Conjunctivitis medication is essential for treating the inflammation and irritation caused by this common eye condition. Understanding the different types of conjunctivitis, their causes, and the medications available is crucial for effective management. Whether it’s a viral, bacterial, or allergic reaction, knowing the right treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
This guide delves into the various types of conjunctivitis medications, their uses, and how to use them safely and effectively. We’ll explore both over-the-counter and prescription options, providing insights into their mechanisms of action and potential side effects. Additionally, we’ll discuss preventative measures to reduce the risk of developing conjunctivitis and when it’s necessary to seek medical attention.
Understanding Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, the transparent membrane that lines the inside of the eyelid and covers the white part of the eye. It’s a very common condition that can affect people of all ages.
There are several types of conjunctivitis, each with its own cause and symptoms. Understanding the different types of conjunctivitis can help you identify the cause and seek appropriate treatment.
Types of Conjunctivitis, Conjunctivitis medication
Conjunctivitis is broadly categorized into three main types:
- Viral Conjunctivitis:This is the most common type of conjunctivitis, caused by viruses such as adenovirus. It’s highly contagious and spreads through close contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis:This type is caused by bacteria, often Staphylococcus aureus or Haemophilus influenzae. It’s also contagious and can spread through direct contact or contaminated objects.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis:This type is caused by an allergic reaction to substances such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. It’s not contagious but can be very irritating and uncomfortable.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
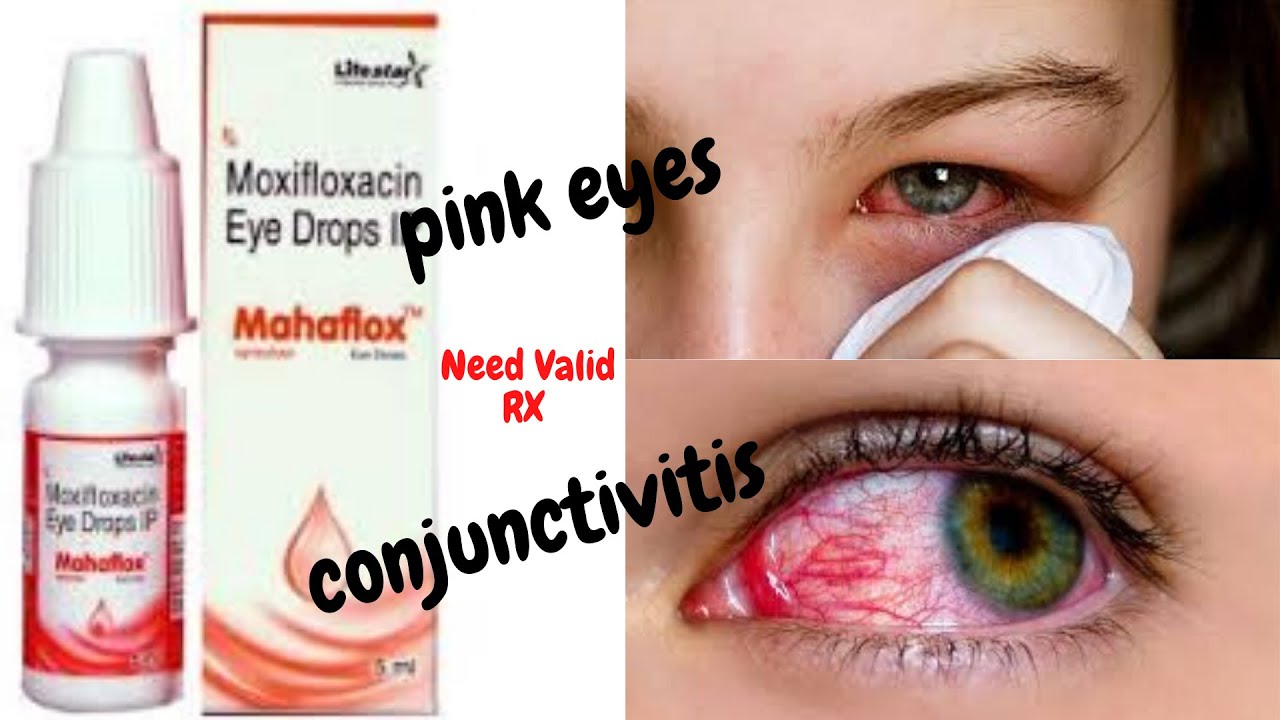
The symptoms of conjunctivitis can vary depending on the type. However, common symptoms include:
- Redness or pinkness of the white part of the eye
- Itching
- Watery discharge
- Crusting of the eyelids, especially in the morning
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred vision
Viral conjunctivitis is often accompanied by a clear or white discharge, while bacterial conjunctivitis typically has a thicker, yellow or green discharge. Allergic conjunctivitis is often characterized by intense itching and watery eyes.
Causes and Risk Factors
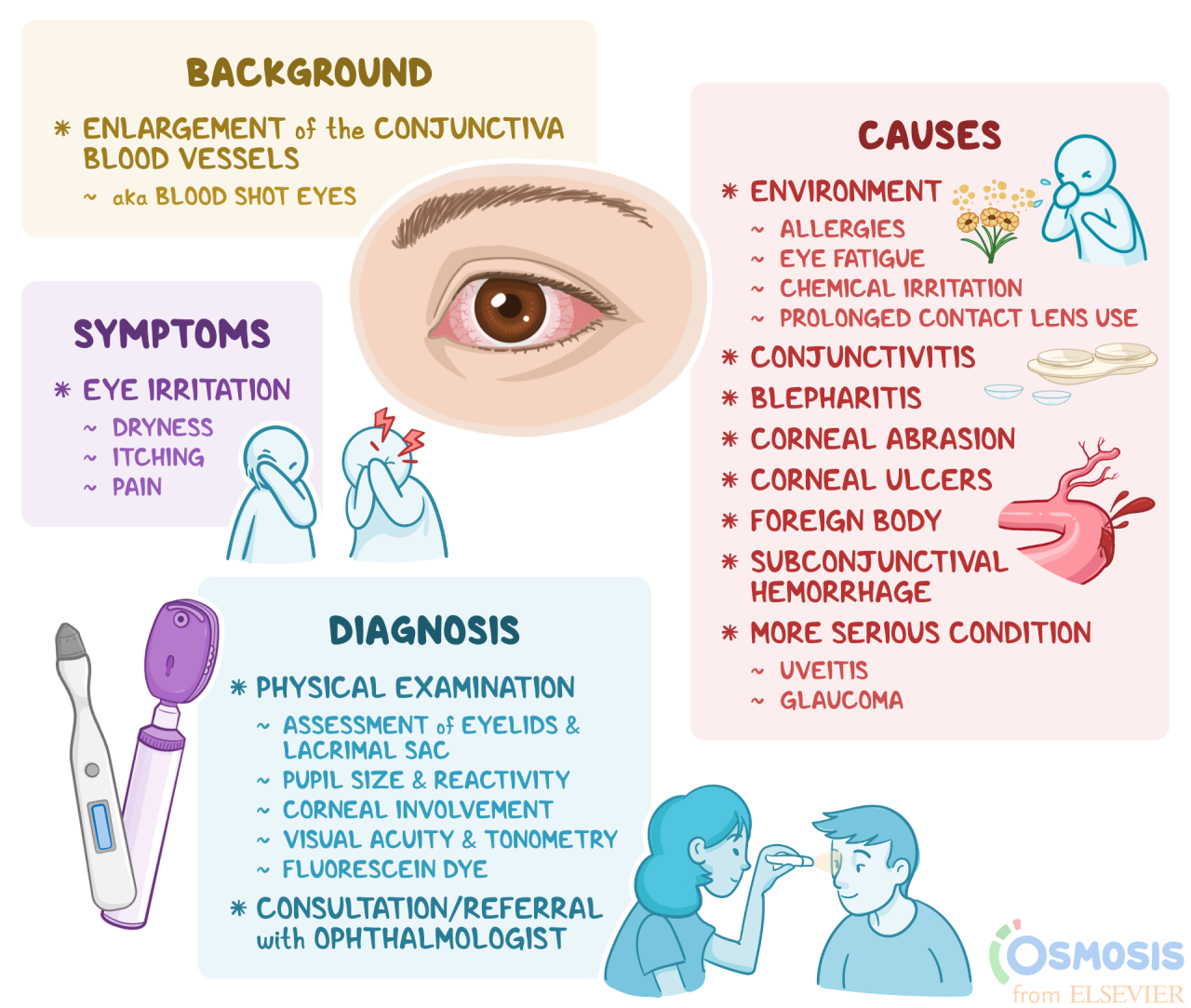
The causes of conjunctivitis vary depending on the type. As mentioned earlier, viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses, bacterial conjunctivitis by bacteria, and allergic conjunctivitis by allergens. Here are some risk factors that can increase your chances of developing conjunctivitis:
- Close contact with infected individuals
- Poor hygiene practices, such as not washing hands frequently
- Exposure to allergens
- Wearing contact lenses improperly or for extended periods
- Weakened immune system
Conjunctivitis Medication: Types and Uses
Treatment for conjunctivitis depends on the underlying cause. Medications can help relieve symptoms and speed up recovery. Here’s a look at the common medications used to treat conjunctivitis, categorized by their active ingredients and intended use:
Antibiotics for Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis. They work by killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria, helping to clear the infection.
- Erythromycin:This antibiotic is available as an eye ointment or eye drops. It’s effective against a wide range of bacteria and is commonly used for bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Bacitracin:This antibiotic is also available as an eye ointment. It’s effective against certain types of bacteria and is often combined with polymyxin B for broader coverage.
- Ciprofloxacin:This antibiotic is available as eye drops. It’s effective against a wide range of bacteria and is often used for more severe cases of bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Ofloxacin:This antibiotic is also available as eye drops. It’s effective against a wide range of bacteria and is often used for more severe cases of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Antihistamines for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Antihistamines block the action of histamine, a chemical released by the body during allergic reactions. This helps reduce inflammation and itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
- Olopatadine:This antihistamine is available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing itching, redness, and watery eyes associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
- Ketotifen:This antihistamine is also available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing itching, redness, and watery eyes associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
- Emedastine:This antihistamine is available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing itching, redness, and watery eyes associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
Artificial Tears for Dry Eye Conjunctivitis
Dry eye conjunctivitis occurs when the eyes don’t produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. Artificial tears can help lubricate the eyes and relieve dryness, irritation, and discomfort.
- Lubricating Eye Drops:These drops are available over-the-counter and contain ingredients like hyaluronic acid or glycerin to provide moisture and lubrication to the eyes.
Steroid Eye Drops for Severe Conjunctivitis
Steroid eye drops are sometimes used to treat severe cases of conjunctivitis, especially when inflammation is significant. They work by reducing inflammation but are not used for bacterial conjunctivitis as they can mask the infection.
- Prednisolone:This steroid is available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing inflammation and swelling but should be used under the guidance of a doctor.
- Loteprednol:This steroid is also available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing inflammation and swelling but should be used under the guidance of a doctor.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications for Conjunctivitis
Many OTC medications are available for conjunctivitis, offering relief from symptoms and promoting healing. While OTC medications can be helpful, it’s important to choose the right one for your specific type of conjunctivitis and consult a doctor if your symptoms worsen or persist.
OTC Medications for Allergic Conjunctivitis
OTC antihistamine eye drops can be effective in reducing itching, redness, and watery eyes associated with allergic conjunctivitis. Some common OTC antihistamine eye drops include:
- Naphazoline:This antihistamine is available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing redness and itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
- Pheniramine:This antihistamine is also available as eye drops. It’s effective in reducing redness and itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis.
OTC Medications for Dry Eye Conjunctivitis
OTC lubricating eye drops can provide relief from dryness, irritation, and discomfort associated with dry eye conjunctivitis. These drops contain ingredients like hyaluronic acid or glycerin to moisturize the eyes.
Choosing the Right OTC Medication
When choosing an OTC medication for conjunctivitis, it’s essential to consider the type of conjunctivitis you have and your symptoms. If you’re unsure about the cause of your conjunctivitis, consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Prescription Medications for Conjunctivitis
Prescription medications are often used for more severe cases of conjunctivitis or when OTC medications are ineffective. These medications can be more potent and targeted to the specific type of conjunctivitis.
Prescription Medications for Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Prescription antibiotics are often used for bacterial conjunctivitis, especially for severe cases or when OTC antibiotics are not effective. These antibiotics are available as eye drops or ointments and are often prescribed for a longer duration than OTC antibiotics.
Prescription Medications for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Prescription antihistamine eye drops are available for allergic conjunctivitis. These medications are more potent than OTC antihistamine eye drops and can provide longer-lasting relief.
Prescription Medications for Dry Eye Conjunctivitis
Prescription lubricating eye drops are available for dry eye conjunctivitis. These drops contain ingredients like cyclosporine or lifitegrast, which help stimulate tear production and reduce inflammation.
Benefits and Limitations of Prescription Medications
Prescription medications offer several benefits over OTC options, including:
- Higher potency:Prescription medications are often more potent than OTC options, providing faster and more effective relief.
- Targeted treatment:Prescription medications can be tailored to the specific type of conjunctivitis and individual needs.
- Longer duration of action:Prescription medications can provide longer-lasting relief than OTC options.
However, prescription medications also have some limitations, including:
- Potential side effects:Prescription medications can have more side effects than OTC options.
- Cost:Prescription medications are typically more expensive than OTC options.
- Need for a doctor’s prescription:You need a doctor’s prescription to obtain prescription medications.
Obtaining Prescription Medications
To obtain prescription medications for conjunctivitis, you need to see a doctor. They will diagnose your condition, determine the appropriate medication, and write you a prescription. You can then fill your prescription at a pharmacy.
Using Conjunctivitis Medication Safely and Effectively
Properly administering conjunctivitis medication is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing side effects. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to administer eye drops and ointments:
Administering Eye Drops
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Tilt your head back slightly and look up.
- Pull down the lower eyelid to create a small pocket.
- Hold the dropper about 1/2 inch above the eye and gently squeeze one drop into the pocket.
- Close your eye for a few seconds.
- Gently press on the inner corner of the eye (near the nose) for about 30 seconds to prevent the medication from draining out.
- Repeat the steps for the other eye if necessary.
Administering Eye Ointment
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Tilt your head back slightly and look up.
- Pull down the lower eyelid to create a small pocket.
- Squeeze a thin line of ointment into the pocket.
- Close your eye for a few seconds.
- Gently rub your eyelid with a clean finger to spread the ointment evenly.
- Repeat the steps for the other eye if necessary.
Tips for Safe and Effective Use
- Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage, frequency, and duration of treatment.
- Avoid touching the tip of the dropper or ointment tube to your eye or any other surface.
- Do not share eye drops or ointments with others.
- Dispose of eye drops or ointments according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- If you experience any adverse effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Conjunctivitis medications can cause side effects, although they are generally mild. Common side effects include:
- Burning or stinging
- Redness
- Itching
- Blurred vision
Some medications can interact with other medications or medical conditions. It’s essential to inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and vitamins.
Preventing Conjunctivitis
While conjunctivitis is often contagious, several preventative measures can help reduce your risk of developing this condition. Good hygiene practices, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and protecting your eyes from irritants and allergens are key.
Good Hygiene Practices
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching your eyes, nose, or mouth.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands.
- Clean your contact lenses according to the manufacturer’s instructions and replace them regularly.
- Don’t share eye makeup, towels, or washcloths.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling contaminated objects, such as used tissues or eye drops.
Avoiding Contact with Infected Individuals
- Stay away from people with conjunctivitis.
- If you have conjunctivitis, avoid close contact with others to prevent spreading the infection.
Protecting Your Eyes from Irritants and Allergens
- Wear protective eyewear, such as goggles or sunglasses, when working with chemicals or dust.
- Avoid smoke and other irritants.
- If you have allergies, try to avoid allergens or take allergy medications to reduce your symptoms.
- Use a cool compress or artificial tears to soothe irritated eyes.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Most cases of conjunctivitis are mild and resolve on their own within a few days or weeks. However, some cases may require medical attention. It’s essential to see a doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Severe pain in your eye
- Vision changes, such as blurred vision or double vision
- Excessive discharge or pus
- Swelling of the eyelids or surrounding area
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Symptoms that persist for more than a week
- Symptoms that worsen despite home treatment
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
Untreated conjunctivitis can lead to complications, including:
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body
- Permanent vision loss
- Corneal ulcers
If you have any concerns about your symptoms, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention. A doctor can properly diagnose your condition and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Wrap-Up
Conjunctivitis can be a bothersome condition, but with proper treatment and preventative measures, it can be effectively managed. Understanding the different types of conjunctivitis and the available medication options empowers you to make informed decisions about your eye health.
Remember, if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.