Lake Mead water level has been a topic of intense discussion in recent years, as the iconic reservoir, nestled on the border of Nevada and Arizona, has been steadily shrinking. This shrinking reservoir, a vital source of water for millions in the Southwest, is a stark reminder of the challenges posed by drought and the impact of human activities on our natural resources.
Lake Mead, formed by the Hoover Dam, is not just a source of water; it’s a crucial component of the Southwest’s ecosystem, playing a critical role in hydropower generation, recreation, and even the cultural heritage of the region. Its water level, a reflection of the health of the Colorado River basin, has been in decline for decades, raising concerns about the future of this vital resource.
Lake Mead: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges: Lake Mead Water Level
Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States, is a symbol of the American West and a vital resource for millions of people. Its history is intertwined with the development of the region, and its future is uncertain as it faces the challenges of a changing climate and increasing water demands.
Lake Mead’s Significance
Lake Mead’s significance extends far beyond its size and beauty. It holds historical, cultural, and economic importance, playing a crucial role in the lives of millions.
- Historical and Cultural Significance:Formed by the construction of Hoover Dam in the 1930s, Lake Mead embodies the engineering prowess and ambition of the era. It has become a symbol of American ingenuity and a testament to the power of human endeavor. The lake’s waters have also played a significant role in the cultural history of the Southwest, providing a source of recreation and a place for Native American tribes to gather and celebrate their traditions.
- Water Source for the Southwest:Lake Mead serves as the primary water source for millions of people in Nevada, Arizona, and California. It supplies water for agriculture, industry, and residential use, making it a vital resource for the region’s economic and social well-being.
- Economic and Tourism Impact:Lake Mead is a major economic driver for the region, attracting millions of tourists annually. Recreation activities such as boating, fishing, and camping generate significant revenue and support local businesses. The lake also plays a role in the region’s energy production, as Hoover Dam generates hydroelectric power that supplies electricity to millions of homes.
Current Water Level and Trends
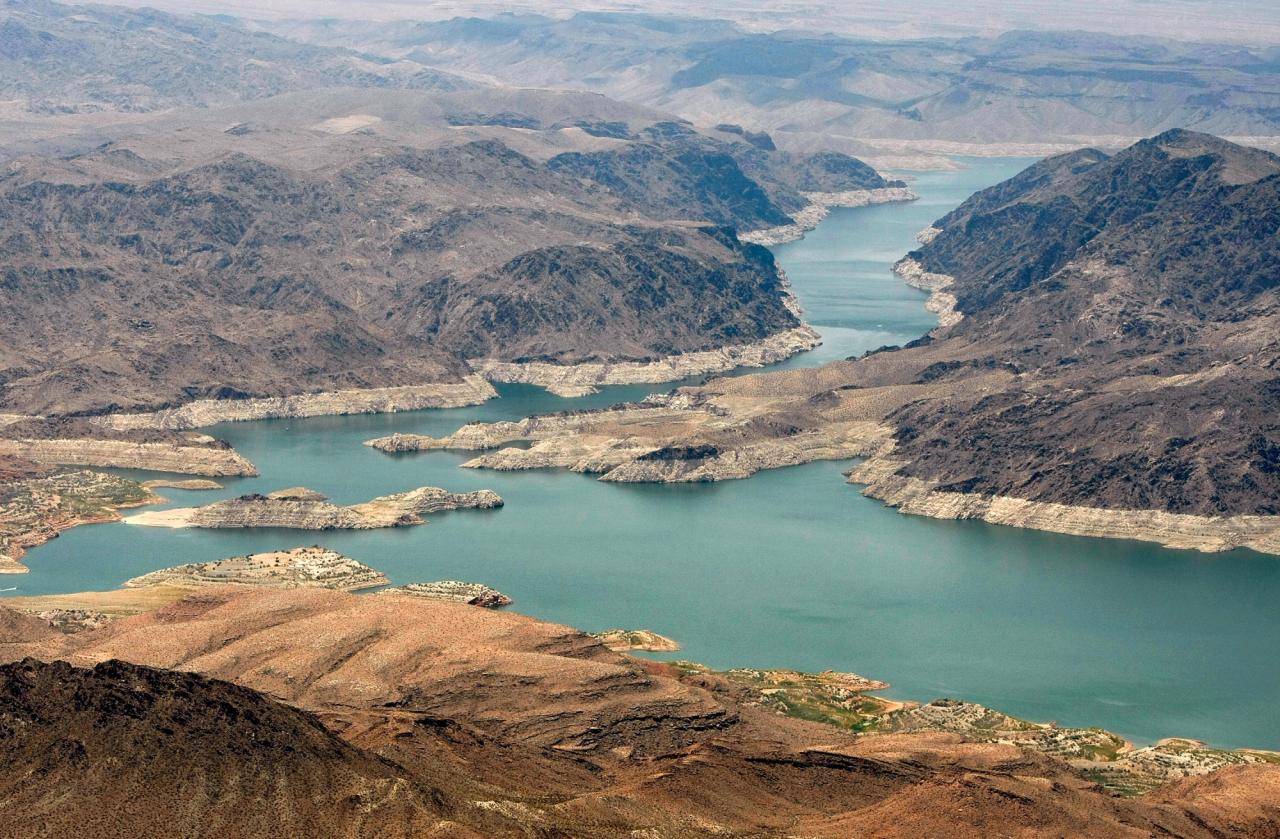

The water level of Lake Mead has been steadily declining for decades, raising concerns about the future of this vital resource. The current water level is a stark reminder of the challenges facing the Southwest.
- Current Water Level:As of [date], the water level of Lake Mead is [current water level], significantly below its historical average and the lowest level recorded since the lake was filled in the 1930s.
- Historical Trends:Over the past several decades, Lake Mead’s water level has experienced significant fluctuations, largely driven by changes in precipitation and water usage. The lake’s water level has been declining steadily since the late 1990s, with particularly sharp drops during periods of drought.
- Comparison to Historical Highs and Lows:The current water level is well below the lake’s historical high of [historical high water level] and significantly lower than the previous low of [previous low water level] recorded in [year]. The current decline is a cause for concern as it surpasses previous lows and highlights the severity of the current drought.
Factors Affecting Water Levels, Lake mead water level
The decline in Lake Mead’s water level is a complex issue influenced by a combination of factors, including climate change, drought, and human activities.
- Climate Change:Climate change is contributing to the decline in water levels by altering precipitation patterns and increasing evaporation rates. Rising temperatures are causing more water to evaporate from the lake, further reducing its volume.
- Drought:The Southwest has been experiencing a prolonged drought, with several years of below-average rainfall. This lack of precipitation has significantly reduced the amount of water flowing into Lake Mead, leading to a decline in its water level.
- Human Activities:Human activities, such as agricultural irrigation and urban water use, also contribute to the decline in water levels. The increasing population and agricultural demands in the region have placed a strain on water resources, leading to increased withdrawals from Lake Mead.
Impacts of Low Water Levels
The declining water level of Lake Mead has significant consequences for the region, affecting water supply, hydroelectric power generation, recreation, and tourism.
- Water Supply:The low water level has raised concerns about the availability of water for millions of people in the region. As the lake’s water level continues to decline, the amount of water available for use may become insufficient to meet the demands of the growing population.
- Hydroelectric Power Generation:The declining water level has reduced the amount of hydroelectric power generated by Hoover Dam. The lower water level decreases the amount of water flowing through the dam’s turbines, impacting the region’s energy production.
- Recreation and Tourism:The low water level has significantly impacted recreation and tourism activities at Lake Mead. The shrinking shoreline has made it difficult for boats to navigate, and many popular beaches and boat ramps have become inaccessible. The decline in recreational opportunities has negatively impacted the local economy and tourism industry.
Mitigation and Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the severity of the situation, authorities and stakeholders are implementing various measures to conserve water and mitigate the impacts of the declining water level.
- Water Conservation Measures:Several water conservation measures are being implemented to reduce water consumption and protect Lake Mead’s water supply. These measures include promoting water-efficient landscaping, encouraging water-saving appliances, and implementing stricter water restrictions.
- Water Management Strategies:The Colorado River Basin states are working together to develop and implement water management strategies to ensure the equitable distribution of water resources and protect Lake Mead. These strategies involve adjusting water allocations, implementing water conservation programs, and exploring alternative water sources.
- Effectiveness of Mitigation Efforts:The effectiveness of these mitigation efforts is still being assessed, but they are crucial for slowing the decline in Lake Mead’s water level and ensuring the long-term sustainability of this vital resource.
Future Outlook
The future of Lake Mead remains uncertain, and the long-term impacts of climate change and increasing water demands pose significant challenges. However, ongoing efforts to conserve water and manage resources offer hope for the future of this vital resource.
- Projections for Future Water Level:Projections for the future water level of Lake Mead vary depending on the severity of future droughts and the effectiveness of conservation efforts. However, if current trends continue, the lake’s water level is expected to continue declining, potentially reaching critically low levels in the coming years.
- Potential for Long-Term Solutions:To address the long-term challenges of water scarcity, the region needs to explore and implement innovative solutions, such as desalination plants, water recycling technologies, and increased water storage capacity. These solutions can help ensure the sustainable management of water resources and protect Lake Mead’s future.
- Implications of Continued Decline:The continued decline in Lake Mead’s water level could have significant implications for the region’s economy, environment, and social well-being. It could lead to water shortages, reduced hydroelectric power generation, and a decline in tourism, impacting the lives of millions of people.
Ending Remarks
As Lake Mead continues to shrink, it serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our environment and the need for sustainable water management. While the challenges are significant, there is hope in the ongoing efforts to conserve water, implement new management strategies, and explore long-term solutions to address water scarcity.
The future of Lake Mead, and the region it sustains, hinges on our ability to act responsibly and prioritize the health of this vital resource.