects like diarrhea and yeast infections.
- Anti-emetics:These medications can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and other side effects.
- Intravenous Fluids:While necessary in some cases, intravenous fluids can carry risks like infection and fluid overload.
Closing Notes
While gastroenteritis can be a disruptive and uncomfortable experience, armed with knowledge about its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments, you can navigate this illness with confidence. Remember, maintaining good hygiene practices, staying hydrated, and seeking medical attention when necessary are key to minimizing the impact of gastroenteritis.
With the right information and a proactive approach, you can conquer this common ailment and regain your health and well-being.