Why the US Suffers More Mental Health Issues
Why the us suffers mental health compared to the world – Why the US suffers more mental health issues compared to the world is a complex question with no single answer. It’s a multifaceted problem woven from the threads of healthcare access, societal attitudes, socioeconomic factors, and public health infrastructure. This exploration delves into these interwoven aspects, examining how they contribute to the disparity in mental health outcomes between the US and other developed nations.
The high cost of healthcare, coupled with significant insurance barriers, prevents many Americans from seeking necessary mental health treatment. Simultaneously, deeply ingrained societal stigmas surrounding mental illness discourage individuals from openly discussing their struggles and seeking help. These factors, compounded by socioeconomic inequalities and a potentially under-resourced public health system, create a perfect storm for a mental health crisis in the US.
Healthcare Access and Affordability in the US
The US healthcare system, while advanced in many aspects, presents significant challenges regarding access and affordability of mental healthcare compared to other developed nations. This disparity contributes substantially to the nation’s higher rates of untreated mental illness. The interplay of insurance coverage, cost-sharing, and geographical limitations creates a complex web of barriers that disproportionately affects vulnerable populations.
It’s interesting to consider why some clinical psychiatrists might avoid community mental health settings; you can find some insights on this at why would clinical psychiatrist shy away from community mental health. However, the importance of holistic care is undeniable, and that includes physical health. For patients struggling with mental health, incorporating physical activity is key, and resources like worksheets on physical health education for mental health adults can be incredibly beneficial in promoting a healthier lifestyle.
This integrated approach is crucial for long-term well-being.
US Mental Healthcare Accessibility and Affordability Compared to Other Developed Nations
Compared to countries with universal healthcare systems like Canada, the UK, and many European nations, the US system exhibits considerably lower accessibility and affordability for mental healthcare. Universal healthcare models often provide comprehensive coverage for mental health services, including therapy, medication, and hospitalization, with minimal out-of-pocket costs. In contrast, the US relies heavily on a private insurance system, leaving many uninsured or underinsured, facing substantial financial barriers to accessing necessary care.
This leads to delayed or forgone treatment, exacerbating existing mental health conditions.
Impact of Insurance Coverage and Cost-Sharing on Mental Healthcare Utilization
Insurance coverage in the US varies widely, and even with insurance, high deductibles, co-pays, and limited networks of providers can deter individuals from seeking mental healthcare. Many insurance plans have limitations on the number of therapy sessions covered, forcing patients to choose between financial strain and necessary care. The high cost of prescription medications, even with insurance, is another significant barrier, particularly for individuals with chronic mental illnesses requiring long-term medication management.
This financial burden frequently leads to treatment non-adherence and poorer health outcomes.
Barriers to Accessing Mental Healthcare in the US
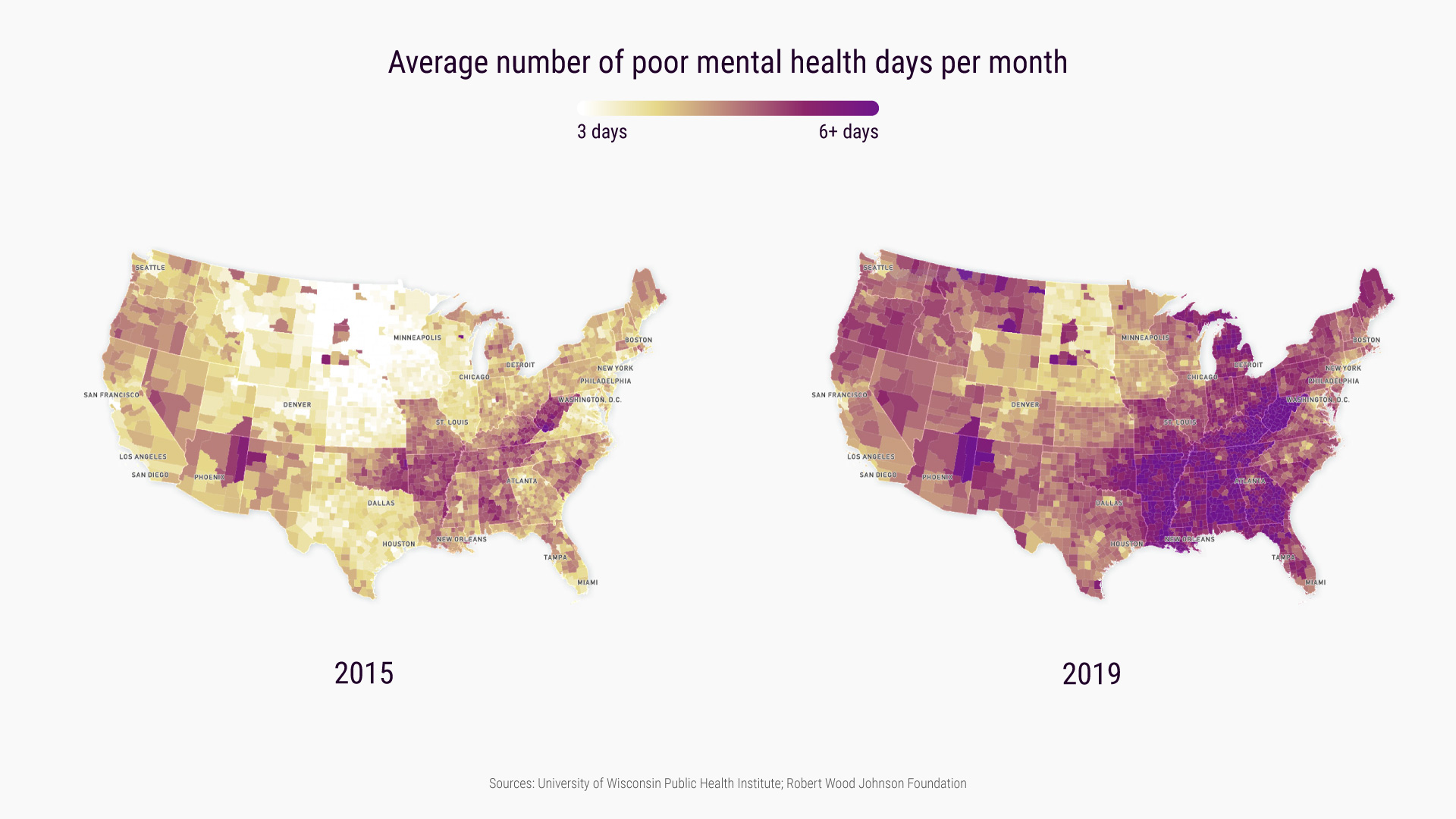
Beyond financial constraints, geographical limitations and a shortage of specialized mental health providers pose significant obstacles to accessing care. Rural areas often lack sufficient mental health professionals, forcing individuals to travel long distances for appointments, which can be particularly challenging for those with mobility issues or limited transportation options. The lack of specialized providers, such as child psychiatrists or trauma specialists, further restricts access to appropriate and effective treatment.
Social Determinants of Mental Health in the US
Socioeconomic factors significantly influence mental health outcomes in the US. Poverty, income inequality, and housing instability are strongly linked to increased rates of mental illness and poorer treatment outcomes. These factors create a complex interplay of stressors that negatively impact mental well-being and access to care.
Influence of Socioeconomic Factors on Mental Health Outcomes
Individuals living in poverty often experience higher rates of stress, trauma, and limited access to resources, including healthcare. Income inequality creates disparities in access to quality education, stable housing, nutritious food, and safe neighborhoods, all of which contribute to mental health vulnerabilities. Housing instability, including homelessness, is strongly associated with increased rates of mental illness and substance abuse.
The cumulative effect of these factors creates a cycle of disadvantage that perpetuates poor mental health outcomes.
Prevalence of Mental Health Issues in Different Socioeconomic Groups
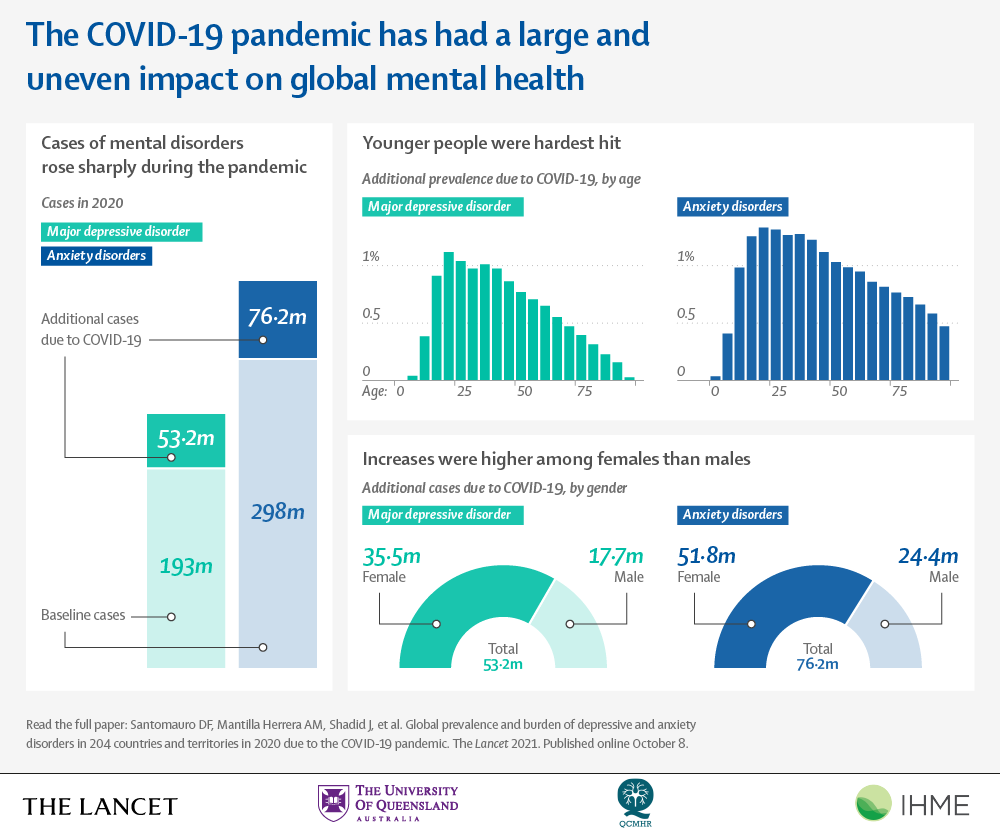
Studies consistently demonstrate higher rates of mental illness among individuals with lower socioeconomic status. This disparity is observed across various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders. Access to mental healthcare is often inversely related to socioeconomic status, with those in lower socioeconomic brackets facing greater barriers to accessing timely and appropriate care. This contributes to worse outcomes, including higher rates of hospitalization and suicide.
Social Programs and Policies to Mitigate the Impact of Social Determinants, Why the us suffers mental health compared to the world
Addressing the social determinants of mental health requires a multi-pronged approach involving expanding access to affordable housing, increasing minimum wages, strengthening social safety nets, and investing in community-based support programs. Examples include initiatives aimed at reducing poverty and income inequality, providing affordable housing assistance, and expanding access to food security programs. Furthermore, investments in early childhood development and educational opportunities can help to build resilience and reduce the risk of mental health problems later in life.
Cultural and Societal Attitudes Towards Mental Illness in the US
Societal attitudes towards mental illness in the US are complex and evolving, but stigma remains a significant barrier to help-seeking behavior. While awareness and acceptance are growing, deeply ingrained cultural beliefs and misconceptions continue to influence how mental illness is perceived and addressed. These attitudes, coupled with cultural factors specific to certain populations, create unique mental health challenges.
Prevailing Societal Attitudes Towards Mental Illness
Historically, mental illness has been stigmatized in the US, often associated with weakness, shame, and even dangerousness. This stigma prevents many individuals from seeking help, fearing judgment, discrimination, or social isolation. While there has been progress in reducing stigma through public awareness campaigns and increased media representation, significant challenges remain. A comparison with other countries reveals that some nations have implemented more comprehensive destigmatization campaigns and integrated mental healthcare more effectively into their broader healthcare systems.
The Role of Stigma in Preventing Individuals from Seeking Help
The fear of judgment and social repercussions is a major reason why individuals avoid seeking mental health services. Stigma can lead to delayed treatment, worsening of symptoms, and even suicide. This is particularly true for certain populations, such as veterans, minorities, and LGBTQ+ individuals, who may face additional layers of stigma related to their identity. The internalized stigma, where individuals themselves believe negative stereotypes about mental illness, further exacerbates the problem.
Cultural Factors Contributing to Unique Mental Health Challenges
Cultural factors significantly influence the experience and expression of mental illness. For example, cultural norms and expectations may shape how individuals cope with stress or express emotional distress. Certain cultural groups may face unique challenges due to discrimination, language barriers, or limited access to culturally competent mental health services. The experiences of immigrant communities, racial and ethnic minorities, and LGBTQ+ individuals often highlight the intersection of cultural factors and mental health disparities.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Addressing Mental Health
The US public health infrastructure dedicated to mental health has significant strengths and weaknesses when compared to other developed nations. While there have been improvements, substantial gaps remain in access, quality, and integration of services. A comprehensive improvement plan is needed to address these deficiencies.
Comparison of US Mental Health Infrastructure with Other Developed Nations
Many other developed countries have invested more heavily in community-based mental health services, integrating mental healthcare more effectively into primary care settings. This approach often leads to earlier intervention and improved outcomes. The US, in contrast, has historically relied more on institutional care, leading to challenges in providing timely and accessible services to those in need. This difference in approach contributes to disparities in access and quality of care.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the US Mental Health Service Delivery System
Strengths of the US system include a robust network of specialized mental health professionals and advanced treatment modalities. However, weaknesses include significant disparities in access to care, particularly in rural areas and underserved communities. The fragmented nature of the system, with a lack of coordination between different levels of care, further contributes to challenges in providing comprehensive and effective services.
The high cost of care and insurance coverage issues remain major barriers.
Potential Improvement Plan for US Mental Health Public Health Infrastructure
An improvement plan should focus on increasing funding for community-based mental health services, expanding access to telehealth, and improving coordination of care across different settings. Investing in workforce development to increase the number of mental health professionals, particularly in underserved areas, is crucial. Integrating mental healthcare into primary care settings and expanding access to early intervention programs can also improve outcomes.
Finally, addressing the social determinants of mental health is essential for long-term improvement.
The Impact of Stressful Life Events and Trauma on Mental Health in the US
Stressful life events and trauma significantly impact mental health in the US, contributing to a high prevalence of PTSD and other trauma-related disorders. The impact of these events varies depending on individual resilience, social support, and access to care. Understanding the long-term consequences and the effectiveness of existing programs is crucial for improving mental health outcomes.
Impact of Stressful Life Events on Mental Health
Events such as violence, natural disasters, and economic hardship can trigger or exacerbate mental health conditions. Exposure to violence, whether directly or indirectly, is a significant risk factor for PTSD, anxiety, and depression. Natural disasters can cause widespread trauma, leading to increased rates of mental health problems in affected communities. Economic hardship and unemployment contribute to stress, anxiety, and depression, particularly among individuals with limited financial resources and social support.
Prevalence of PTSD and Other Trauma-Related Disorders
The US has a relatively high prevalence of PTSD and other trauma-related disorders compared to some other developed nations. This may be due to several factors, including higher rates of exposure to violence and trauma, as well as potential differences in help-seeking behavior and access to care. Understanding the specific risk factors and developing effective prevention and intervention strategies are essential.
Effectiveness of Existing Trauma-Informed Care Programs
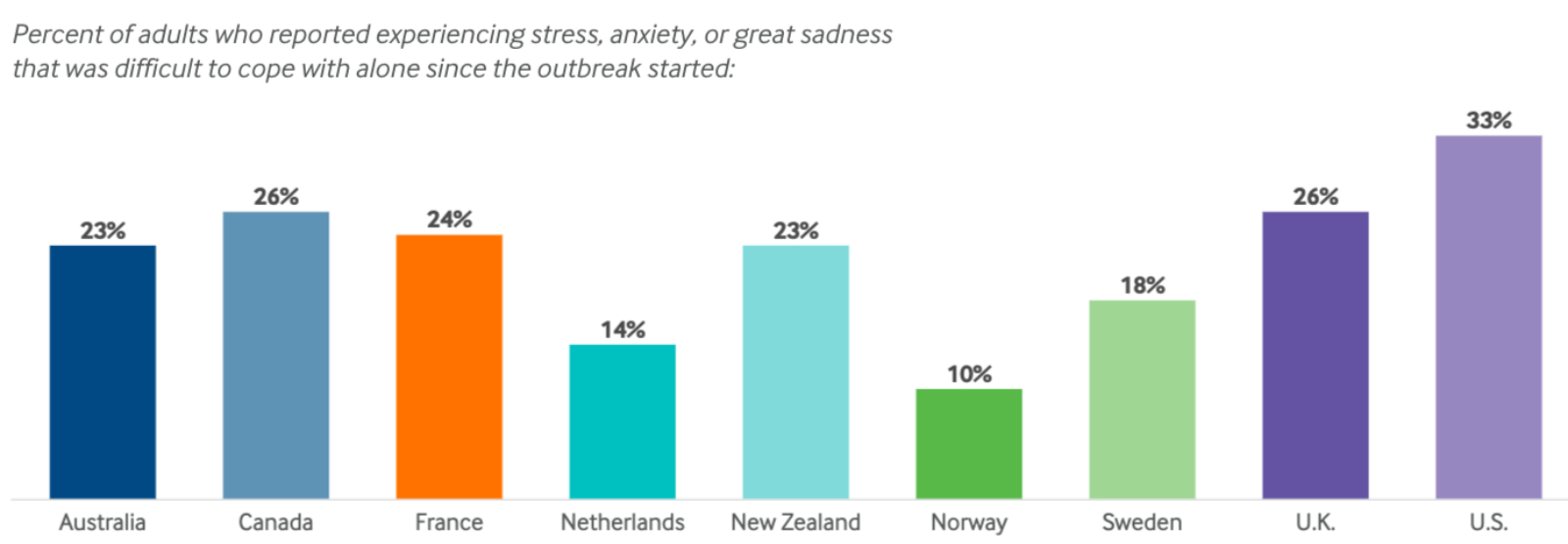
Trauma-informed care approaches, which recognize the impact of trauma on individuals’ lives and tailor services accordingly, have shown promise in improving mental health outcomes for those who have experienced trauma. These programs focus on creating safe and supportive environments, empowering individuals, and fostering collaboration. However, the widespread adoption and implementation of trauma-informed care remain a challenge.
Substance Use and its Correlation with Mental Health in the US: Why The Us Suffers Mental Health Compared To The World
Substance use disorders are strongly correlated with mental health issues in the US, with many individuals experiencing co-occurring disorders. This complex relationship requires integrated treatment approaches that address both substance use and mental health conditions simultaneously. Understanding the prevalence of co-occurring disorders and effective treatment strategies is critical.
Relationship Between Substance Use Disorders and Mental Health Issues
Substance use can be both a cause and a consequence of mental health problems. Individuals may use substances to cope with symptoms of mental illness, leading to a cycle of dependence. Conversely, substance use itself can trigger or worsen mental health conditions. This complex interplay highlights the need for integrated treatment approaches.
Rates of Co-occurring Substance Use and Mental Health Disorders
The US has high rates of co-occurring substance use and mental health disorders compared to some other countries. This may be due to several factors, including increased access to substances, higher rates of trauma and stress, and potentially differences in help-seeking behavior and treatment availability. Further research is needed to understand these variations.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Co-occurring Disorders
Effective treatment for co-occurring disorders requires an integrated approach that addresses both substance use and mental health conditions simultaneously. This often involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support services. Evidence-based treatments such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing (MI) have proven effective in treating co-occurring disorders.
Access to Mental Health Professionals and Treatment Options
The availability of mental health professionals and the range of treatment options in the US vary significantly depending on geographical location and socioeconomic factors. Limited access to specialized care impacts treatment outcomes, emphasizing the need for improved distribution of resources and increased investment in mental health services.
Availability of Mental Health Professionals per Capita
The US faces a shortage of mental health professionals, particularly in rural and underserved areas. This shortage limits access to timely and appropriate care, contributing to longer wait times for appointments and increased reliance on less effective or inappropriate treatments. A comparison with other developed nations reveals that some countries have a higher density of mental health professionals per capita, leading to improved access and outcomes.
Range of Mental Health Treatment Options and Their Effectiveness
The US offers a wide range of mental health treatment options, including medication, psychotherapy, and other evidence-based interventions. However, the effectiveness of these treatments can vary depending on individual needs and the quality of care received. Access to specialized treatment modalities, such as trauma-focused therapy or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), may be limited in some areas.
Impact of Limited Access to Specialized Mental Health Care on Treatment Outcomes
Limited access to specialized mental health care can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Individuals may receive less effective treatments or experience delays in receiving appropriate care, leading to worsening symptoms, increased disability, and poorer quality of life. This disparity underscores the need for improved access to a wider range of mental health services, including specialized care for specific conditions and populations.
Policy and Legislation Related to Mental Healthcare in the US
US legislation and policies concerning mental healthcare have evolved over time, but significant challenges remain in ensuring equitable access and quality of care. A comparison with other countries highlights key differences and similarities in approaches to mental health policy, informing potential improvements in the US system.
Overview of US Legislation and Policies Concerning Mental Healthcare
The Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008 mandated that group health plans and health insurance issuers provide mental health and substance use disorder benefits comparable to medical and surgical benefits. However, implementation and enforcement have been inconsistent, leading to continued disparities in coverage. Other legislation and policies have focused on improving access to care for specific populations, such as veterans and children.
Comparison of US Mental Health Policies with Those of Other Countries
Compared to countries with universal healthcare systems, the US system relies more heavily on a private insurance market, leading to greater variability in coverage and access to care. Other countries have implemented more comprehensive mental health policies that emphasize prevention, early intervention, and integration of mental healthcare into primary care. These differences contribute to variations in access, quality, and outcomes.
It’s interesting to consider why some clinical psychiatrists might avoid community mental health settings; you can find some insights on this at why would clinical psychiatrist shy away from community mental health. However, the benefits of integrated care are undeniable. For example, improving physical health is crucial for mental well-being, and resources like worksheets on physical health education for mental health adults can be incredibly helpful in promoting holistic wellness within these communities.
Analysis of the Effectiveness of Current US Mental Health Policies
The effectiveness of current US mental health policies is mixed. While some progress has been made in improving access to care for certain populations, significant disparities remain. The high cost of care, lack of access to specialized services, and persistent stigma continue to pose major challenges. A comprehensive evaluation of current policies and their impact is needed to inform future policy development.
Addressing the Mental Health Needs of Specific Populations
Specific populations in the US, such as veterans, minorities, and LGBTQ+ individuals, face unique mental health challenges due to intersecting factors of trauma, discrimination, and limited access to culturally competent care. Addressing these disparities requires tailored interventions and improved service delivery.
Unique Mental Health Challenges Faced by Specific Populations
Veterans often experience high rates of PTSD, depression, and substance use disorders due to combat exposure and other military-related stressors. Minorities face additional mental health challenges due to systemic racism, discrimination, and limited access to culturally competent care. LGBTQ+ individuals experience higher rates of mental health conditions due to discrimination, stigma, and minority stress. These populations often face barriers to accessing appropriate and effective care.
Comparison of Mental Health Outcomes of Specific Populations to the General Population
Studies consistently demonstrate that veterans, minorities, and LGBTQ+ individuals experience higher rates of mental illness and poorer mental health outcomes compared to the general population. These disparities are often linked to factors such as trauma, discrimination, and limited access to culturally competent care. Addressing these disparities requires targeted interventions and policies.
Strategies for Improving Mental Health Services for Vulnerable Groups
Strategies for improving mental health services for these vulnerable groups include increasing access to culturally competent care, providing trauma-informed services, and addressing systemic issues that contribute to mental health disparities. This requires collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers to create more equitable and accessible systems of care.
The Role of Prevention and Early Intervention in Mental Health
Investing in mental health prevention and early intervention programs is crucial for improving long-term outcomes and reducing the burden of mental illness on individuals, families, and society. Effective strategies focus on building resilience, identifying at-risk individuals, and providing timely support.
Importance of Mental Health Prevention and Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention is critical in mitigating the long-term effects of mental illness. Early identification and treatment can prevent the progression of conditions, reduce the severity of symptoms, and improve overall outcomes. Prevention programs aim to build resilience and protective factors that reduce the risk of developing mental health problems.
Effectiveness of Different Prevention and Early Intervention Strategies
Effective prevention and early intervention strategies include school-based programs that promote mental health literacy and resilience, community-based support groups, and early childhood interventions that focus on social-emotional development. Universal screening programs can help to identify individuals at risk for mental health problems, while targeted interventions can address specific needs and risk factors.
Plan for Improving Access to and Effectiveness of Mental Health Prevention Programs
Improving access to and effectiveness of mental health prevention programs requires increased funding, improved coordination between different sectors, and the development of evidence-based programs tailored to specific populations. Community-based partnerships and collaborations are crucial for successful implementation. Furthermore, ongoing evaluation and adaptation of programs are essential to ensure their effectiveness and relevance.
Ultimately, addressing the US’s mental health crisis requires a multi-pronged approach. Improving healthcare access and affordability, dismantling the stigma surrounding mental illness, and strengthening social support systems are crucial steps. Furthermore, investing in preventative measures, expanding access to mental health professionals, and implementing trauma-informed care are vital for creating a healthier and more supportive society. Only through comprehensive and collaborative efforts can the US hope to meaningfully improve its mental health outcomes and better support its citizens.
Share this content:
