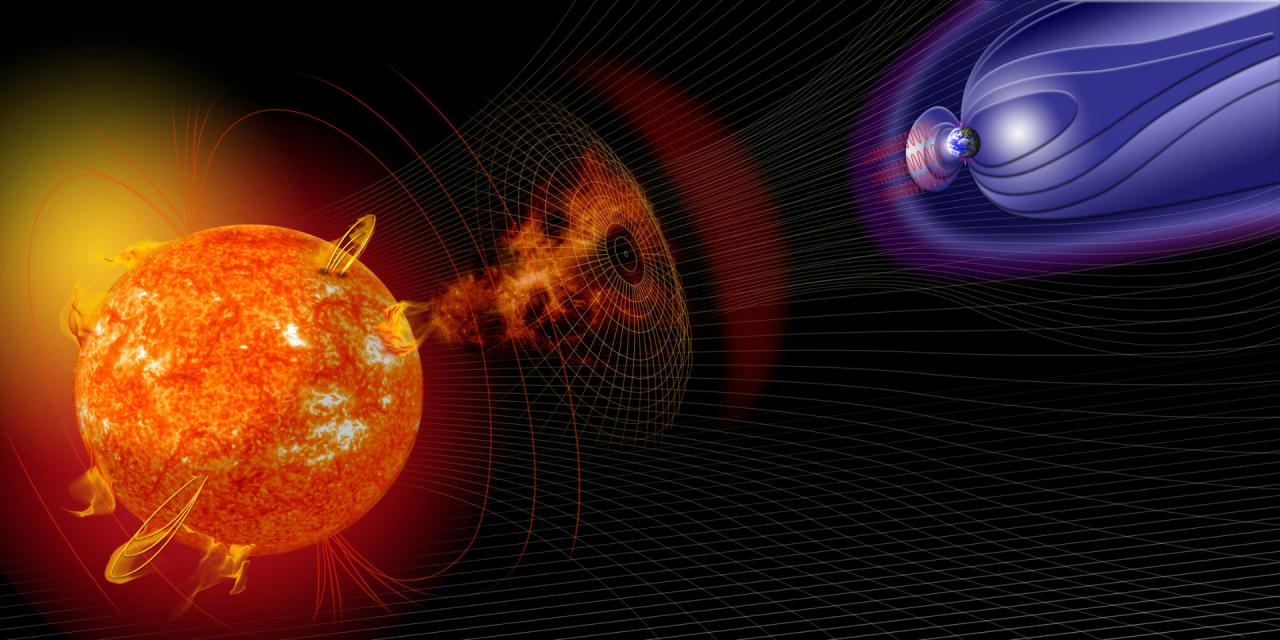
Solar storn – Solar storms, colossal bursts of energy emanating from our sun, pose a significant threat to Earth’s infrastructure and technology. Their origins, impacts, and mitigation strategies form the crux of this comprehensive exploration, shedding light on the profound consequences of these celestial events.
Sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections play pivotal roles in the formation of solar storms, which can range from minor disruptions to catastrophic events. Their interaction with Earth’s magnetosphere can disrupt power grids, communications systems, and satellites, as evidenced by historical events such as the 1859 Carrington Event.
Solar Storms and Their Origins

Solar storms are powerful bursts of energy from the sun that can have significant impacts on Earth. They are caused by the interaction of the sun’s magnetic field with the plasma in its atmosphere.
The sun’s magnetic field is constantly changing, and when it becomes twisted and tangled, it can create areas of intense magnetic activity called sunspots. Sunspots are cooler than the surrounding areas of the sun, and they appear as dark spots on its surface.
When the magnetic field around a sunspot becomes too strong, it can break through the sun’s surface and create a solar flare. Solar flares are sudden bursts of energy that can release large amounts of radiation and charged particles into space.
The impending solar storm is expected to hit Earth soon, but the exact timing remains uncertain. Experts predict that it could arrive as early as tonight or as late as tomorrow afternoon. Meanwhile, in basketball news, Utah Jazz point guard Mike Conley continues to impress with his stellar performance.
The 35-year-old veteran has been averaging 14.8 points, 7.5 assists, and 3.4 rebounds per game this season. Conley’s stats are a testament to his unwavering dedication and leadership on the court.
If the magnetic field around a solar flare is strong enough, it can also create a coronal mass ejection (CME). CMEs are huge clouds of plasma that can travel through space at speeds of up to several million miles per hour.
When a CME reaches Earth, it can interact with the Earth’s magnetic field and create a geomagnetic storm. Geomagnetic storms can cause a variety of problems, including power outages, communications disruptions, and damage to satellites.
Impact of Solar Storms on Earth
Solar storms can have a significant impact on Earth’s infrastructure and technology.
- Power outages: Solar storms can cause power outages by damaging transformers and other electrical equipment.
- Communications disruptions: Solar storms can disrupt communications systems by interfering with radio waves and satellite signals.
- Damage to satellites: Solar storms can damage satellites by exposing them to high levels of radiation.
In addition to these impacts, solar storms can also cause health problems, such as skin cancer and cataracts.
Forecasting and Monitoring Solar Storms, Solar storn
Solar storms can be difficult to predict, but there are a number of methods that scientists use to forecast and monitor them.
- Sunspot observations: Scientists can observe sunspots to track the sun’s magnetic activity and identify areas where solar flares and CMEs are likely to occur.
- Solar flare monitoring: Scientists can use satellites and other instruments to monitor solar flares and CMEs as they occur.
- Geomagnetic storm forecasting: Scientists can use computer models to forecast geomagnetic storms based on the data collected from sunspot observations and solar flare monitoring.
By forecasting and monitoring solar storms, scientists can help to mitigate their impacts on Earth.
Mitigating the Effects of Solar Storms
There are a number of strategies that can be used to mitigate the effects of solar storms on infrastructure and technology.
The impending solar storm, predicted to hit Earth sometime this week, has raised concerns among scientists and the public alike. Experts at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) are closely monitoring the situation, using satellites to track the storm’s progress.
While the exact time of impact remains uncertain, the latest updates from NOAA can be found at what time will the solar storm hit earth .
- Surge protectors: Surge protectors can help to protect electrical equipment from damage caused by power surges.
- Shielding: Shielding can be used to protect satellites and other equipment from radiation.
- Redundancy: Redundancy can be used to ensure that critical systems are still able to operate in the event of a solar storm.
In addition to these strategies, international cooperation is also essential for mitigating the effects of solar storms. By sharing data and resources, countries can help to improve solar storm forecasting and warning systems.
Final Wrap-Up: Solar Storn

Forecasting and monitoring solar storms through space weather centers and early warning systems is crucial for minimizing their impact. Mitigation strategies, including surge protectors, shielding, and redundancy, can safeguard infrastructure from power outages. International cooperation is also essential in coordinating response efforts and ensuring global preparedness.
In other news, Utah Jazz point guard Mike Conley continues to impress this season, averaging 13.8 points, 3.2 rebounds, and 8.0 assists per game. Conley’s mike conley stats have helped lead the Jazz to a 23-22 record, currently sitting in eighth place in the Western Conference.
Understanding solar storms is not merely an academic pursuit but a practical necessity in an increasingly interconnected world. By delving into their intricacies, we empower ourselves to protect our vital systems and mitigate the potential disruptions caused by these cosmic tempests.