Lake mead lake powell water levels – Lake Mead and Lake Powell, two of the largest reservoirs in the United States, are facing a dire situation as their water levels plummet. These iconic bodies of water, once symbols of abundance, are now stark reminders of the effects of drought, population growth, and unsustainable water usage.
The Colorado River, which feeds these reservoirs, is experiencing its worst drought in centuries, leading to a cascade of consequences that threaten the livelihoods of millions of people and the delicate ecosystems of the Southwest.
This decline in water levels is not just a natural phenomenon; it’s a symptom of a complex interplay of factors. Increased demand for water, coupled with changing precipitation patterns and the effects of climate change, have put immense pressure on the Colorado River system.
The impact of this decline extends beyond the immediate shores of the reservoirs, affecting hydropower generation, water supply for cities and agriculture, and the delicate balance of the surrounding environment.
Historical Water Levels: Lake Mead Lake Powell Water Levels
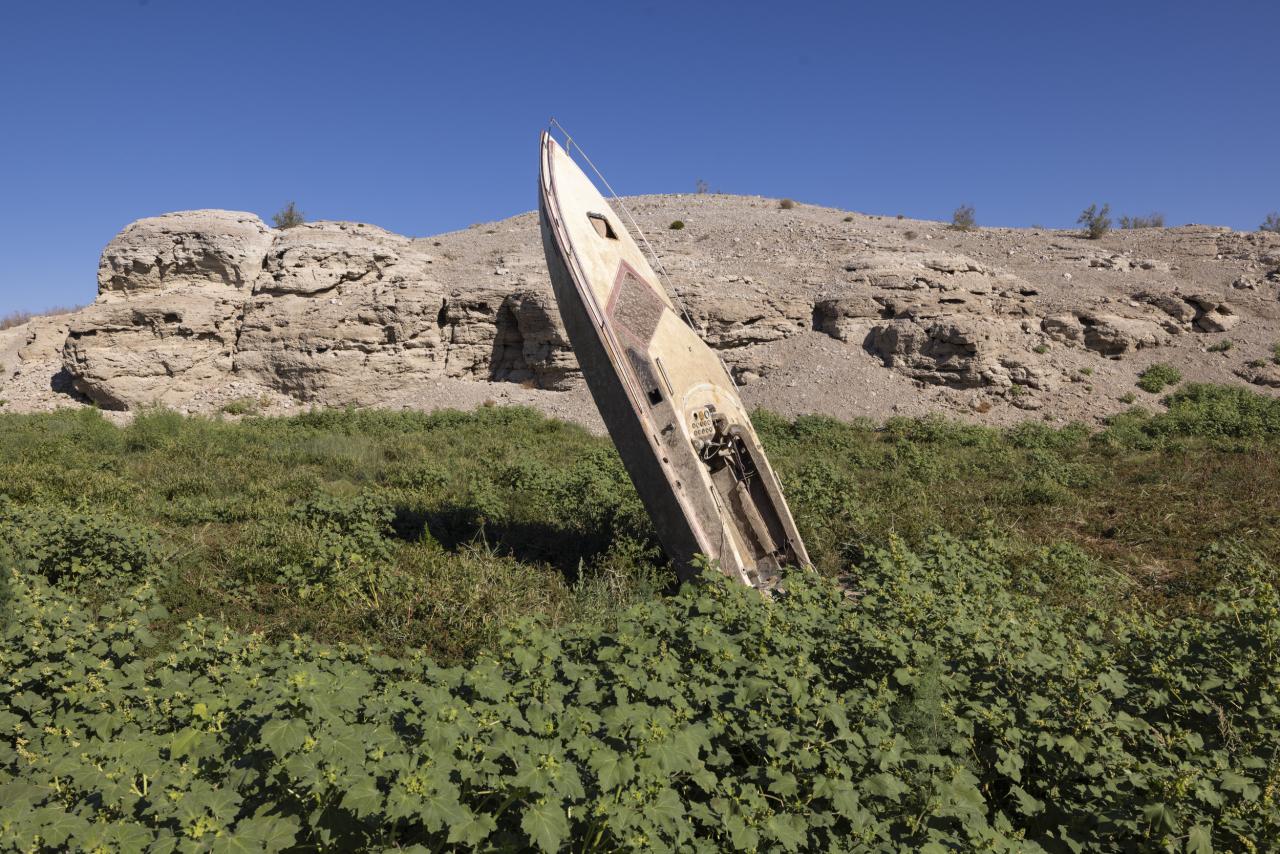

Lake Mead and Lake Powell, the two largest reservoirs in the United States, have been experiencing a dramatic decline in water levels over the past several decades. These reservoirs, formed by the construction of Hoover Dam and Glen Canyon Dam respectively, have played a crucial role in supplying water to millions of people and powering homes and businesses across the Southwest.
However, the declining water levels have raised serious concerns about the future of these vital water sources.
Historical Water Levels Comparison
Since their creation, both Lake Mead and Lake Powell have experienced significant fluctuations in water levels, influenced by a combination of factors, including precipitation patterns, drought cycles, and human water use. Comparing the historical water levels of these reservoirs provides valuable insights into the long-term trends and the challenges facing the Colorado River Basin.
- Lake Mead:The reservoir’s water levels have been declining steadily since the late 1990s, reaching record lows in recent years. This decline is primarily attributed to the prolonged drought conditions in the Colorado River Basin and increased water demands from the growing population in the Southwest.
- Lake Powell:Similar to Lake Mead, Lake Powell’s water levels have also been experiencing a significant decline, particularly since the early 2000s. The reservoir’s storage capacity has been significantly reduced, raising concerns about the long-term sustainability of water supply to the region.
Factors Contributing to Water Level Decline
The decline in water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell can be attributed to a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Drought:The Colorado River Basin has been experiencing prolonged drought conditions, with below-average precipitation and increased evaporation rates. These factors have significantly reduced the flow of the Colorado River, leading to lower reservoir levels.
- Population Growth:The population in the Southwest has been growing steadily, increasing the demand for water for residential, agricultural, and industrial purposes. This increased demand has put a strain on the Colorado River’s water supply, contributing to the decline in reservoir levels.
- Agricultural Use:Agriculture is a major water user in the Colorado River Basin, with significant water allocations for irrigation. The increasing demand for agricultural products has led to increased water withdrawals, further contributing to the decline in reservoir levels.
Historical Precipitation Patterns
Analyzing historical precipitation patterns in the Colorado River Basin provides valuable insights into the long-term trends and the factors influencing water availability. Historical data reveals that:
- Variability:Precipitation patterns in the Colorado River Basin have historically been highly variable, with periods of drought alternating with periods of above-average precipitation.
- Declining Trends:Recent decades have witnessed a declining trend in precipitation, particularly in the upper Colorado River Basin, where most of the snowpack originates. This trend has contributed to the decline in water flow and reservoir levels.
- Climate Change:Climate change is expected to exacerbate these trends, with projections suggesting a warmer and drier future for the Colorado River Basin. This could lead to further reductions in precipitation and snowpack, further impacting water availability.
Current Water Levels and Impacts
The current water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell are at historically low levels, raising serious concerns about the long-term sustainability of these vital water resources. The declining water levels have significant consequences for various sectors, including hydropower generation, water supply, recreation, and the environment.
Current Water Level Analysis
As of [current date], the water level in Lake Mead is at [current level], which is significantly lower than the historical average. Similarly, the water level in Lake Powell is at [current level], also significantly below the historical average. These low water levels have triggered a series of actions to address the water scarcity and mitigate the potential impacts.
Consequences of Low Water Levels
The low water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell have a range of consequences, including:
- Hydropower Generation:The declining water levels have significantly reduced the capacity of Hoover Dam and Glen Canyon Dam to generate hydropower. This has led to increased reliance on other energy sources, potentially increasing energy costs.
- Water Supply:The reduced reservoir levels have raised concerns about the reliability of water supply to millions of people in the Southwest. Water conservation measures have been implemented, and there are concerns about potential water shortages in the future.
- Recreation:The shrinking reservoirs have impacted recreational activities, such as boating, fishing, and swimming. The decline in water levels has made it challenging to access certain areas and has affected the overall recreational experience.
Environmental Effects
The shrinking reservoirs have significant environmental effects, including:
- Habitat Loss:The declining water levels have resulted in the loss of aquatic habitats, affecting fish populations and other wildlife that rely on these ecosystems. The shrinking shorelines have also impacted vegetation and bird species.
- Increased Salinity:As water levels decline, the concentration of salts in the remaining water increases. This increased salinity can harm aquatic life and impact water quality for human consumption.
- Sediment Exposure:The receding water levels expose sediment that has been submerged for years, releasing nutrients and contaminants into the water. This can further degrade water quality and impact the health of the ecosystem.
Future Projections and Solutions
Predicting future water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell is a complex task, influenced by various factors, including climate change, population growth, and water management strategies. However, based on current trends and climate models, projections suggest a continued decline in water levels, highlighting the urgency of addressing the water scarcity challenge.
Projected Future Water Levels
Climate models project a warmer and drier future for the Colorado River Basin, with reduced precipitation and increased evaporation rates. These factors are expected to exacerbate the decline in water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell. The projected future water levels depend on various assumptions, including water conservation measures, infrastructure improvements, and inter-basin water transfers.
- Scenario 1:Under a scenario of continued drought and limited water conservation efforts, the water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell are projected to continue declining, potentially reaching critically low levels within the next few decades.
- Scenario 2:Under a scenario of aggressive water conservation measures, infrastructure improvements, and inter-basin water transfers, the water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell could be stabilized, but it would require significant investments and collaboration among stakeholders.
Potential Solutions
Addressing the declining water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell requires a multifaceted approach, involving a combination of water conservation measures, infrastructure improvements, and inter-basin water transfers.
- Water Conservation Measures:Implementing water conservation measures, such as reducing outdoor water use, improving irrigation efficiency, and promoting water-efficient appliances, can significantly reduce water demand and help stabilize reservoir levels.
- Infrastructure Improvements:Upgrading existing infrastructure, such as pipelines and canals, to reduce water losses through leakage and evaporation can improve water delivery efficiency and help conserve water resources.
- Inter-Basin Water Transfers:Transferring water from other river basins to the Colorado River Basin could potentially supplement the water supply and help mitigate the decline in reservoir levels. However, this approach raises concerns about environmental impacts and potential conflicts with other water users.
Comparison of Water Management Strategies, Lake mead lake powell water levels
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Water Conservation Measures | Cost-effective, reduces water demand, improves water use efficiency | Requires behavioral changes, can be challenging to implement, may not be sufficient to address the problem alone |
| Infrastructure Improvements | Reduces water losses, improves water delivery efficiency, can be implemented in conjunction with other strategies | Requires significant investments, can be complex and time-consuming to implement |
| Inter-Basin Water Transfers | Provides additional water supply, can help stabilize reservoir levels | Raises concerns about environmental impacts, potential conflicts with other water users, can be expensive and complex to implement |
Economic and Social Impacts
The declining water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell have significant economic and social impacts on communities and industries reliant on the Colorado River. The water scarcity has led to increased water costs, reduced agricultural production, and potential conflicts over water resources.
The social consequences include potential displacement and changes in livelihoods.
Economic Impacts
The low water levels have a range of economic impacts, including:
- Agriculture:Farmers and ranchers in the Southwest rely heavily on the Colorado River for irrigation. The declining water levels have led to reduced water allocations, impacting crop yields and livestock production. This has resulted in economic losses for farmers and ranchers, potentially affecting food security and agricultural prices.
- Tourism:The decline in water levels has impacted recreational activities, such as boating, fishing, and swimming, leading to a decrease in tourism revenue. This has affected businesses reliant on tourism, including hotels, restaurants, and marinas.
- Hydropower Generation:The reduced capacity of Hoover Dam and Glen Canyon Dam to generate hydropower has led to increased reliance on other energy sources, potentially increasing energy costs for businesses and consumers.
Social Impacts
The water scarcity has social consequences, including:
- Potential Conflicts:The declining water levels have created tensions between different water users, such as agriculture, urban areas, and Native American tribes. These conflicts could escalate as water resources become scarcer, potentially leading to legal disputes and social unrest.
- Displacement:In some cases, communities reliant on the Colorado River may face displacement as water resources become increasingly scarce. This could involve the relocation of families and businesses, leading to social disruption and economic hardship.
- Community Adaptation:Communities in the Southwest are adapting to the changing water conditions by implementing water conservation measures, developing alternative water sources, and promoting water-efficient practices. These efforts aim to mitigate the impacts of water scarcity and ensure the long-term sustainability of water resources.
International Cooperation and Agreements
The Colorado River is an international river, shared by the United States and Mexico. Managing the water resources of this shared river requires international cooperation and agreements to ensure equitable distribution and sustainable use. The Colorado River Compact, a landmark agreement signed in 1922, has played a crucial role in managing the river’s water resources for decades.
Role of International Agreements
International agreements, such as the Colorado River Compact, provide a framework for managing shared water resources, addressing issues such as water allocation, water quality, and environmental protection. These agreements establish mechanisms for cooperation, conflict resolution, and monitoring to ensure the sustainable use of shared water resources.
Challenges and Opportunities for Cooperation
Despite the existence of international agreements, managing the Colorado River’s water resources presents challenges and opportunities for cooperation between the United States and Mexico.
- Challenges:The increasing water scarcity, coupled with the growing population and changing climate, poses challenges to managing the shared water resources. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach to ensure equitable distribution and sustainable use.
- Opportunities:The shared water scarcity provides an opportunity for the United States and Mexico to strengthen their cooperation and develop innovative solutions for managing the Colorado River’s water resources. This includes investing in water conservation measures, improving infrastructure, and promoting sustainable water use practices.
Examples of Collaborative Efforts
The United States and Mexico have a long history of collaborating on water management issues. Examples of successful collaborative efforts include:
- The Minute 319 Agreement:This agreement, signed in 2012, provides for the release of water from Lake Mead to the Colorado River Delta in Mexico, benefiting both countries. The agreement aims to restore the ecological health of the delta and improve water quality.
- The International Boundary and Water Commission (IBWC):The IBWC is a binational commission responsible for managing the boundary waters between the United States and Mexico, including the Colorado River. The commission plays a crucial role in resolving water disputes, monitoring water quality, and promoting sustainable water management practices.
Conclusion
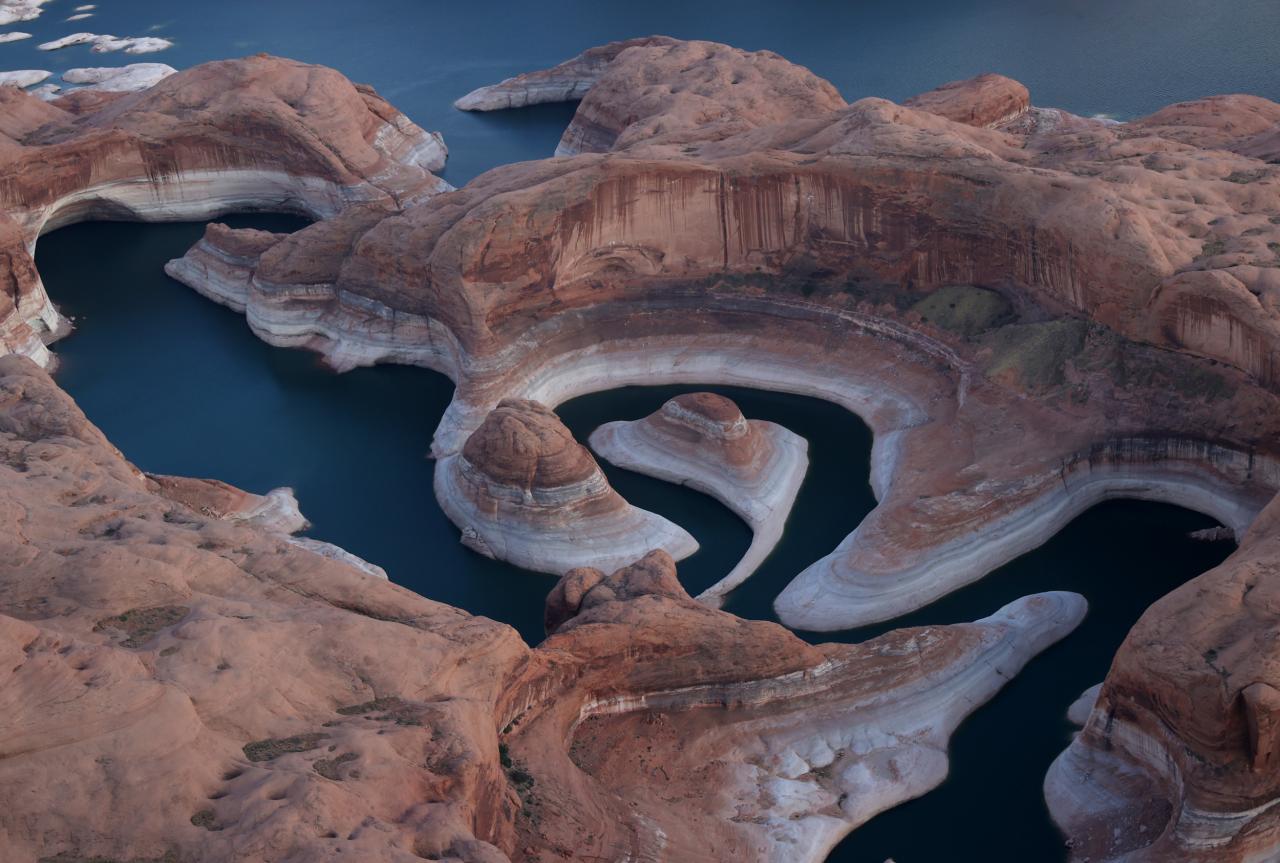

The future of Lake Mead and Lake Powell hangs in the balance. While the situation is dire, there is hope. By embracing sustainable water management practices, investing in infrastructure improvements, and fostering international cooperation, we can mitigate the effects of declining water levels and ensure the long-term health of these vital resources.
The challenges we face are significant, but the stakes are even higher. The future of the Southwest, and the well-being of millions of people, depends on our collective action to address this critical issue.