Why Will Chronic & Mental Health Increase?
Why will chronic and mental health increased over the years – Why will chronic and mental health increase over the years? This question is increasingly crucial as we face a global rise in both physical and mental health challenges. The interconnectedness of these issues, driven by lifestyle factors, environmental influences, and societal pressures, paints a complex picture demanding immediate attention. Understanding the contributing factors is the first step towards developing effective solutions.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted reasons behind this concerning trend, examining lifestyle choices, environmental impacts, healthcare system limitations, and the crucial role of public health initiatives. We’ll also explore the interplay between chronic physical illnesses and mental health disorders, highlighting the urgent need for integrated care models. Ultimately, we aim to shed light on the projected future burden and potential strategies for mitigating the rise in chronic and mental health issues.
The recent controversy surrounding the Yale Law case banning a student from campus over mental health concerns highlights the complexities of mental health in academic settings. It’s a stark contrast to the services offered at places like the Winnebago Mental Health Institute, 4100 Treffert Drive, Oshkosh, WI 54901 , which provides comprehensive care, though access to such resources remains a significant challenge for many.
The disparity between these two situations underscores the urgent need for better mental health support and understanding across all levels of society.
The Rising Prevalence of Chronic and Mental Health Issues

The past few decades have witnessed a dramatic increase in the global burden of chronic illnesses and mental health disorders. This surge presents significant challenges to healthcare systems, economies, and individual well-being. Understanding the contributing factors, societal impacts, and potential solutions is crucial for mitigating this growing crisis.
The recent controversy surrounding the Yale law case banning a student from campus over mental health concerns highlights the complexities of addressing mental health in academic settings. This contrasts sharply with the more traditional approach of a facility like the Winnebago Mental Health Institute, 4100 Treffert Drive, Oshkosh, WI 54901 , which provides inpatient care. The difference underscores the need for a more nuanced and supportive approach to mental health across all environments, from universities to dedicated treatment centers.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Chronic Diseases
Several interconnected factors contribute to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases globally. These factors encompass lifestyle choices, socioeconomic disparities, environmental influences, and the complex interplay between these elements.
- Lifestyle Choices: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, and tobacco use significantly increase the risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. The increasing consumption of processed foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, coupled with sedentary lifestyles fueled by technological advancements, contributes to this alarming trend. Smoking, a known carcinogen, remains a major risk factor for numerous diseases.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: Chronic disease rates often disproportionately affect lower socioeconomic groups due to limited access to healthcare, nutritious food, safe environments, and opportunities for physical activity. Individuals in these groups may also experience higher levels of stress, further exacerbating their health risks.
- Geographic Variations: The prevalence of specific chronic diseases varies across geographic regions, reflecting differences in environmental exposures, lifestyle patterns, and access to healthcare. For instance, certain regions may have higher rates of specific cancers due to environmental pollution or higher rates of cardiovascular disease due to dietary habits.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental toxins, air and water pollution, and other environmental hazards plays a significant role in the development of chronic illnesses. Long-term exposure to pollutants can damage various organ systems, increasing the risk of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and cancers.
The Growing Burden of Mental Health Issues
The global prevalence of mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and others, is steadily increasing. This rise is associated with significant societal and economic consequences, highlighting the urgent need for improved prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies.
Statistics and Societal Impact of Mental Health Disorders
Numerous studies reveal a substantial increase in the global prevalence of mental health disorders. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) reports a significant rise in anxiety and depression cases, particularly among young adults. Untreated mental health issues contribute to reduced productivity, increased healthcare costs, and a decreased quality of life for individuals and their families. The economic burden on society is substantial.
- Risk Factors for Mental Illness: Genetic predisposition, early childhood experiences, exposure to trauma, chronic stress, and social isolation are all known risk factors for the development of mental illness. The interplay between biological vulnerability and environmental stressors significantly influences an individual’s mental health trajectory.
- Impact of Stress, Trauma, and Social Isolation: Prolonged exposure to stress, particularly in the absence of adequate coping mechanisms, can significantly increase the risk of developing mental health problems. Traumatic experiences, such as abuse or violence, can have profound and lasting impacts on mental well-being. Social isolation and lack of social support further exacerbate these risks.
The Interplay Between Chronic and Mental Health
Chronic physical illnesses and mental health disorders are frequently intertwined in a bidirectional relationship, where one condition can significantly influence the other. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for developing effective integrated care models.
Bidirectional Relationship Between Chronic and Mental Health, Why will chronic and mental health increased over the years
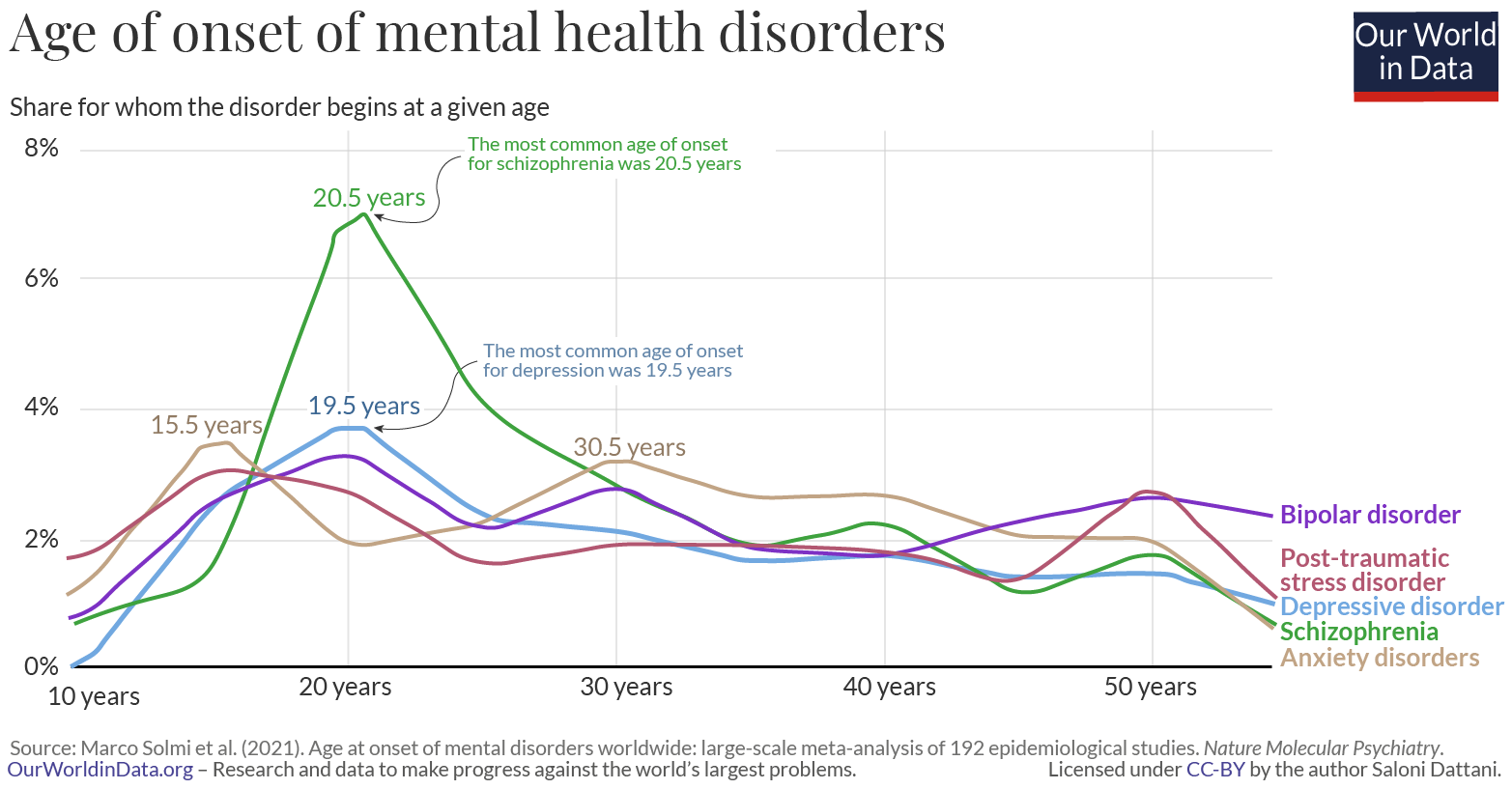
Chronic pain, fatigue, and other physical symptoms associated with chronic illnesses can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. Conversely, untreated mental health issues can negatively impact the management and prognosis of chronic diseases. For instance, individuals with depression may be less likely to adhere to treatment plans for chronic conditions, leading to poorer health outcomes. Similarly, anxiety can exacerbate the symptoms of chronic illnesses.
- Integrated Care Models: Effective integrated care models address both chronic physical and mental health needs simultaneously. These models emphasize collaboration between healthcare professionals, patient empowerment, and a holistic approach to care. Examples include collaborative care models, where primary care physicians work closely with mental health specialists to provide coordinated care.
Healthcare System Challenges and Responses
Healthcare systems worldwide face significant challenges in addressing the growing burden of chronic and mental illnesses. These challenges include limited resources, inadequate access to care, and the need for innovative prevention and treatment strategies.
- Preventative Health Measures: Implementing effective preventative health measures, such as promoting healthy lifestyles, early detection programs, and targeted interventions, can significantly reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Public health campaigns focused on diet, exercise, and smoking cessation are crucial.
- Healthcare Access and Affordability: Access to affordable and quality healthcare is essential for improving health outcomes. Financial barriers, geographical limitations, and systemic inequities significantly hinder access to care, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Strategies for Early Detection and Treatment: Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for improving outcomes for both chronic and mental health conditions. This requires increased investment in screening programs, improved diagnostic tools, and readily accessible treatment options.
The Role of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a vital role in promoting healthy lifestyles, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and addressing the stigma surrounding mental health issues.
Public Health Campaigns and Government Policies
Comprehensive public health campaigns promoting healthy diets, regular physical activity, and tobacco cessation are crucial for preventing chronic diseases. Mental health awareness campaigns are essential for reducing stigma and encouraging help-seeking behaviors. Government policies and regulations can play a significant role in creating supportive environments that promote health and well-being. This includes policies that address social determinants of health, such as access to healthy food, safe housing, and quality education.
- Different Approaches to Public Health Interventions: Public health interventions addressing chronic and mental health issues can take various forms, including educational campaigns, community-based programs, policy changes, and technological innovations. A multi-pronged approach that combines different strategies is often most effective.
Future Trends and Predictions: Why Will Chronic And Mental Health Increased Over The Years
Based on current trends, the future burden of chronic and mental illnesses is projected to increase significantly. Addressing this challenge requires innovative solutions, technological advancements, and a concerted effort from healthcare systems, governments, and individuals.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
The aging global population, increasing urbanization, and environmental changes will likely exacerbate the prevalence of chronic and mental health issues in the coming decades. However, advancements in technology, such as telehealth and AI-powered diagnostic tools, offer opportunities for improved early detection, personalized treatment, and remote monitoring. Investing in research, developing innovative treatment strategies, and addressing social determinants of health are crucial for mitigating the projected increase in chronic and mental health issues.
- Potential Solutions: Potential solutions include strengthening primary care, expanding access to mental health services, investing in preventive care, and promoting healthy lifestyles through public health campaigns. A multi-sectoral approach involving healthcare providers, policymakers, communities, and individuals is essential for addressing this complex challenge.
In conclusion, the rising prevalence of chronic and mental health conditions presents a significant global challenge. While the contributing factors are complex and interconnected, ranging from lifestyle choices and environmental factors to societal pressures and healthcare system limitations, proactive strategies are crucial. By focusing on preventative measures, improving access to affordable healthcare, promoting mental health awareness, and fostering integrated care models, we can work towards a healthier future and lessen the projected increase in these debilitating conditions.
The future requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing individual responsibility, systemic change, and collaborative effort.
Share this content:
