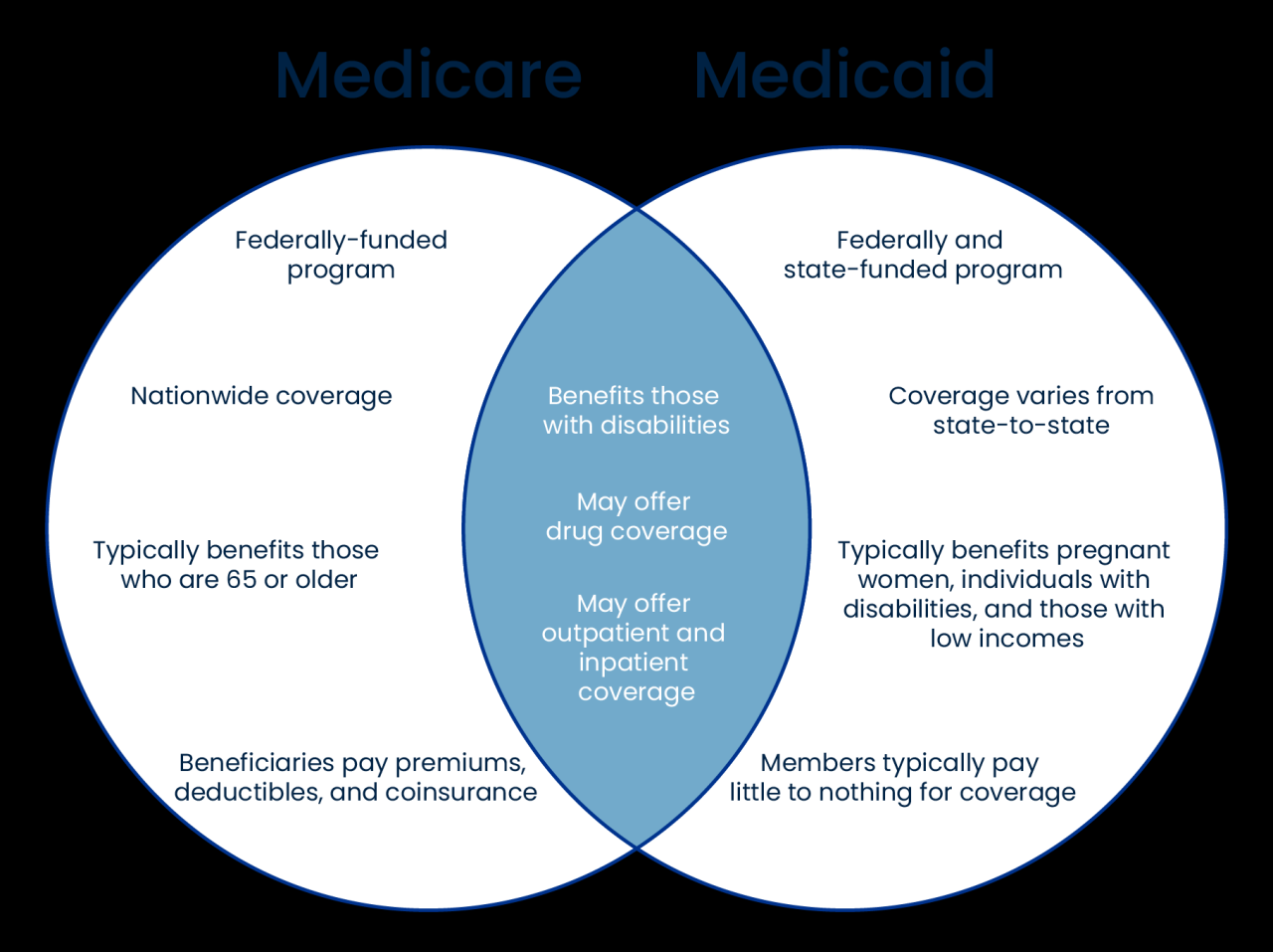
What is Medicaid? It’s a government-funded health insurance program that provides coverage for low-income individuals and families across the United States. Medicaid plays a crucial role in ensuring access to healthcare for millions of Americans, offering a lifeline to those who might otherwise struggle to afford essential medical services.
The program’s roots stretch back to the 1960s, evolving over the years to address changing healthcare needs. Medicaid’s eligibility criteria are based on factors like income, age, disability status, and family size, with varying rules and benefits across different states.
Medicaid: A Comprehensive Overview: What Is Medicaid
Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program that provides health coverage to low-income Americans. It is a vital part of the US healthcare system, providing access to essential medical services for millions of people who would otherwise be uninsured. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Medicaid, exploring its purpose, history, eligibility criteria, benefits, funding, administration, impact, and future directions.
The Purpose of Medicaid
Medicaid’s primary purpose is to ensure that all eligible individuals and families have access to affordable and comprehensive healthcare services. It aims to:
- Reduce the number of uninsured Americans.
- Improve health outcomes and reduce health disparities.
- Provide financial assistance for healthcare services.
- Support the health and well-being of vulnerable populations.
A Brief History of Medicaid
Medicaid was established in 1965 as part of President Lyndon B. Johnson’s Great Society programs. Its initial focus was on providing healthcare coverage to low-income families with children, pregnant women, and the elderly. Over the years, Medicaid has expanded to cover a wider range of individuals, including people with disabilities, individuals in nursing homes, and certain working adults.
Key milestones in Medicaid’s history include:
- 1965:Medicaid is established as part of the Social Security Act.
- 1972:States are required to cover individuals in families with incomes below the federal poverty level.
- 1988:The Medicare Catastrophic Coverage Act expands Medicaid coverage for certain individuals with disabilities.
- 1997:The Balanced Budget Act introduces managed care into Medicaid programs.
- 2010:The Affordable Care Act (ACA) expands Medicaid eligibility to include adults with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level.
Eligibility Criteria for Medicaid
Medicaid eligibility is determined by a combination of factors, including income, age, disability status, family size, and residency.
- Income:Medicaid eligibility is generally based on income levels that are below a certain threshold. These thresholds vary by state and family size.
- Age:Medicaid covers individuals of all ages, including children, adults, and seniors.
- Disability:Individuals with disabilities are eligible for Medicaid, regardless of their age or income.
- Pregnancy:Pregnant women are eligible for Medicaid, even if they do not meet the usual income requirements.
- Citizenship:Most legal residents are eligible for Medicaid, including US citizens, legal permanent residents, and refugees.
Who is Eligible for Medicaid?, What is medicaid
Medicaid covers a wide range of individuals and families, including:
- Children:Children from low-income families are eligible for Medicaid, regardless of their parents’ immigration status.
- Pregnant Women:Pregnant women are eligible for Medicaid, even if they do not meet the usual income requirements.
- Seniors:Seniors who meet certain income and asset requirements are eligible for Medicaid.
- People with Disabilities:Individuals with disabilities are eligible for Medicaid, regardless of their age or income.
- Families:Families with low incomes are eligible for Medicaid, even if they do not have children.
Medicaid Benefits and Coverage
Medicaid provides a comprehensive range of essential health benefits, including:
- Preventive Care:Medicaid covers preventive services such as vaccinations, screenings, and health education.
- Hospitalizations:Medicaid covers inpatient hospital stays, including emergency room visits and critical care.
- Prescription Drugs:Medicaid covers a wide range of prescription drugs, with some variations in coverage across states.
- Mental Health Services:Medicaid covers mental health services, including counseling, therapy, and medication.
- Long-Term Care:Medicaid covers long-term care services for individuals who meet certain eligibility requirements.
How Medicaid is Funded and Administered
Medicaid is funded jointly by the federal and state governments. The federal government provides matching funds to states based on their per capita income. States have the flexibility to design their own Medicaid programs within federal guidelines.
- Federal Funding:The federal government provides a significant portion of Medicaid funding, with the exact amount varying by state.
- State Funding:States contribute to Medicaid funding through state taxes and other sources.
- State Administration:Medicaid programs are administered at the state level, with each state having its own eligibility requirements and benefit packages.
- Managed Care:Many states use managed care organizations (MCOs) to administer Medicaid benefits, providing a network of providers and services.
The Impact of Medicaid on Health Outcomes
Medicaid has a significant impact on access to healthcare, health outcomes, and health disparities. Studies have shown that Medicaid:
- Reduces the number of uninsured Americans.
- Improves access to healthcare services, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Leads to better health outcomes, including lower mortality rates and improved chronic disease management.
- Reduces health disparities by providing healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families.
Current Challenges and Future Directions for Medicaid
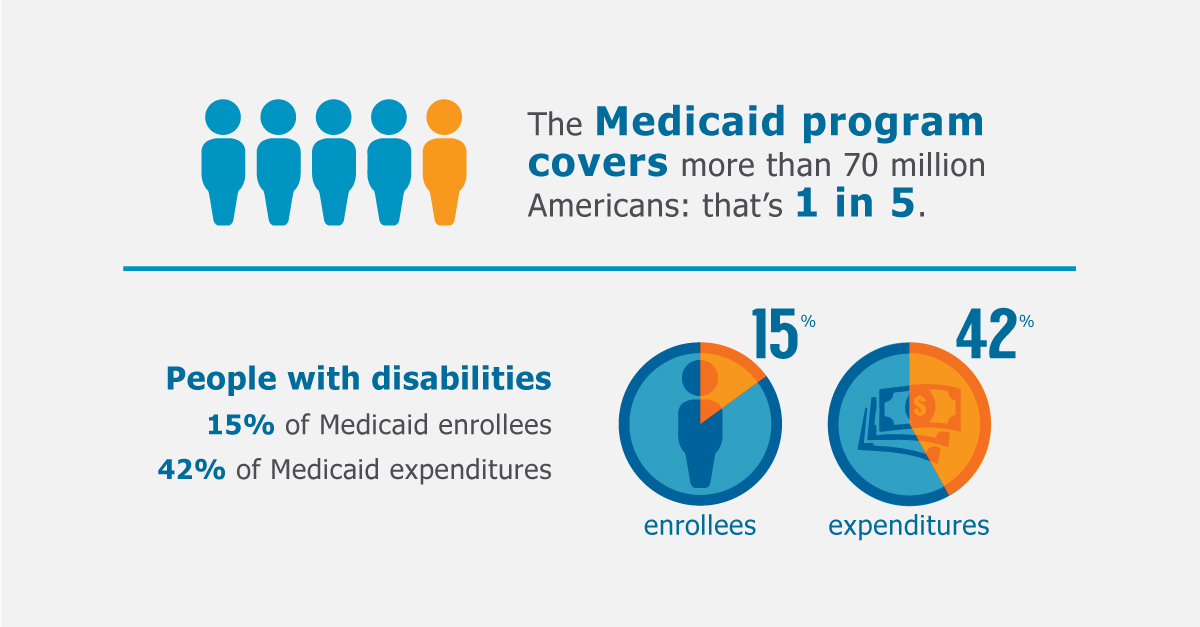
Medicaid faces several challenges, including:
- Funding Constraints:Medicaid is a major expense for state governments, and funding constraints can limit program expansion and service delivery.
- Increasing Healthcare Costs:Rising healthcare costs put pressure on Medicaid budgets, requiring states to find ways to control spending.
- Changing Demographics:The aging population and increasing number of individuals with chronic conditions are placing greater demands on Medicaid.
Despite these challenges, Medicaid remains a vital component of the US healthcare system. Future directions for Medicaid include:
- Expanding Coverage:Expanding Medicaid eligibility to more individuals could further reduce the number of uninsured and improve health outcomes.
- Improving Efficiency and Effectiveness:Reforms aimed at improving the efficiency and effectiveness of Medicaid programs are essential to ensure that the program remains sustainable.
- Integration with Other Healthcare Programs:Integrating Medicaid with other healthcare programs, such as Medicare and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), could streamline access to care and reduce administrative burdens.
Closure
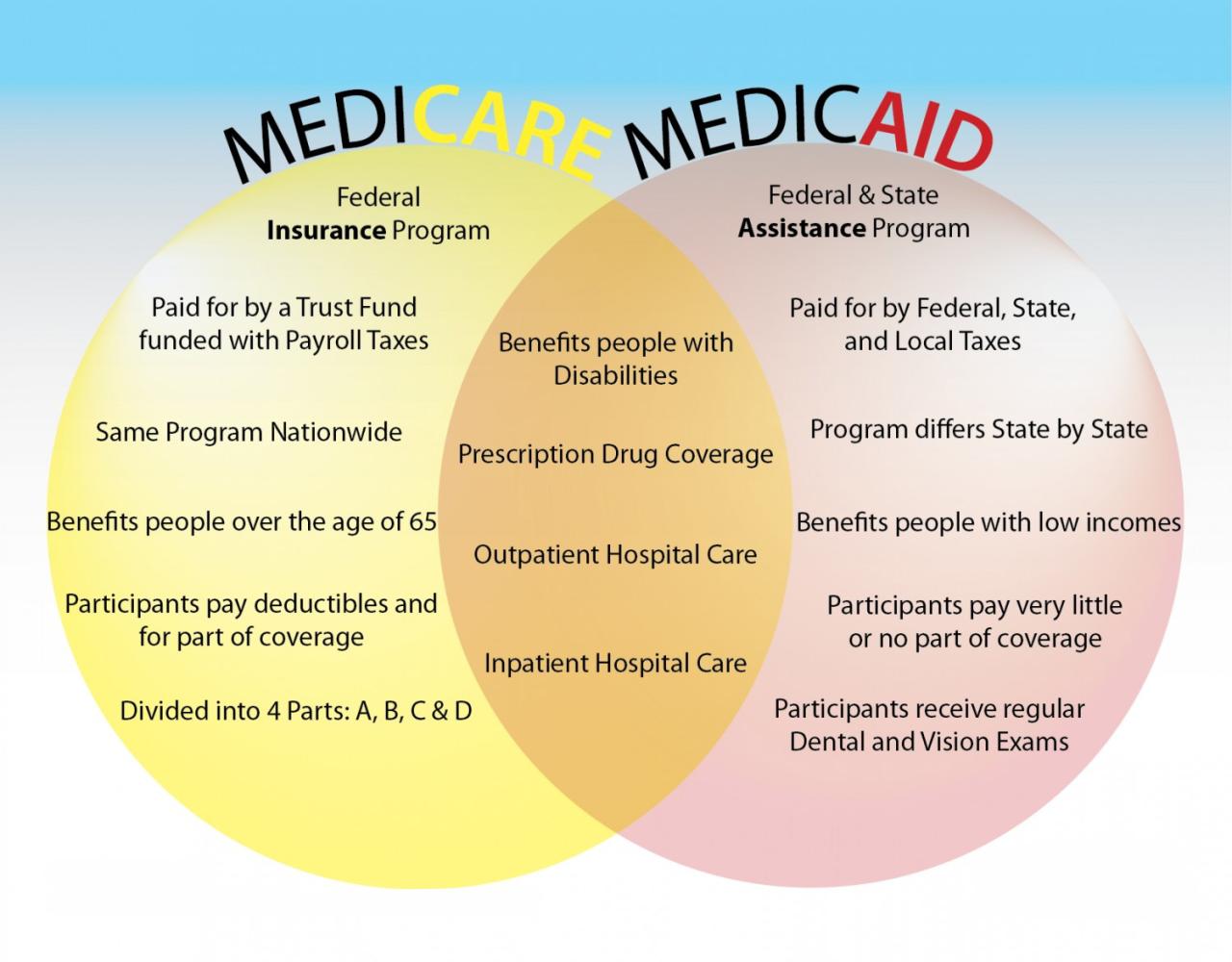
Medicaid remains a vital component of the American healthcare landscape, offering essential health coverage to a significant portion of the population. While challenges exist, ongoing efforts to improve the program’s efficiency and expand its reach aim to ensure that all eligible individuals have access to the care they need.
As we look towards the future, Medicaid’s role in providing a safety net for vulnerable Americans is likely to remain critical.