Ringworm medication is essential for effectively treating this common fungal infection. Ringworm, despite its name, isn’t caused by a worm but by a fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments. It’s characterized by itchy, red, circular rashes that can appear on the skin, scalp, or nails.
Understanding the different types of ringworm, their causes, and the various medications available is crucial for successful treatment and prevention.
This article delves into the world of ringworm medication, exploring both topical and oral treatments. We’ll discuss the effectiveness, limitations, and potential side effects of each type of medication, providing you with a comprehensive overview of your treatment options.
Understanding Ringworm
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. It’s caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments. These fungi live naturally in the environment and can be easily spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or through contact with contaminated objects.
Symptoms of Ringworm
The most common symptom of ringworm is a red, itchy, circular rash that may have a raised, scaly border. The rash can appear on any part of the body, but it is most common on the scalp, feet, hands, and groin.
Other symptoms of ringworm can include:
- Blisters
- Hair loss
- Nail discoloration and thickening
- Pain and tenderness
Types of Ringworm
There are different types of ringworm, each with its own specific characteristics, depending on the location of the infection:
- Tinea corporis: This is the most common type of ringworm, affecting the body. It causes a circular, red rash with a raised, scaly border.
- Tinea cruris: Also known as “jock itch,” this type of ringworm affects the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. It causes a red, itchy rash that may have a scaly border.
- Tinea pedis: This is the common “athlete’s foot” infection that affects the feet, especially between the toes. It causes itching, scaling, and cracking of the skin.
- Tinea capitis: This type of ringworm affects the scalp, causing patches of hair loss, scaling, and inflammation.
- Tinea unguium: This type of ringworm affects the nails, causing discoloration, thickening, and brittleness.
Ringworm Medication Overview
There are various medications available to treat ringworm infections. These medications can be classified into two main categories: topical antifungals and oral antifungals. The choice of medication depends on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the patient’s individual needs and medical history.
You might have heard the term “CVA” in a medical context, but what does it stand for? It’s actually a common abbreviation for a serious condition called a cerebrovascular accident, more commonly known as a stroke. To learn more about this condition and its potential consequences, check out this resource on the cva medical abbreviation here.
Topical Antifungal Medications
Topical antifungal medications are applied directly to the affected area of skin. They are typically the first-line treatment for mild to moderate cases of ringworm. Common topical antifungal medications include:
- Clotrimazole: Available in cream, lotion, and solution forms. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Miconazole: Available in cream, lotion, and powder forms. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Terbinafine: Available in cream and solution forms. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Ketoconazole: Available in cream and shampoo forms. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Butenafine: Available in cream and solution forms. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
Topical antifungal medications are generally safe for most people, but they can cause mild side effects such as skin irritation, redness, and dryness. In some cases, allergic reactions may occur.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal medications are taken by mouth and work by killing the fungi that cause ringworm. They are typically used for severe or widespread infections, or for infections that are resistant to topical treatment. Common oral antifungal medications include:
- Terbinafine: This medication is taken orally for a period of 2 to 4 weeks. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Itraconazole: This medication is taken orally for a period of 1 to 2 weeks. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
- Fluconazole: This medication is taken orally for a period of 1 to 2 weeks. It is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes.
Oral antifungal medications can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, headache, and diarrhea. In some cases, they can also cause liver damage, so it is important to talk to your doctor about any potential risks before taking these medications.
Topical Antifungal Medications
Topical antifungal medications are applied directly to the affected area of skin. They are typically the first-line treatment for mild to moderate cases of ringworm. The application procedure and frequency of use vary depending on the specific medication and the type of ringworm infection.
However, in general, topical antifungal medications are applied once or twice a day for 2 to 4 weeks.
Here’s a closer look at different types of topical antifungal medications:
- Creams and Lotions: These are often the preferred choice for ringworm on the body, groin, and feet. They are easy to apply and spread evenly over the affected area.
- Solutions: These are typically used for ringworm on the scalp. They can be applied directly to the affected area or diluted with water and used as a rinse.
- Powders: These are often used for ringworm on the feet. They help to absorb moisture and prevent the growth of fungi.
It is important to apply topical antifungal medications to all affected areas and to continue using them for the full duration of treatment, even if the symptoms have improved. This will help to prevent the infection from returning.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Topical antifungal medications are generally safe for most people. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as:
- Skin irritation, redness, or dryness
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Allergic reactions
It is important to discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional if you experience any severe side effects. Some individuals may also be allergic to certain ingredients in topical antifungal medications. It’s essential to review the ingredients and consult your doctor if you have any known allergies.
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal medications are taken by mouth and work by killing the fungi that cause ringworm. They are typically used for severe or widespread infections, or for infections that are resistant to topical treatment.
Here’s a look at some commonly prescribed oral antifungal medications:
- Terbinafine: This medication is effective against a wide range of dermatophytes and is typically taken for 2 to 4 weeks.
- Itraconazole: This medication is also effective against a wide range of dermatophytes and is typically taken for 1 to 2 weeks.
- Fluconazole: This medication is often used for infections of the scalp and nails and is typically taken for 1 to 2 weeks.
The dosage and duration of treatment for oral antifungal medications vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual’s needs. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Potential Side Effects and Drug Interactions, Ringworm medication
Oral antifungal medications can cause side effects such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Liver damage
It’s important to talk to your doctor about any potential risks before taking oral antifungal medications, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking other medications. Oral antifungal medications can also interact with other medications, so it’s important to inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking.
Home Remedies and Prevention
While home remedies are not a substitute for proper medical treatment, they can help manage ringworm symptoms and prevent the spread of infection. Some common home remedies include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Diluted tea tree oil can be applied topically to the affected area. It has antifungal properties that may help fight ringworm.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar can be applied topically to the affected area. It may help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Garlic: Garlic has antifungal properties. Applying crushed garlic to the affected area may help reduce the infection.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has soothing properties that may help relieve itching and inflammation. Apply aloe vera gel to the affected area.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any home remedies, especially if you have sensitive skin or any underlying medical conditions.
Preventing the Spread of Ringworm
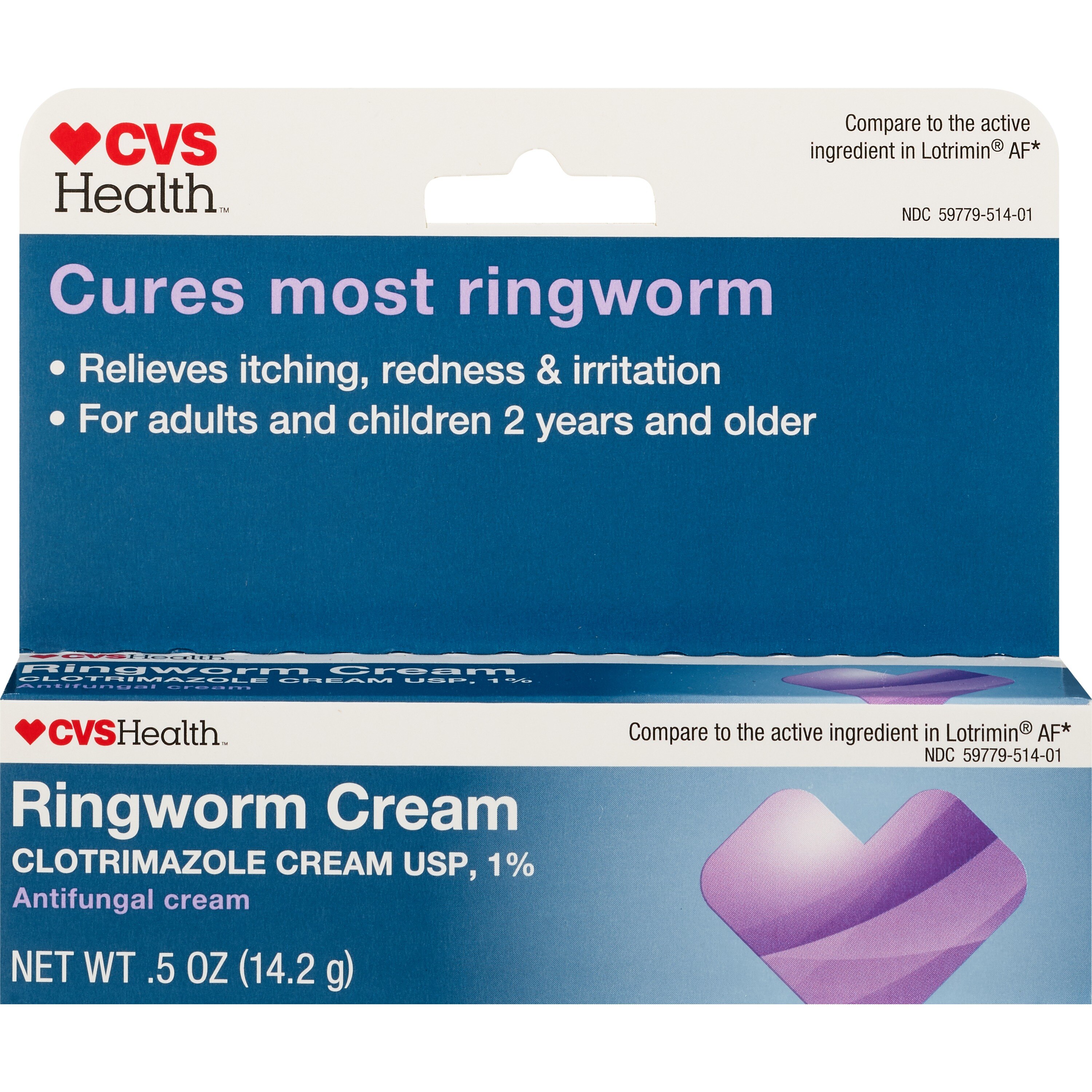
Preventing the spread of ringworm is essential, especially in shared spaces like locker rooms, pools, and gyms. Here are some tips:
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, especially after touching an infected area.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Don’t share towels, combs, brushes, or other personal items with infected individuals.
- Clean contaminated surfaces: Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces that may have come into contact with ringworm, such as showers, floors, and towels.
- Wear appropriate footwear: Wear sandals or flip-flops in public showers and locker rooms.
- Keep your skin dry: Change out of sweaty clothes promptly and allow your skin to air dry.
- Treat pets: If your pet has ringworm, treat it promptly to prevent further spread.
Seeking Medical Advice: Ringworm Medication
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan for ringworm. They can examine the affected area, identify the type of ringworm, and recommend the most appropriate medication.
Ever wondered what “CVA” stands for in medical terms? It’s actually a common abbreviation for Cerebrovascular Accident , which is a more formal way of saying stroke. Understanding these abbreviations can be helpful when navigating medical information, especially when dealing with health records or discussing medical conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- The rash is spreading or worsening despite home remedies
- You have a fever or other systemic symptoms
- The infection is on your scalp or nails
- You have a weakened immune system
A healthcare professional can help determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of your infection and your individual needs. They can also advise on the most effective medications, dosage, and duration of treatment.
Ultimate Conclusion
Armed with knowledge about ringworm medication and its various forms, you can confidently approach treatment and prevention. Remember, seeking medical advice is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available options, you can effectively manage ringworm and maintain healthy skin.