Lake Mungo, nestled in the heart of Australia’s arid interior, is more than just a dry lake bed. It’s a window into the past, a testament to the resilience of human life, and a powerful reminder of the profound impact of climate change.
For thousands of years, Lake Mungo has been a focal point for Aboriginal culture, its shores echoing with ancient stories and traditions. Archaeological discoveries here have rewritten our understanding of early human migration and the depths of human ingenuity in surviving harsh environments.
Lake Powell is a beautiful reservoir in the American Southwest, but its water level has been declining in recent years. The lake powell water level is currently at its lowest point in decades, which is causing concern for the environment and the local economy.
From the iconic Mungo Lady, one of the oldest human remains ever found, to the intricate stone tools and ancient campsites, Lake Mungo offers a glimpse into a world long gone. The geological history of the lake itself is fascinating, with dramatic shifts in climate and water levels shaping the landscape we see today.
This unique environment, shaped by both human and natural forces, continues to captivate and inspire researchers, archaeologists, and travelers alike.
Lake Mungo’s Geological History
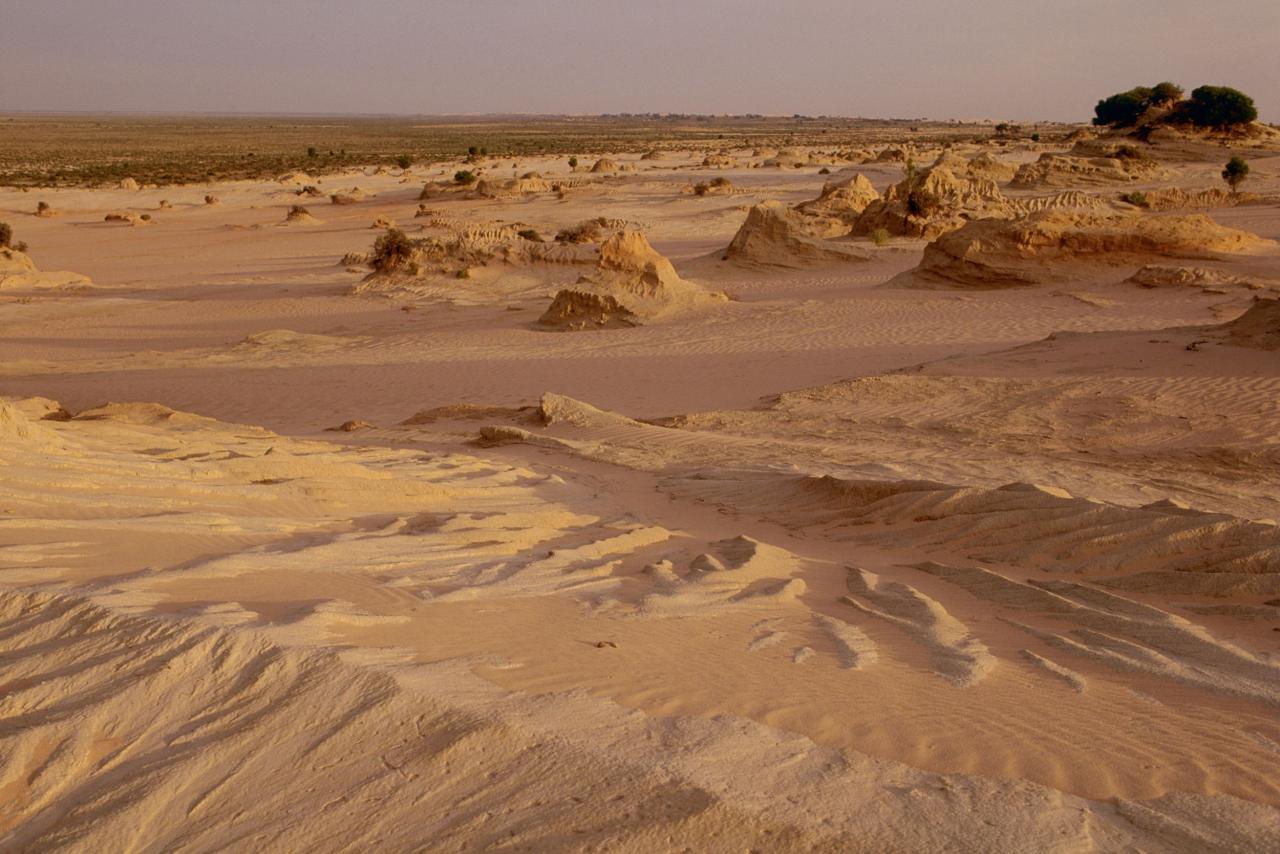

Lake Mungo, a vast, arid landscape in the Willandra Lakes Region of western New South Wales, Australia, holds a rich geological history that stretches back millions of years. Its formation and evolution are intertwined with the dynamic forces of tectonic activity, climate change, and the ebb and flow of ancient rivers and lakes.
Formation of Lake Mungo
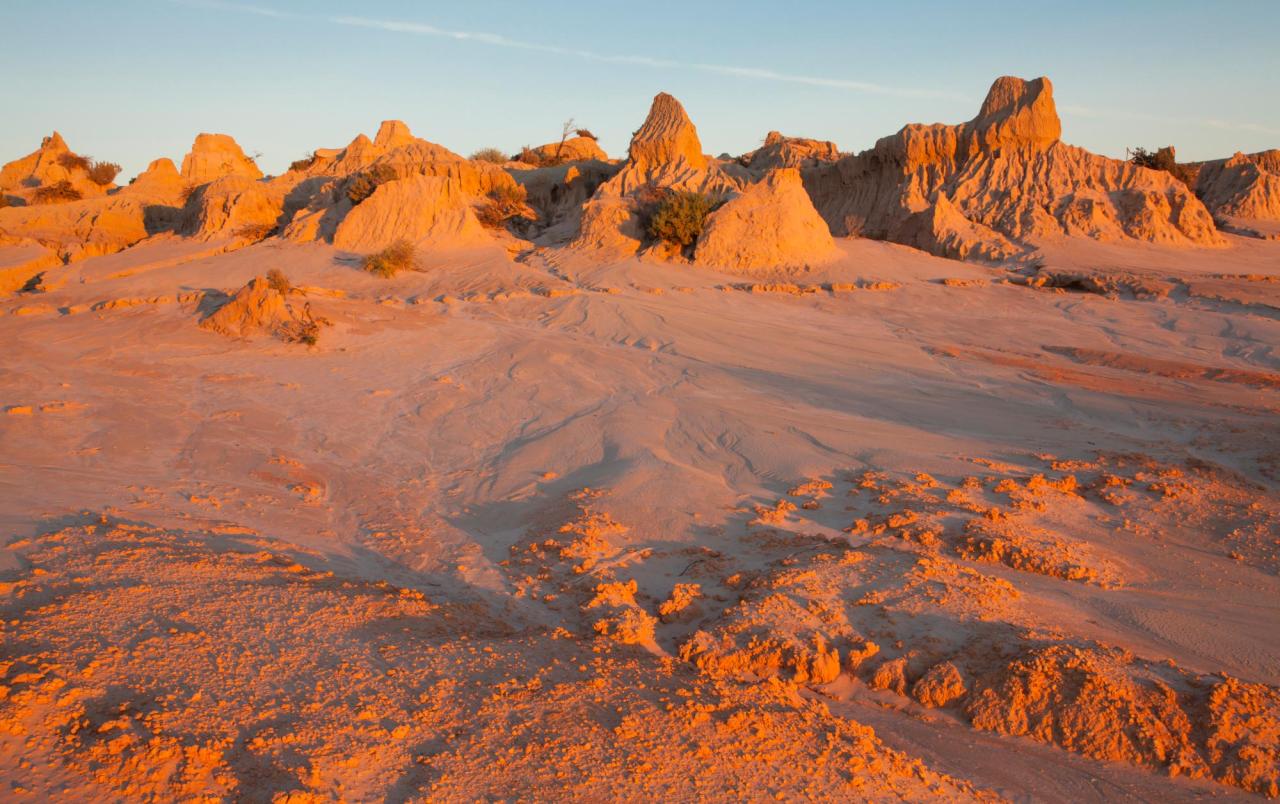

The formation of Lake Mungo is a complex story that begins with the breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, which started around 180 million years ago. As Australia drifted northward, the landscape was sculpted by tectonic forces, creating the vast Murray-Darling Basin, which encompasses Lake Mungo.
The basin’s formation played a pivotal role in shaping the lake’s landscape, creating the depressions that would eventually fill with water.
Over millions of years, the climate in the region fluctuated between wet and dry periods, influencing the formation of Lake Mungo. During wetter periods, ancient rivers like the Darling River flowed into the basin, creating vast inland lakes. The lake’s water levels rose and fell with the changing climate, leaving behind layers of sediment that tell a story of past environments.
Geological Features of Lake Mungo
Lake Mungo is characterized by a variety of unique geological features that offer insights into its ancient history. These features include:
- Lunette Dunes:These crescent-shaped dunes are formed by wind action and are a defining feature of Lake Mungo’s landscape. They are made up of fine-grained sand and silt deposited by the wind, and they provide valuable information about past wind patterns and climate conditions.
- Ancient Shorelines:The lake’s ancient shorelines, marked by layers of sediment and fossils, provide evidence of past water levels and the lake’s shrinking and expanding over time. These shorelines offer a glimpse into the dramatic fluctuations in climate that have shaped the region.
- Willandra Lakes Region World Heritage Area:The Willandra Lakes Region, which includes Lake Mungo, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1981, recognizing its exceptional geological and archaeological significance. The region’s diverse geological features and rich archaeological discoveries offer a unique window into Australia’s past.
Impact of Climate Change on Lake Mungo
Climate change has played a profound role in the evolution of Lake Mungo. The lake has experienced periods of significant drying and flooding, influenced by natural cycles such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and long-term climatic trends. During periods of drought, the lake shrank and eventually dried up, leaving behind a vast, arid landscape.
During wetter periods, the lake expanded, providing a habitat for diverse flora and fauna. The lake’s fluctuating water levels have left behind a rich record of past environments, providing scientists with valuable insights into the history of climate change in Australia.
The evidence of past climate change at Lake Mungo is a stark reminder of the fragility of our planet’s ecosystems and the need for responsible environmental stewardship.
Aboriginal Significance of Lake Mungo
Lake Mungo holds immense cultural and spiritual significance for the Aboriginal people of the region, particularly the Wiradjuri people, who have been custodians of the land for thousands of years. Their connection to the lake is deeply rooted in their traditions, beliefs, and ancestral history.
Cultural and Spiritual Importance
For the Aboriginal people, Lake Mungo is a sacred place, a place of creation, and a place where ancestral spirits reside. The lake’s landscape is imbued with stories, songs, and ceremonies that have been passed down through generations. The lake’s unique features, such as the lunettes and the ancient shorelines, are seen as tangible expressions of their ancestral heritage.
History of Aboriginal Occupation
The Wiradjuri people have a long and continuous history of occupation in the Lake Mungo region, dating back tens of thousands of years. They have adapted to the region’s harsh conditions, developing a deep understanding of the land’s resources and a sophisticated system of resource management.
Their knowledge of the lake’s ecology, its flora and fauna, and its water sources has enabled them to thrive in this challenging environment.
Archaeological evidence suggests that the Aboriginal people of the region were highly skilled hunters and gatherers, adept at utilizing the resources available to them. They developed sophisticated tools and technologies, including stone tools, hunting weapons, and fishing implements, which enabled them to survive and prosper in this unique environment.
Mungo Lady and Other Archaeological Discoveries
The discovery of the Mungo Lady, a 40,000-year-old skeleton, in 1969, revolutionized our understanding of human history in Australia. The Mungo Lady, along with other significant archaeological discoveries at Lake Mungo, such as the Mungo Man and the remains of other early human settlements, provide a glimpse into the lives of the first people to inhabit Australia.
These discoveries have shed light on the cultural practices, burial rituals, and technological advancements of these early human populations.
The Mungo Lady’s remains, along with other archaeological finds at Lake Mungo, are considered to be among the most significant archaeological discoveries in Australia. They offer valuable insights into the early history of human occupation in the region and have helped to rewrite our understanding of human evolution in Australia.
Lake Mungo’s Archaeological Discoveries
Lake Mungo is renowned for its rich archaeological heritage, offering a unique window into the history of human occupation in Australia. The site has yielded some of the most significant archaeological discoveries in the country, providing evidence of human presence dating back tens of thousands of years.
Significant Archaeological Finds
Lake Mungo has yielded a wealth of archaeological finds, including:
- Mungo Lady:The discovery of the Mungo Lady, a 40,000-year-old skeleton, in 1969, revolutionized our understanding of human history in Australia. The Mungo Lady is one of the oldest human remains ever found in Australia and is considered to be a significant example of early human occupation in the region.
She was found buried in a deliberate burial, indicating that the people who lived in the region had complex social and spiritual beliefs.
- Mungo Man:The remains of Mungo Man, a 42,000-year-old skeleton, were discovered in 1974. Mungo Man is considered to be one of the oldest known examples of cremated human remains in the world. The discovery of Mungo Man provided further evidence of the sophisticated cultural practices of the early inhabitants of the region.
- Stone Tools:Numerous stone tools have been discovered at Lake Mungo, dating back thousands of years. These tools provide evidence of the technological skills and resourcefulness of the early inhabitants of the region. The tools, including axes, hand axes, and spear points, reveal that these people were skilled hunters and gatherers, capable of adapting to the harsh conditions of the Australian outback.
- Fire Hearths:Evidence of fire hearths has been found at Lake Mungo, dating back to the early stages of human occupation. These hearths provide insights into the daily lives of the early inhabitants of the region, including their use of fire for cooking, warmth, and protection.
- Rock Art:While not as extensive as in other parts of Australia, some rock art sites have been discovered at Lake Mungo. These sites provide a glimpse into the artistic expressions and beliefs of the early inhabitants of the region.
Importance of the Mungo Lady and Mungo Man
The Mungo Lady and Mungo Man remains are considered to be among the most significant archaeological discoveries in Australia. They provide a unique window into the lives of the first people to inhabit Australia, offering insights into their cultural practices, burial rituals, and technological advancements.
These discoveries have helped to rewrite our understanding of human evolution in Australia and have contributed significantly to our understanding of the early history of human occupation in the region.
Archaeological Evidence of Human Settlement
The archaeological evidence found at Lake Mungo provides a compelling narrative of human settlement in the region, spanning tens of thousands of years. The site’s rich archaeological record, including the Mungo Lady and Mungo Man remains, stone tools, fire hearths, and rock art, offers a unique glimpse into the lives of the first people to inhabit Australia.
These discoveries have helped to shed light on the cultural practices, technological advancements, and adaptation strategies of these early human populations, providing valuable insights into the history of human occupation in Australia.
Lake Mungo’s Landscape and Ecology
Lake Mungo’s landscape is a captivating blend of ancient geological features, arid beauty, and ecological resilience. The lake’s unique features, including the lunettes, the ancient shorelines, and the vast, open plains, create a dramatic and evocative landscape.
Diverse Landscape
Lake Mungo’s landscape is characterized by a variety of unique features, including:
- Lunette Dunes:The lunettes, crescent-shaped dunes formed by wind action, are a defining feature of Lake Mungo’s landscape. They are made up of fine-grained sand and silt deposited by the wind, and they provide valuable information about past wind patterns and climate conditions.
The lunettes are a striking sight, creating a series of rolling hills that stretch across the landscape.
- Ancient Shorelines:The lake’s ancient shorelines, marked by layers of sediment and fossils, provide evidence of past water levels and the lake’s shrinking and expanding over time. These shorelines offer a glimpse into the dramatic fluctuations in climate that have shaped the region.
The ancient shorelines are a testament to the lake’s long and dynamic history.
- Open Plains:The vast, open plains that surround Lake Mungo are a defining feature of the region. These plains are characterized by their aridity, sparse vegetation, and the occasional presence of saltbush and other drought-tolerant plants. The plains provide a habitat for a variety of wildlife, including kangaroos, emus, and a variety of bird species.
- Red Sand Dunes:The red sand dunes of Lake Mungo are a striking feature of the landscape, created by the erosion of ancient rocks. The dunes are constantly shifting, creating a dynamic and ever-changing landscape.
Ecological Significance
Despite its aridity, Lake Mungo is an ecologically significant area, supporting a diverse range of plant and animal life. The lake’s unique features, including the lunettes, the ancient shorelines, and the open plains, create a variety of habitats that support a range of species.
The lake’s vegetation includes saltbush, bluebush, and other drought-tolerant plants, while its fauna includes kangaroos, emus, and a variety of bird species.
Impact of Human Activity, Lake mungo
Human activity has had a significant impact on the lake’s ecosystem. The introduction of grazing animals, such as sheep and cattle, has led to changes in vegetation patterns and soil erosion. The extraction of water for agricultural purposes has also had a significant impact on the lake’s water levels.
Conservation efforts are underway to mitigate the impact of human activity on the lake’s ecosystem and to protect its unique natural heritage.
Lake Powell, a stunning reservoir on the Colorado River, has been facing a significant water shortage in recent years. The lake powell water level has been steadily declining, raising concerns about the future of this iconic destination. As the water level drops, more of the lake’s shoreline is exposed, revealing the stark reality of the drought and the need for water conservation.
Lake Mungo’s Tourism and Conservation
Lake Mungo is a popular destination for tourists seeking to experience Australia’s unique natural and cultural heritage. The lake’s rich archaeological discoveries, its dramatic landscape, and its ecological significance make it a fascinating and rewarding destination.
Tourism Opportunities
Tourism opportunities at Lake Mungo include:
- Archaeological Tours:Guided tours of the lake’s archaeological sites, including the Mungo Lady and Mungo Man remains, offer visitors a chance to learn about the region’s ancient history and its significance to the Aboriginal people.
- Scenic Drives:Scenic drives along the lake’s perimeter offer breathtaking views of the lunettes, the ancient shorelines, and the vast, open plains. These drives provide a chance to appreciate the beauty and diversity of the lake’s landscape.
- Hiking and Walking Trails:A variety of hiking and walking trails are available, offering visitors the opportunity to explore the lake’s diverse landscapes and to observe the region’s unique flora and fauna.
- Camping:Camping facilities are available at Lake Mungo, allowing visitors to experience the tranquility and beauty of the region firsthand. Camping offers a chance to stargaze under the vast Australian sky and to enjoy the peace and quiet of the outback.
- Cultural Experiences:Visitors can participate in cultural experiences led by Aboriginal guides, learning about the region’s traditional beliefs, stories, and ceremonies.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts at Lake Mungo are focused on protecting the lake’s cultural and natural heritage. These efforts include:
- Protecting Archaeological Sites:Efforts are underway to protect the lake’s archaeological sites, including the Mungo Lady and Mungo Man remains, from damage and vandalism. These efforts involve monitoring the sites, conducting archaeological research, and educating visitors about the importance of preserving these sites.
- Managing Water Resources:Efforts are underway to manage the lake’s water resources sustainably, ensuring that the lake’s ecosystem is protected from the impacts of drought and human activity. These efforts involve monitoring water levels, conducting research on water management strategies, and working with local communities to develop sustainable water use practices.
- Protecting Biodiversity:Efforts are underway to protect the lake’s biodiversity, including its unique flora and fauna. These efforts involve monitoring the populations of endangered species, conducting research on habitat restoration, and working with local communities to reduce the impacts of human activity on the lake’s ecosystem.
Challenges and Opportunities
Sustainable tourism at Lake Mungo presents both challenges and opportunities. The challenges include balancing the need to protect the lake’s cultural and natural heritage with the desire to provide visitors with a rewarding and enriching experience. The opportunities include promoting responsible tourism practices, supporting local communities, and educating visitors about the importance of conservation.
By working together, the tourism industry, conservation organizations, and local communities can ensure that Lake Mungo remains a place of wonder and discovery for generations to come.
Closing Notes: Lake Mungo
Lake Mungo is a place of profound beauty and historical significance. It stands as a powerful reminder of the enduring spirit of humanity and the importance of protecting our planet’s cultural and natural heritage. The lessons learned from Lake Mungo continue to guide us in understanding our past and shaping a sustainable future.
Whether you’re an archaeologist, a nature enthusiast, or simply seeking a glimpse into the ancient world, Lake Mungo offers a truly unforgettable experience.