The Great Lakes, a collection of five freshwater giants, stand as a testament to the power of nature. Formed by glacial activity over thousands of years, these lakes hold an immense amount of water, shaping the landscapes and economies of both the United States and Canada.
Their vastness and beauty have attracted people for centuries, inspiring exploration, commerce, and cultural development.
From the largest, Lake Superior, to the most southerly, Lake Ontario, each lake possesses unique characteristics. The Great Lakes’ depths and surrounding ecosystems support a diverse array of plant and animal life, making them a vital part of North America’s biodiversity.
Their importance extends beyond their natural splendor; they are a critical source of drinking water, transportation, and economic activity for millions of people.
Geography and Formation: Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, a collection of five freshwater lakes located in North America, are a testament to the transformative power of geological forces. These majestic bodies of water, known as Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, were formed over millennia through a complex interplay of glacial activity, tectonic shifts, and erosion.
Geological Processes
The formation of the Great Lakes can be traced back to the last glacial period, which began about 2.6 million years ago and ended roughly 11,700 years ago. During this period, massive ice sheets, known as continental glaciers, covered much of North America.
These glaciers, weighing billions of tons, exerted immense pressure on the land, carving out vast depressions and shaping the landscape. As the climate warmed and the glaciers retreated, these depressions filled with meltwater, eventually forming the Great Lakes.
Unique Geographical Features
- Lake Superior:The largest and deepest of the Great Lakes, Lake Superior boasts a surface area of 31,700 square miles and a maximum depth of 1,333 feet. Its vastness and surrounding boreal forests contribute to its wild and rugged beauty.
- Lake Michigan:The second-largest Great Lake, Lake Michigan is known for its sandy beaches and charming coastal towns. It is the only one of the Great Lakes that is entirely within the United States, with its shoreline shared by Michigan, Wisconsin, Illinois, and Indiana.
- Lake Huron:The third-largest lake, Lake Huron is renowned for its stunning sunsets and numerous islands, including the Manitoulin Island, the world’s largest freshwater island. It shares a border with Lake Michigan through the Straits of Mackinac.
- Lake Erie:The shallowest of the Great Lakes, Lake Erie is known for its rich biodiversity and abundance of fish species. It is also home to the Niagara Falls, a spectacular natural wonder.
- Lake Ontario:The smallest of the Great Lakes, Lake Ontario is located at the eastern end of the Great Lakes system. It is known for its picturesque shorelines and its role in connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean through the St.
Lawrence Seaway.
Role of Glaciers
The glaciers played a crucial role in shaping the Great Lakes region. Their immense weight and movement carved out the basins that would later become the lakes. The glaciers also deposited vast quantities of sediment, creating the fertile soils that support the region’s diverse ecosystems.
Moreover, the glacial retreat left behind a network of rivers and streams that connect the lakes and provide vital water sources.
Hydrology and Water Resources
The Great Lakes are not just a collection of isolated bodies of water; they are interconnected through a complex system of rivers, streams, and canals, creating a dynamic and ever-changing hydrological network.
Water Flow Patterns
Water flows through the Great Lakes in a predictable pattern, starting with Lake Superior, the highest lake in the system. Water from Lake Superior flows eastward into Lake Huron, then through the Straits of Mackinac into Lake Michigan. From Lake Michigan, water flows southward into Lake Erie and finally into Lake Ontario.
The St. Lawrence River then carries water from Lake Ontario eastward into the Atlantic Ocean.
Water Levels and Fluctuations
The water levels of the Great Lakes fluctuate naturally due to factors such as precipitation, evaporation, and seasonal changes. However, in recent years, human activities, including water withdrawals for agricultural and industrial purposes, have contributed to significant water level fluctuations.
These fluctuations can have a profound impact on the Great Lakes ecosystem, affecting navigation, shoreline erosion, and the habitats of various species.
Importance of Water Resources
The Great Lakes are a vital source of drinking water for millions of people in the region. They also support a wide range of industries, including shipping, fishing, tourism, and manufacturing. The lakes’ vast water resources are essential for hydroelectric power generation, agriculture, and recreational activities.
The Great Lakes also play a significant role in regional and national trade, facilitating the movement of goods and people throughout the continent.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
The Great Lakes are renowned for their rich biodiversity, hosting a diverse range of plant and animal species. The lakes and their surrounding ecosystems provide vital habitats for numerous fish, birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. The Great Lakes ecosystem is a complex and interconnected web of life, with each species playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the system.
Diverse Range of Species
The Great Lakes are home to over 3,500 species of plants and animals, including iconic species like the Great Lakes sturgeon, lake trout, bald eagle, and American white pelican. The lakes also support a variety of habitats, from coastal wetlands and marshes to deepwater reefs and rocky shorelines, each providing a unique niche for different species.
Ecological Significance
The Great Lakes ecosystem is of immense ecological significance. The lakes provide essential breeding grounds for numerous migratory birds, serve as important stopover points for waterfowl, and support diverse fish populations that are vital for the food chain. The surrounding forests, wetlands, and grasslands also play a crucial role in regulating water quality, filtering pollutants, and providing habitats for various wildlife.
Challenges Faced by the Ecosystem
The Great Lakes ecosystem faces a number of challenges, including:
- Invasive Species:The introduction of non-native species, such as zebra mussels and sea lampreys, has had a devastating impact on the native ecosystem, disrupting food webs and competing with native species for resources.
- Pollution:Pollution from industrial and agricultural sources, including fertilizers, pesticides, and sewage, can contaminate the water and harm aquatic life.
- Climate Change:Climate change is altering the water temperature, ice cover, and precipitation patterns of the Great Lakes, affecting the habitats and distribution of various species.
Economic Importance and Industries
The Great Lakes have played a pivotal role in the economic development of the region, supporting a diverse range of industries and generating significant economic activity.
Key Industries
- Shipping:The Great Lakes have long been a vital transportation route for goods and people, with major ports located along their shorelines. The lakes are connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the St. Lawrence Seaway, facilitating international trade.
- Fishing:The Great Lakes are renowned for their abundant fish populations, supporting a thriving commercial fishing industry. Fish species such as lake trout, walleye, and perch are harvested for consumption and export.
- Tourism:The Great Lakes region attracts millions of tourists each year, drawn to its scenic beauty, recreational opportunities, and cultural attractions. Tourism contributes significantly to the local economy, supporting hotels, restaurants, and recreational businesses.
- Manufacturing:The Great Lakes region has a long history of manufacturing, with industries such as automotive, steel, and chemicals heavily reliant on the lakes’ water resources and transportation infrastructure.
Economic Impact
The Great Lakes have a significant economic impact on surrounding communities. The industries that rely on the lakes provide jobs, generate revenue, and support local economies. The lakes also contribute to the overall economic well-being of the region, attracting investment and promoting economic growth.
Role in Regional and National Trade
The Great Lakes play a crucial role in regional and national trade. They facilitate the movement of goods between the United States and Canada, connecting major industrial centers and agricultural regions. The lakes also provide a cost-effective and efficient transportation route for raw materials and finished products, contributing to the economic competitiveness of the region.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Great Lakes region is rich in history and culture, with stories and events that have shaped the identity of the region and its people.
Stories and Historical Events
The Great Lakes have been a source of inspiration for countless stories and legends. Native American tribes have long inhabited the region, leaving behind a rich cultural heritage. The arrival of European explorers in the 17th century marked a new chapter in the region’s history, with the fur trade, settlement, and conflict playing a significant role in shaping the landscape.
The Great Lakes also played a crucial role in the development of the United States and Canada, serving as a transportation route for westward expansion and the growth of industry.
Role in Development of the United States and Canada
The Great Lakes were instrumental in the development of both the United States and Canada. They facilitated trade and transportation, connecting different parts of the continent and fostering economic growth. The lakes also played a role in the westward expansion of both countries, providing access to new territories and resources.
Cultural Landmarks and Traditions
The Great Lakes region is home to a variety of cultural landmarks and traditions. From historic lighthouses and maritime museums to vibrant festivals and local art scenes, the region offers a rich tapestry of cultural experiences. The Great Lakes have also inspired countless works of art, literature, and music, reflecting the region’s unique beauty and character.
Environmental Issues and Sustainability
The Great Lakes face a number of environmental challenges, including pollution, climate change, and invasive species. These challenges threaten the health of the lakes and the well-being of the communities that rely on them. However, ongoing efforts to protect and restore the Great Lakes ecosystem are making progress, with a focus on sustainable practices and collaborative solutions.
Environmental Challenges
- Pollution:Pollution from industrial and agricultural sources continues to pose a threat to the Great Lakes. Runoff from farms and factories can carry fertilizers, pesticides, and other pollutants into the lakes, harming aquatic life and impacting water quality.
- Climate Change:Climate change is altering the water temperature, ice cover, and precipitation patterns of the Great Lakes. Warmer water temperatures can lead to increased algae blooms and changes in fish populations.
- Invasive Species:Invasive species, such as zebra mussels and sea lampreys, continue to disrupt the Great Lakes ecosystem. These species can outcompete native species for resources and cause significant ecological damage.
Protection and Restoration Efforts
Efforts to protect and restore the Great Lakes ecosystem are ongoing, involving governments, agencies, organizations, and communities. These efforts include:
- Water Quality Monitoring:Monitoring programs are in place to track water quality and identify sources of pollution.
- Invasive Species Management:Programs are being implemented to control invasive species, such as zebra mussels and sea lampreys.
- Habitat Restoration:Projects are underway to restore degraded habitats, such as wetlands and coastal areas.
- Public Education:Educational campaigns are raising awareness about the importance of the Great Lakes and the threats they face.
Sustainable Practices and Initiatives
Sustainable practices and initiatives are crucial for protecting the Great Lakes. These include:
- Reducing Pollution:Industries and farms are implementing practices to reduce pollution, such as using less fertilizer and improving wastewater treatment.
- Conserving Water:Individuals and businesses are encouraged to conserve water through measures such as using water-efficient appliances and landscaping.
- Protecting Coastal Areas:Efforts are underway to protect coastal areas from development and erosion, preserving valuable habitats.
- Supporting Local Businesses:Supporting local businesses that are committed to sustainable practices can help protect the Great Lakes.
Tourism and Recreation
The Great Lakes region offers a wide range of tourist destinations and recreational activities, attracting millions of visitors each year. From scenic cruises and fishing expeditions to hiking trails and cultural events, the region provides something for everyone.
Popular Tourist Destinations, Great lakes
- Niagara Falls:A spectacular natural wonder, Niagara Falls is a must-see destination for any visitor to the Great Lakes region.
- Mackinac Island:A charming island located in the Straits of Mackinac, Mackinac Island is known for its horse-drawn carriages, historic architecture, and stunning views.
- Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore:A stunning national park located on the shores of Lake Michigan, Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore offers hiking trails, scenic overlooks, and pristine beaches.
- Toronto:Canada’s largest city, Toronto is a vibrant metropolis located on the shores of Lake Ontario, offering a diverse range of attractions, including museums, theaters, and restaurants.
- Chicago:A bustling city located on the shores of Lake Michigan, Chicago is renowned for its architecture, culture, and vibrant nightlife.
Unique Experiences and Attractions
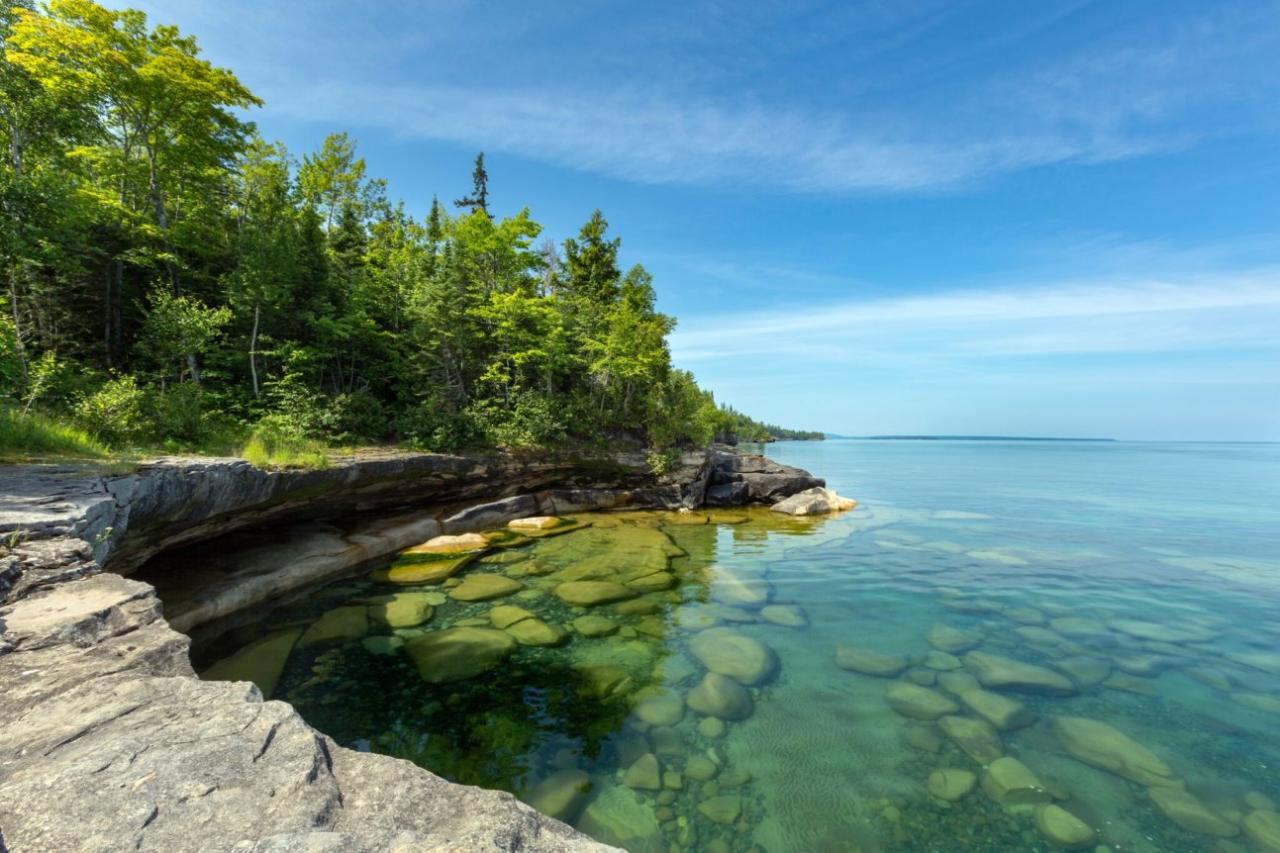

The Great Lakes region offers a variety of unique experiences and attractions, including:
- Scenic Cruises:Take a scenic cruise on one of the Great Lakes, enjoying stunning views of the shoreline and islands.
- Fishing Expeditions:Cast a line in the Great Lakes, hoping to catch a variety of fish species, including trout, walleye, and bass.
- Hiking and Biking Trails:Explore the region’s diverse landscapes on hiking and biking trails, enjoying stunning views and fresh air.
- Cultural Events:Attend festivals, concerts, and art exhibitions, celebrating the region’s rich culture and history.
- Water Sports:Engage in a variety of water sports, such as swimming, boating, kayaking, and windsurfing.
Impact of Tourism
Tourism has a significant impact on the Great Lakes region, supporting local economies and creating jobs. However, it is important to manage tourism sustainably to minimize its environmental impact and preserve the region’s natural beauty.
Last Point
The Great Lakes are more than just a collection of bodies of water; they are a vital resource, a historical treasure, and a reminder of the interconnectedness of nature and humanity. As we navigate the challenges of climate change and environmental protection, understanding the Great Lakes’ significance and the ongoing efforts to preserve them becomes paramount.
Their story is a testament to the power of nature, the resilience of ecosystems, and the importance of responsible stewardship.