COVID medications have become a crucial part of the fight against the pandemic, offering a range of treatment options for individuals infected with the virus. From antiviral medications targeting the virus itself to immunomodulatory drugs that help regulate the immune response, these treatments aim to reduce symptoms, prevent severe illness, and improve patient outcomes.
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of COVID medications available, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and ongoing research efforts. We’ll also delve into ethical considerations surrounding access and distribution, patient perspectives, and future directions in COVID-19 treatment research.
Overview of COVID-19 Medications
The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred intense research and development efforts to create effective treatments. As a result, a range of medications have been developed to combat the virus and mitigate its impact on patients. These medications target different aspects of the disease, from inhibiting viral replication to modulating the immune response.
Types of COVID-19 Medications
COVID-19 medications can be broadly categorized into several classes, each with distinct mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications.
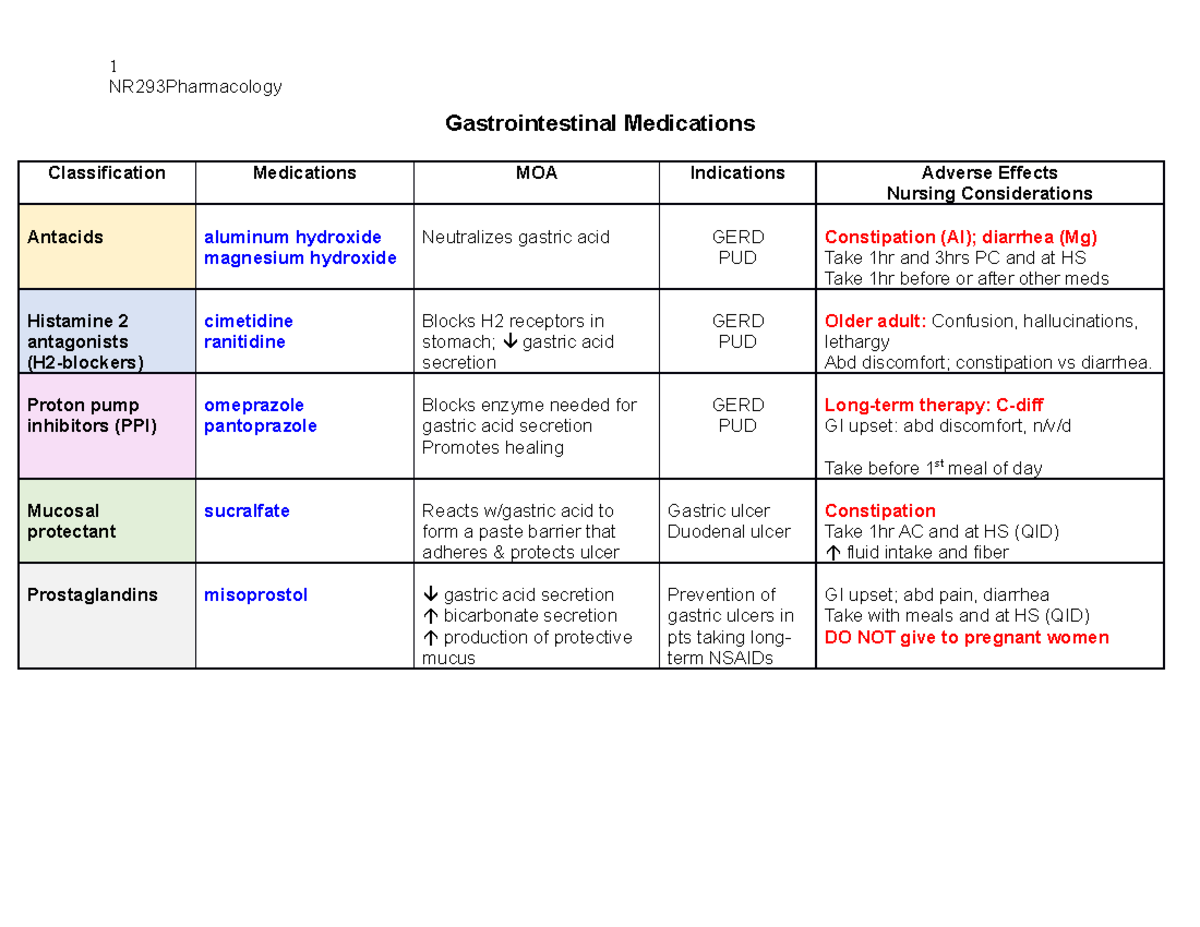
- Antiviral Medications: These medications directly target the virus, preventing its replication and spread within the body. Examples include remdesivir, molnupiravir, and Paxlovid.
- Immunomodulatory Medications: These medications regulate the immune response to COVID-19, helping to control inflammation and prevent excessive immune system activation. Examples include corticosteroids, such as dexamethasone, and IL-6 inhibitors, such as tocilizumab.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: These medications are laboratory-produced antibodies that bind to the virus, neutralizing its ability to infect cells. Examples include bamlanivimab, casirivimab, and imdevimab.
- Other Medications: Some other medications, such as anticoagulants and anti-inflammatory drugs, are used to address specific complications associated with COVID-19, such as blood clots and inflammation.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms of action for COVID-19 medications vary depending on their class and specific target.
- Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications typically work by interfering with the virus’s ability to replicate, either by inhibiting its enzymes or by disrupting its genetic material. For example, remdesivir inhibits the viral RNA polymerase, preventing the virus from copying its genetic material.
- Immunomodulatory Medications: Immunomodulatory medications aim to regulate the immune response to COVID-19. Corticosteroids, for example, suppress inflammation by reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines. IL-6 inhibitors block the activity of the IL-6 cytokine, which plays a key role in inflammation and immune dysregulation.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies bind to specific proteins on the surface of the virus, preventing it from attaching to and entering human cells. This effectively neutralizes the virus and prevents infection.
Effectiveness
The effectiveness of COVID-19 medications in treating symptoms and reducing disease severity varies depending on the medication, the severity of the disease, and the individual patient’s characteristics.
- Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications have shown promise in reducing the duration of symptoms and improving outcomes for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. For example, remdesivir has been shown to shorten the time to recovery and improve survival rates in hospitalized patients.
- Immunomodulatory Medications: Immunomodulatory medications have been effective in managing inflammation and preventing severe complications in COVID-19 patients, particularly those with severe disease. For example, dexamethasone has been shown to reduce mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated effectiveness in preventing severe COVID-19 illness, particularly in high-risk individuals. For example, bamlanivimab and casirivimab have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications play a crucial role in the treatment of COVID-19 by directly targeting the virus and inhibiting its replication. This helps to reduce viral load, alleviate symptoms, and prevent the development of severe disease.
Types of Antiviral Medications
Several antiviral medications have been approved or are under investigation for the treatment of COVID-19. These medications target different stages of the viral lifecycle, disrupting the virus’s ability to replicate and spread within the body.
- Remdesivir: Remdesivir is a nucleotide analog that inhibits the viral RNA polymerase, preventing the virus from copying its genetic material. It is administered intravenously and has been shown to reduce the duration of hospitalization in patients with COVID-19.
- Molnupiravir: Molnupiravir is an oral antiviral medication that incorporates itself into the viral RNA, introducing errors that prevent the virus from replicating. It has been authorized for use in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of developing severe disease.
- Paxlovid: Paxlovid is an oral antiviral medication that combines nirmatrelvir, a protease inhibitor, with ritonavir, a booster that increases nirmatrelvir’s effectiveness. It inhibits the viral protease, a key enzyme required for viral replication. Paxlovid has been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Effectiveness of Antiviral Medications
The effectiveness of antiviral medications in treating COVID-19 has been studied extensively, with varying results depending on the medication, the severity of the disease, and the patient’s characteristics.
- Remdesivir: Remdesivir has shown moderate effectiveness in reducing the duration of hospitalization and improving outcomes for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. However, its impact on mortality has been less consistent.
- Molnupiravir: Molnupiravir has been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of developing severe disease. However, its effectiveness may be limited in patients with severe disease.
- Paxlovid: Paxlovid has demonstrated significant effectiveness in reducing the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. It has also shown promise in preventing severe disease in high-risk individuals.
Side Effects and Contraindications
Antiviral medications, like all medications, can have potential side effects and contraindications. It is important to discuss these with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
- Remdesivir: Common side effects of remdesivir include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and elevated liver enzymes. It is contraindicated in patients with severe liver disease.
- Molnupiravir: Common side effects of molnupiravir include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. It is contraindicated in pregnant women due to potential risks to the fetus.
- Paxlovid: Common side effects of Paxlovid include altered taste, diarrhea, and muscle aches. It is contraindicated in patients with severe liver disease or certain kidney problems.
Immunomodulatory Medications
Immunomodulatory medications play a crucial role in managing COVID-19 by regulating the immune response and mitigating the potentially harmful effects of excessive inflammation. These medications help to control inflammation, prevent organ damage, and improve overall outcomes for patients with COVID-19.
Role of Immunomodulatory Medications
The immune response to COVID-19 can be complex and sometimes overwhelming. In some cases, the immune system can become overactive, leading to a cytokine storm, a condition characterized by excessive inflammation that can damage organs and lead to severe complications.
Immunomodulatory medications help to dampen this excessive immune response, restoring balance and protecting the body from harm.
Mechanisms of Action
Immunomodulatory medications work by modulating different aspects of the immune response, such as cytokine production, immune cell activation, and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as dexamethasone, are potent anti-inflammatory agents that suppress the production of inflammatory cytokines. They help to reduce inflammation and prevent organ damage, particularly in patients with severe COVID-19.
- IL-6 Inhibitors: IL-6 inhibitors, such as tocilizumab, block the activity of the IL-6 cytokine, a key player in inflammation and immune dysregulation. They have shown promise in treating patients with severe COVID-19 who have a high level of IL-6.
Examples of Immunomodulatory Medications
Several immunomodulatory medications have been used in the treatment of COVID-19, with varying degrees of effectiveness and safety profiles.
- Dexamethasone: Dexamethasone is a corticosteroid that has been shown to reduce mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19. It is typically administered intravenously or orally.
- Tocilizumab: Tocilizumab is an IL-6 inhibitor that has shown promise in treating patients with severe COVID-19 who have a high level of IL-6. It is typically administered intravenously.
Potential Benefits and Risks

Immunomodulatory medications can offer significant benefits in managing COVID-19, but they also carry potential risks. It is essential to weigh these risks and benefits carefully before initiating treatment.
- Benefits: Immunomodulatory medications can help to control inflammation, prevent organ damage, and improve overall outcomes for patients with COVID-19, particularly those with severe disease.
- Risks: Immunomodulatory medications can increase the risk of infections, worsen existing conditions, and have other side effects. It is important to discuss these risks with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced antibodies that target specific proteins on the surface of the virus, effectively neutralizing its ability to infect cells. They are a promising treatment option for COVID-19, particularly in high-risk individuals who may be at risk of developing severe disease.
Concept of Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies are designed to bind to specific proteins on the surface of the virus, such as the spike protein. This binding action blocks the virus from attaching to and entering human cells, effectively neutralizing the virus and preventing infection.
Types of Monoclonal Antibodies
Several types of monoclonal antibodies have been developed for the treatment of COVID-19, each targeting different parts of the virus or different stages of the infection.
- Bamlanivimab and casirivimab: These monoclonal antibodies target the spike protein of the virus, preventing it from attaching to human cells. They have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
- Imdevimab: Imdevimab is another monoclonal antibody that targets the spike protein of the virus. It has been shown to be effective in preventing severe COVID-19 illness in high-risk individuals.
Effectiveness of Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated effectiveness in preventing severe COVID-19 illness, particularly in high-risk individuals. They have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death, particularly when administered early in the course of infection.
Taking medication as prescribed by your doctor is crucial for managing your health. It’s important to understand the purpose of each medication, potential side effects, and any interactions with other medications or supplements. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to ensure safe and effective treatment.
- Bamlanivimab and casirivimab: These monoclonal antibodies have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization and death in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 who are at high risk of developing severe disease.
- Imdevimab: Imdevimab has been shown to be effective in preventing severe COVID-19 illness in high-risk individuals, such as those with underlying medical conditions.
COVID-19 Medication Development
The development of effective and safe COVID-19 medications is a continuous and evolving process, driven by ongoing research and clinical trials. The goal is to identify new therapeutic targets, optimize existing treatments, and develop novel medications that can effectively combat the virus and mitigate its impact on patients.
Ongoing Research and Development Efforts
Research and development efforts for new COVID-19 medications are ongoing, focusing on a range of approaches, including:
- Novel Antiviral Medications: Researchers are exploring new antiviral medications that target different aspects of the viral lifecycle, aiming to develop more effective and safe treatments.
- Immunomodulatory Therapies: Research is ongoing to develop new immunomodulatory therapies that can more effectively regulate the immune response to COVID-19, preventing excessive inflammation and improving outcomes for patients.
- Combination Therapies: Combining different medications with complementary mechanisms of action may enhance therapeutic efficacy and address the evolving nature of the virus.
- Antiviral Prophylaxis: Researchers are exploring the potential for antiviral medications to prevent infection in high-risk individuals, such as healthcare workers and immunocompromised individuals.
Challenges and Opportunities
Developing effective and safe COVID-19 treatments presents a number of challenges, including:
- Rapid Viral Evolution: The SARS-CoV-2 virus is constantly evolving, making it difficult to develop medications that remain effective against emerging variants.
- Complex Immune Response: The immune response to COVID-19 is complex and can vary significantly between individuals, making it challenging to develop medications that are universally effective.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations are paramount in the development and use of COVID-19 medications, ensuring equitable access and minimizing potential risks.
Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities for advancement in COVID-19 medication research, driven by:
- Advances in Technology: Advances in technology, such as high-throughput screening and artificial intelligence, are accelerating the discovery and development of new medications.
- Global Collaboration: International collaboration and sharing of data are crucial for accelerating research and development efforts.
- Increased Funding: Significant funding has been allocated to COVID-19 research, supporting the development of new treatments.
Future Directions, Covid medications
Future directions in COVID-19 medication research include:
- Developing Broad-Spectrum Antivirals: Developing antiviral medications that are effective against a wide range of viral variants is a key priority.
- Improving Delivery Methods: Developing more convenient and effective delivery methods for COVID-19 medications, such as oral or inhaled formulations, is essential.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and disease characteristics can improve outcomes.
- Pan-Coronavirus Therapeutics: Developing medications that are effective against a range of coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 and potential future emerging coronaviruses, is a long-term goal.
Access to COVID-19 Medications: Covid Medications
Ensuring equitable access to COVID-19 medications is a critical global health priority. However, a number of challenges and barriers hinder access to these essential treatments, particularly in low-resource settings.
Challenges and Barriers
Several factors contribute to the unequal distribution and access to COVID-19 medications worldwide:
- High Costs: Many COVID-19 medications are expensive, making them inaccessible to individuals and healthcare systems in low-resource settings.
- Limited Supply: Production and distribution challenges can limit the availability of COVID-19 medications, particularly in areas with weak healthcare infrastructure.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, including storage facilities, transportation systems, and trained personnel, can impede the delivery of COVID-19 medications to those in need.
- Disparities in Healthcare Access: Existing disparities in healthcare access, including socioeconomic inequalities and geographic isolation, exacerbate the challenges of ensuring equitable access to COVID-19 medications.
Strategies for Improving Access
Addressing the challenges of access to COVID-19 medications requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Price Reductions: Lowering the cost of COVID-19 medications through price negotiations, generic drug production, and financial assistance programs is crucial for expanding access.
- Increased Production: Scaling up production of COVID-19 medications to meet global demand is essential for ensuring adequate supply.
- Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure: Investing in healthcare infrastructure, including storage facilities, transportation systems, and training programs, is critical for delivering COVID-19 medications effectively.
- International Collaboration: Sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise through international collaboration is essential for developing and distributing COVID-19 medications equitably.
Role of Public Health Initiatives and International Collaboration
Public health initiatives and international collaboration are essential for ensuring equitable access to COVID-19 medications.
It’s important to understand your medication and how it affects your body. Make sure to talk to your doctor about any concerns or questions you have, and always follow their instructions carefully.
- Public Health Initiatives: Public health initiatives can play a crucial role in raising awareness about COVID-19 medications, promoting their appropriate use, and addressing access barriers.
- International Collaboration: International collaboration is essential for sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise, ensuring that COVID-19 medications are developed, produced, and distributed equitably across the globe.
Conclusion
As the pandemic continues to evolve, the development of new and improved COVID medications remains a top priority. Ongoing research and clinical trials are crucial for understanding the long-term effects of the virus and identifying more effective and safe treatment options.
With a continued focus on scientific innovation and equitable access to care, we can work towards a future where COVID-19 is effectively managed and its impact minimized.