Bacterial vaginosis medication is a crucial aspect of managing this common vaginal condition. It aims to restore the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Understanding the different types of medication, their effectiveness, and potential side effects is essential for making informed decisions about treatment.
This article explores the various treatment options for bacterial vaginosis, including oral and topical medications. We’ll delve into the factors that influence medication selection, proper dosage and administration, and potential interactions. Additionally, we’ll discuss prevention strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help manage this condition.
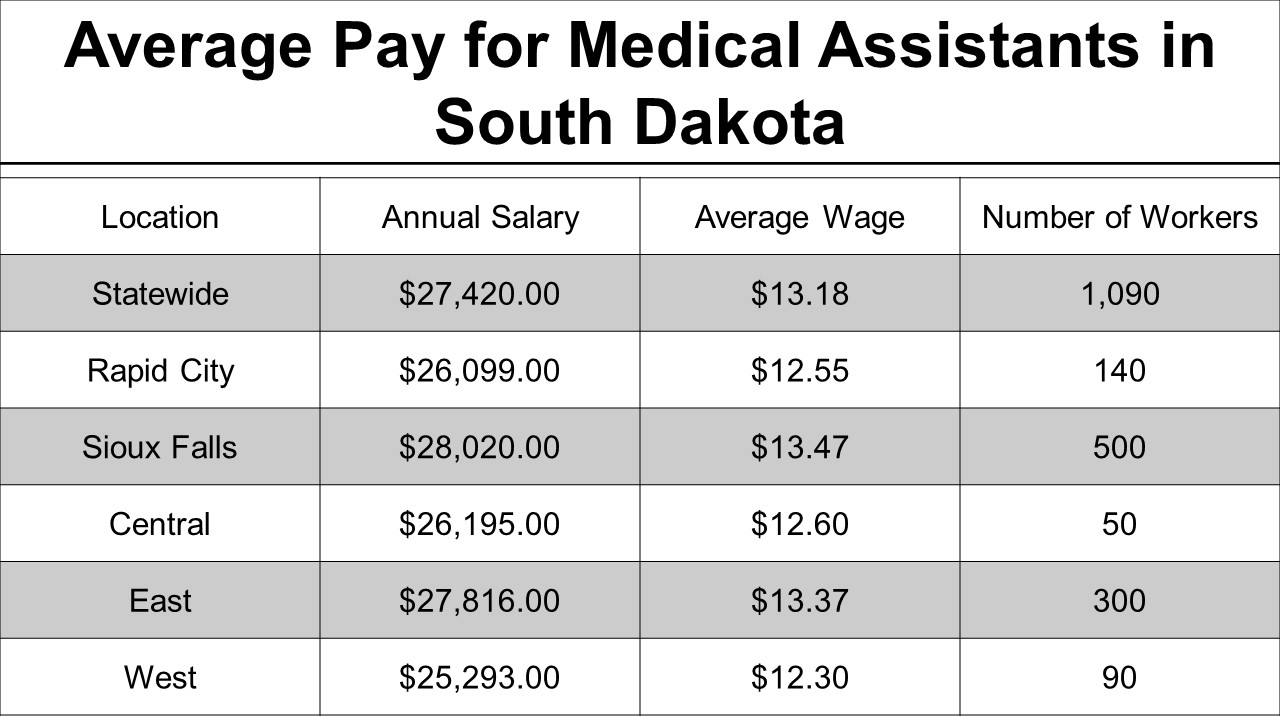
Bacterial Vaginosis: An Overview: Bacterial Vaginosis Medication
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal condition that occurs when there is an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. This imbalance can lead to an overgrowth of certain bacteria, which can cause various symptoms, including vaginal discharge, odor, and irritation.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and potential complications of BV is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Causes of Bacterial Vaginosis, Bacterial vaginosis medication
The exact cause of BV is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These factors include:
- Changes in vaginal pH:The vagina naturally has a slightly acidic pH, which helps to keep harmful bacteria in check. However, certain factors, such as douching, can disrupt this balance and make the vagina more alkaline, favoring the growth of BV-causing bacteria.
- Douching:Douching is the practice of flushing the vagina with water or other solutions. This can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of BV.
- New sexual partners:Having a new sexual partner can introduce new bacteria to the vagina, which may disrupt the balance of bacteria and lead to BV.
- Certain sexual practices:Some sexual practices, such as anal sex, can introduce bacteria from the rectum to the vagina, which may contribute to BV.
- Hormonal changes:Hormonal changes, such as those associated with menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can also affect the balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of BV.
Symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis
BV symptoms can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all. However, common symptoms include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge:This discharge is often described as thin, white or gray, and may have a fishy odor.
- Vaginal odor:The odor is often described as fishy and may be more noticeable after sexual intercourse or during menstruation.
- Vaginal itching or burning:This is a less common symptom of BV.
- Pain during urination:This symptom is also uncommon but may occur in some cases.
Potential Risks and Complications of Untreated Bacterial Vaginosis
While BV is generally not a serious condition, it can lead to complications if left untreated. These complications include:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID):PID is an infection of the reproductive organs that can cause serious complications, such as infertility and ectopic pregnancy.
- Premature birth:BV has been linked to an increased risk of premature birth in pregnant women.
- Increased risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs):BV can make it easier for certain STIs, such as HIV, to be transmitted.
- Complications after gynecological surgery:BV can increase the risk of infection after gynecological surgery.
Treatment Options for Bacterial Vaginosis
The goal of BV treatment is to restore the balance of bacteria in the vagina and alleviate symptoms. Treatment typically involves the use of medications, which can be either oral or topical.
Types of Medications
Several types of medications are used to treat BV, including:
- Metronidazole (Flagyl):This is a commonly used antibiotic that is available in both oral and topical forms.
- Clindamycin (Cleocin):This is another antibiotic that is available in both oral and topical forms.
- Tinidazole (Tindamax):This is an antibiotic that is similar to metronidazole but is only available in oral form.
Effectiveness of Oral and Topical Medications
Both oral and topical medications are effective in treating BV. Oral medications are generally absorbed into the bloodstream and reach the vagina through circulation. Topical medications are applied directly to the vagina, where they work locally to kill bacteria.
Potential Side Effects of Medications
Like all medications, those used to treat BV can cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Gastrointestinal upset:This can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
- Headache:This is a common side effect of metronidazole.
- Metallic taste in the mouth:This is another common side effect of metronidazole.
- Vaginal irritation:This can occur with topical medications.
Medication Selection and Administration
The choice of medication for BV will depend on several factors, including the severity of the symptoms, the patient’s medical history, and any potential drug interactions.
Factors Influencing Medication Choice
Here are some factors that influence the choice of medication for BV:
- Severity of symptoms:For mild symptoms, topical medications may be sufficient. For more severe symptoms, oral medications may be recommended.
- Medical history:Certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, may affect the choice of medication.
- Drug interactions:Some medications can interact with medications used to treat BV, so it is important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking.
- Pregnancy:If you are pregnant, your healthcare provider will recommend a safe and effective medication for BV.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of BV medications will vary depending on the specific medication and the individual patient. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
- Oral medications:Oral medications are typically taken once or twice a day for a period of 7 days.
- Topical medications:Topical medications are typically applied to the vagina once a day for a period of 5 to 7 days.
Medication Interactions and Contraindications
It is important to be aware of potential medication interactions and contraindications when taking medications for BV.
- Alcohol:Avoid alcohol consumption while taking metronidazole or tinidazole, as it can increase the risk of side effects.
- Warfarin:Metronidazole can increase the risk of bleeding in patients taking warfarin, a blood thinner.
- Lithium:Metronidazole can increase the levels of lithium in the blood, which can lead to toxicity.
Prevention and Management
While BV is a common condition, there are several steps you can take to prevent it and manage symptoms if they occur.
Tips for Preventing Bacterial Vaginosis
- Avoid douching:Douching disrupts the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increases the risk of BV.
- Practice safe sex:Use condoms to reduce the risk of BV and other STIs.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing:Tight clothing can trap moisture and create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
- Avoid using scented feminine hygiene products:These products can irritate the vagina and disrupt the balance of bacteria.
- Maintain good hygiene:Wash the genital area with mild soap and water daily.
Lifestyle Modifications
Certain lifestyle modifications can help manage BV symptoms and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing:Tight clothing can trap moisture and create a favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
- Avoid douching:Douching can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and increase the risk of BV.
- Maintain good hygiene:Wash the genital area with mild soap and water daily.
- Avoid using scented feminine hygiene products:These products can irritate the vagina and disrupt the balance of bacteria.
Self-Care and Follow-Up Care
Here is a table highlighting key points of self-care and follow-up care after treatment:
| Self-Care | Follow-Up Care |
|---|---|
| Maintain good hygiene | Schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to ensure the infection has cleared. |
| Avoid douching | Discuss any concerns or questions you may have about BV or its treatment. |
| Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing | Report any recurrence of symptoms to your healthcare provider. |
| Avoid using scented feminine hygiene products | Consider a repeat swab test if symptoms persist or recur. |
Resources and Support
If you have any questions or concerns about BV, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. There are also several resources available to provide information and support.
Reliable Resources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):The CDC provides comprehensive information on BV, including symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention.
- Office on Women’s Health (OWH):The OWH offers information on women’s health issues, including BV.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG):ACOG provides evidence-based information on women’s health, including BV.
Healthcare Organizations
| Organization | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | (800) CDC-INFO (232-4636) |
| Office on Women’s Health (OWH) | (800) 994-WOMAN (9662) |
| American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) | (202) 638-5577 |
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of BV. A healthcare provider can perform a pelvic exam and a swab test to confirm the diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment option. They can also provide guidance on preventing future episodes and managing any associated symptoms.
Outcome Summary
Bacterial vaginosis is a treatable condition, and with the right medication and self-care practices, most women can experience symptom relief and prevent future occurrences. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment is crucial. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your health and make informed decisions about your care.