WI Mental Health Framework, Schools & Trauma-Informed Care
Wi mental health framework for schools and trauma informed care – WI Mental Health Framework for schools and trauma-informed care is crucial for creating a supportive and safe learning environment. This framework addresses the increasing mental health challenges faced by students, acknowledging the significant impact of trauma on their well-being and academic success. By integrating preventative measures, proactive strategies, and collaborative partnerships, schools can effectively identify, support, and address the diverse mental health needs of their student population.
This approach emphasizes early intervention, reducing stigma, and fostering a culture of wellbeing where all students feel valued and supported.
The framework Artikels a comprehensive approach, encompassing policy development, staff training, and community resource integration. It details how to create trauma-sensitive classrooms, implement crisis response plans, and measure the effectiveness of implemented initiatives. A key focus is on ensuring equitable access to mental health services for all students, regardless of background or circumstance, addressing specific challenges and promoting long-term sustainability.
Defining a Whole-School Mental Health Framework
A comprehensive mental health framework for schools prioritizes preventative measures to foster a supportive and inclusive learning environment. This proactive approach contrasts sharply with reactive strategies that only address issues after they arise. Effective frameworks seamlessly integrate with existing community resources, creating a robust support system for students.
Core Components of a School Mental Health Framework
A robust school mental health framework incorporates several key components. These include universal preventative programs targeting all students, such as social-emotional learning (SEL) curricula and school-wide positive behavior interventions and supports (PBIS). Targeted interventions focus on students exhibiting specific risk factors or early signs of mental health challenges. Lastly, intensive interventions provide specialized support for students with diagnosed mental health conditions, often involving collaboration with external mental health professionals.
Preventative measures, such as promoting positive school climate and providing access to mental health resources, are crucial for early intervention and overall student well-being.
Reactive vs. Proactive Approaches to Student Mental Wellbeing
A reactive approach addresses mental health concerns only when they become evident, often through crises or referrals. This can be less effective and more costly in the long run. In contrast, a proactive approach focuses on prevention and early intervention, fostering resilience and promoting mental well-being before problems escalate. Proactive strategies include implementing universal SEL programs, training staff to recognize early warning signs, and creating a supportive school climate.
This approach leads to better student outcomes and a more efficient use of resources.
Integrating School Frameworks with Community Resources
Effective school mental health frameworks actively collaborate with community mental health organizations. This involves establishing referral pathways, sharing information, and coordinating services to ensure students receive comprehensive support. Schools might partner with local mental health clinics, hospitals, or community-based organizations to provide access to therapy, counseling, and other specialized services. This collaborative approach ensures students receive timely and appropriate care, bridging the gap between school and community resources.
Trauma-Informed Care in Schools
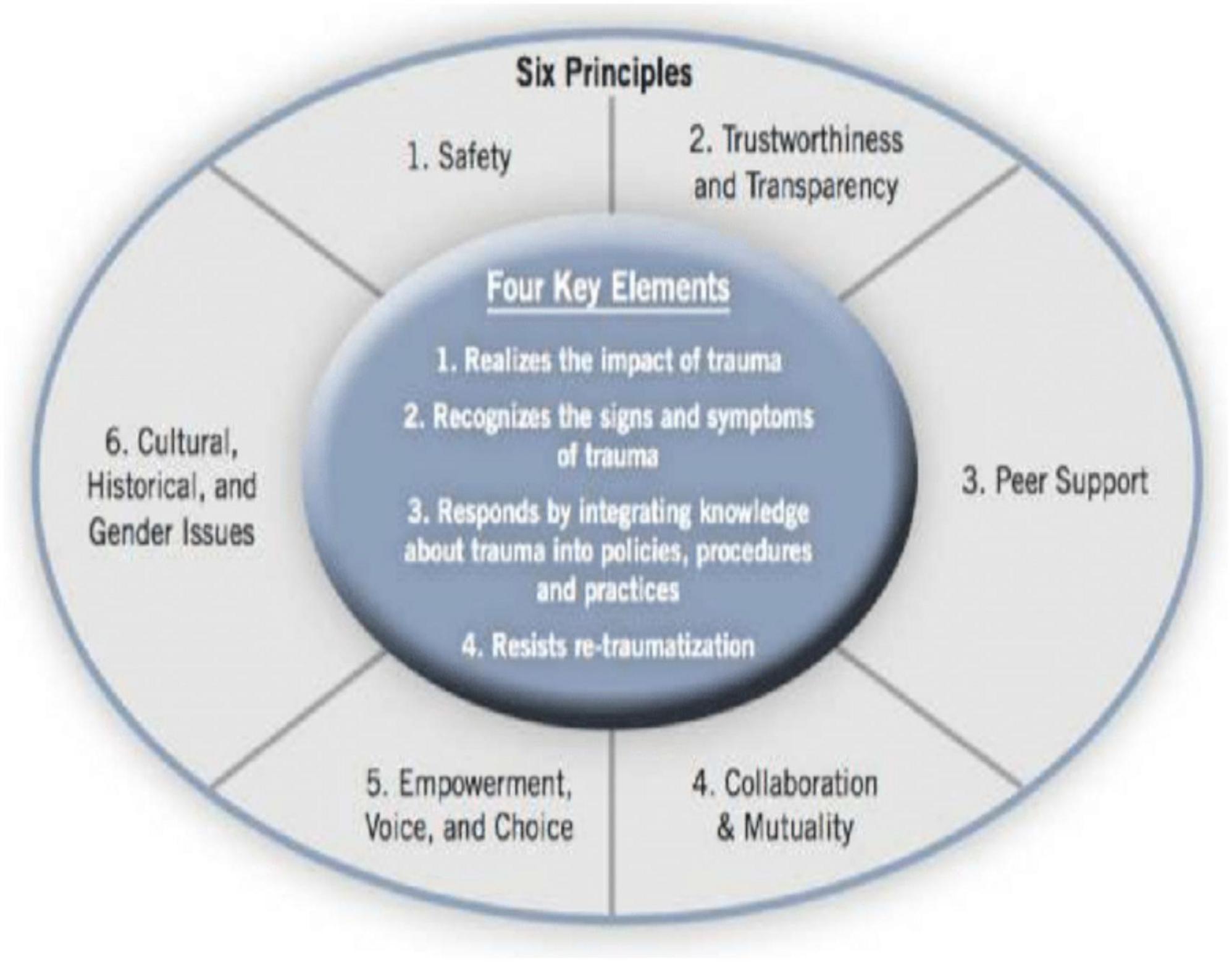
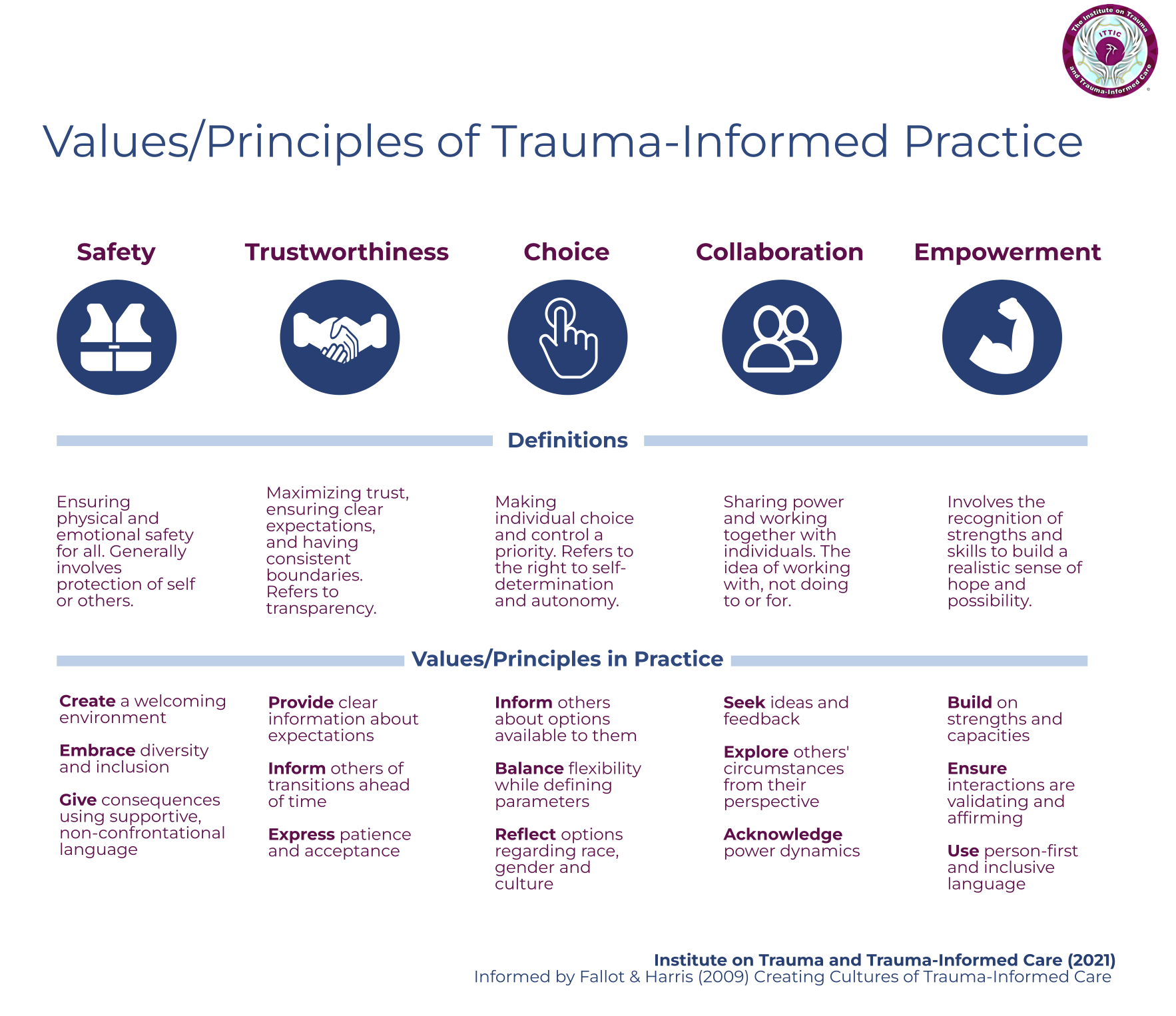
Trauma-informed care recognizes the pervasive impact of trauma on students’ learning, behavior, and mental health. It emphasizes safety, trustworthiness, choice, collaboration, and empowerment. Applying these principles in schools creates a supportive environment where students feel safe and respected, fostering healing and improved academic outcomes.
Principles of Trauma-Informed Care in Schools

The six core principles of trauma-informed care are: safety, trustworthiness and transparency, choice, collaboration and mutuality, empowerment, voice and cultural humility. In a school setting, this translates to creating physically and emotionally safe classrooms, building trusting relationships with students, offering choices whenever possible, collaborating with students and families in decision-making, empowering students to take control of their learning, actively listening to student perspectives, and respecting cultural differences.
Strategies for Creating a Trauma-Sensitive Classroom
Creating a trauma-sensitive classroom involves establishing clear routines and expectations, providing a calm and predictable environment, offering sensory breaks when needed, using positive reinforcement and avoiding punitive measures, and teaching self-regulation strategies. Teachers can incorporate mindfulness practices, flexible seating options, and opportunities for movement to support students’ emotional regulation. A trauma-sensitive classroom emphasizes understanding and validating students’ experiences.
Training Program for School Staff on Trauma
A comprehensive training program for school staff should cover the impact of trauma on learning and behavior, strategies for recognizing signs of trauma in students, and techniques for creating a trauma-informed classroom. The training should also include methods for building rapport with traumatized students, de-escalation techniques, and strategies for collaborating with families and mental health professionals. Role-playing scenarios and case studies can enhance understanding and practical application of learned skills.
Ongoing professional development is crucial for maintaining a trauma-informed approach.
Identifying and Addressing Mental Health Needs
Early identification of students at risk is crucial for effective intervention. This involves utilizing screening tools, monitoring academic performance and behavior, and actively listening to student concerns. A supportive and inclusive school culture reduces stigma and encourages help-seeking. Clear procedures for responding to mental health crises are essential for ensuring student safety and well-being.
Methods for Early Identification of Students at Risk
Early identification strategies include using standardized screening tools, observing changes in behavior or academic performance, and actively engaging in conversations with students. Teacher observations, parent reports, and peer interactions can all provide valuable insights. Regular check-ins with students, especially those identified as vulnerable, can help detect early warning signs.
Creating a Supportive and Inclusive School Culture
A supportive school culture promotes open communication, reduces stigma, and encourages help-seeking behavior. This involves educating staff and students about mental health, providing accessible resources, and celebrating diversity. School-wide campaigns and peer support programs can contribute to creating a positive and inclusive environment where students feel comfortable seeking help.
Responding to a Student Experiencing a Mental Health Crisis, Wi mental health framework for schools and trauma informed care
A step-by-step guide for responding to a mental health crisis should include assessing the immediate situation, ensuring student safety, contacting parents or guardians, and seeking professional help. The guide should also address the need for appropriate documentation and follow-up support. Clear protocols and designated crisis response teams are crucial for effective crisis management.
This World Mental Health Day, it’s crucial to remember the importance of holistic well-being, as highlighted in this article: world mental health day leaders must prioritize the whole person. Supporting mental health shouldn’t be siloed; it’s about integrating physical and emotional health. For those seeking flexible work options, consider the growing field of mental health; there are many work from home jobs in mental health online, like those offered by Ginger , offering a good work-life balance and the chance to make a real difference.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration between school staff, parents, and community mental health professionals is paramount. A well-defined communication plan ensures timely and appropriate information sharing. School counselors and other mental health professionals play a vital role in supporting students and coordinating care.
Importance of Collaboration
Collaboration among school staff, parents, and community mental health professionals enhances the effectiveness of mental health support. Sharing information and coordinating services ensures students receive comprehensive and consistent care. Regular meetings, shared case management, and clear communication channels facilitate collaboration.
Communication Plan for Mental Health Resources
A comprehensive communication plan involves utilizing various channels, such as school newsletters, websites, parent meetings, and individual communication with families. The plan should clearly Artikel available resources, contact information, and procedures for accessing support. Regular updates and feedback mechanisms ensure the plan remains relevant and effective.
Role of School Counselors and Mental Health Professionals
School counselors and mental health professionals provide direct support to students, conduct assessments, develop intervention plans, and collaborate with teachers and parents. They play a crucial role in coordinating care, advocating for students’ needs, and providing crisis intervention services. Their expertise is vital for ensuring students receive appropriate mental health support.
Developing Policies and Procedures
Clear policies and procedures are essential for addressing student mental health concerns. A comprehensive crisis response plan Artikels steps for handling emergencies. Effective school-wide initiatives promote mental health and well-being.
School Policy for Addressing Mental Health Concerns
A school policy should Artikel procedures for identifying, assessing, and addressing student mental health needs. The policy should address confidentiality, parental involvement, and access to resources. It should also detail the roles and responsibilities of various staff members.
Crisis Response Plan
A crisis response plan should clearly define roles, responsibilities, and procedures for handling emergencies. It should include contact information for emergency services, protocols for communication with parents and staff, and procedures for providing immediate support to affected students. Regular drills and training are crucial for effective crisis response.
Examples of Effective School-Wide Mental Health Initiatives
Examples of effective school-wide initiatives include implementing social-emotional learning (SEL) programs, promoting mindfulness practices, establishing peer support networks, and creating a positive school climate. These initiatives contribute to a culture of well-being and resilience.
Measuring the Effectiveness of the Framework: Wi Mental Health Framework For Schools And Trauma Informed Care
Evaluating the impact of a school’s mental health framework requires collecting data on student well-being, utilizing key metrics to assess the success of trauma-informed care initiatives, and gathering feedback from students, staff, and parents.
World Mental Health Day is a crucial reminder of the importance of mental wellbeing, and this year’s focus, as highlighted in the article ” world mental health day leaders must prioritize the whole … “, emphasizes a holistic approach. This is especially relevant given the increasing demand for mental health services. Fortunately, there are also opportunities for flexible work arrangements, such as the ” work from home jobs in mental health online ginger ” options, allowing for better work-life balance and potentially improved mental health for those in the field.
Methods for Evaluating the Framework’s Impact
Methods for evaluating the framework’s impact include collecting data on student attendance, academic performance, behavior, and mental health indicators. Surveys, focus groups, and interviews can gather feedback from students, staff, and parents. Analyzing this data helps assess the effectiveness of implemented strategies and identify areas for improvement.
Key Metrics for Assessing Trauma-Informed Care
Key metrics for assessing trauma-informed care include improvements in student behavior, reduced disciplinary incidents, increased student engagement, and enhanced teacher-student relationships. Qualitative data, such as student and staff feedback, can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of trauma-informed practices.
Data Collection and Feedback Strategies
Data collection strategies include using standardized assessments, tracking behavioral data, and conducting regular surveys. Feedback mechanisms should involve multiple stakeholders, including students, staff, and parents. This comprehensive approach ensures a holistic understanding of the framework’s impact.
Addressing Specific Challenges and Considerations
Implementing a mental health framework in diverse school settings presents unique challenges. Potential barriers to implementing trauma-informed care include lack of resources, staff training, and administrative support. A resource guide can help school staff access relevant training and support.
Challenges in Diverse School Settings
Implementing mental health frameworks in diverse school settings requires addressing cultural differences, language barriers, and varying levels of access to resources. Culturally responsive practices and equitable resource allocation are crucial for ensuring all students receive appropriate support.
Overcoming Barriers to Trauma-Informed Care
Overcoming barriers to trauma-informed care requires securing adequate funding, providing comprehensive staff training, and building strong partnerships with community organizations. Addressing systemic issues, such as inequities in resource allocation, is crucial for ensuring equitable access to support.
Resource Guide for School Staff
A resource guide for school staff should include information on relevant training opportunities, professional development programs, and access to mental health consultation services. The guide should also provide contact information for community resources and support organizations.
Building a Culture of Wellbeing
Promoting positive mental health and resilience involves implementing strategies such as social-emotional learning (SEL) programs, mindfulness practices, and school-wide campaigns to raise awareness and reduce stigma. Successful school-based programs foster social-emotional learning and build resilience.
Strategies for Promoting Positive Mental Health
Strategies for promoting positive mental health include incorporating SEL into the curriculum, teaching mindfulness techniques, and providing opportunities for physical activity and healthy eating. Creating a supportive and inclusive school climate is also crucial for fostering student well-being.
School-Wide Campaign to Reduce Stigma
A school-wide campaign to reduce stigma can involve educational workshops, awareness events, and peer support programs. The campaign should promote open conversations about mental health and encourage help-seeking behavior.
Examples of Successful School-Based Programs
Examples of successful school-based programs include programs that promote social-emotional learning, mindfulness, and resilience-building skills. These programs often incorporate interactive activities, group discussions, and individual support.
Ensuring Equity and Accessibility
Equitable access to mental health services for all students is crucial. Addressing disparities in mental health outcomes requires culturally responsive practices and equitable resource allocation. A plan for providing culturally responsive mental health support is essential for achieving equity.
Importance of Equitable Access to Services
Equitable access to mental health services ensures all students, regardless of background or identity, receive the support they need. This requires addressing systemic barriers and ensuring resources are distributed fairly.
Addressing Disparities in Mental Health Outcomes
Addressing disparities in mental health outcomes involves identifying and addressing systemic factors that contribute to inequities. This includes considering factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, gender, and sexual orientation. Culturally responsive practices are crucial for providing effective support to diverse student populations.
Plan for Providing Culturally Responsive Mental Health Support
A plan for providing culturally responsive mental health support should involve training staff on cultural competence, providing culturally relevant resources, and engaging families and community members in the process. This ensures support is tailored to the specific needs and experiences of diverse student populations.
Sustaining the Framework Over Time
Ensuring the long-term sustainability of a school’s mental health framework requires ongoing professional development, securing funding, and establishing strong partnerships.
Strategies for Long-Term Sustainability
Strategies for long-term sustainability include securing ongoing funding, establishing strong partnerships with community organizations, and providing ongoing professional development for staff. Regular evaluation and adaptation of the framework are also crucial for maintaining its effectiveness.
Plan for Ongoing Professional Development
A plan for ongoing professional development should include regular training opportunities for staff on mental health topics, trauma-informed care, and culturally responsive practices. This ensures staff have the knowledge and skills needed to provide effective support to students.
Securing Ongoing Funding and Resources
Securing ongoing funding and resources involves developing strong proposals, seeking grants, and building partnerships with community organizations. Demonstrating the effectiveness of the framework through data collection and evaluation is crucial for securing continued support.
Ultimately, the successful implementation of a WI Mental Health Framework for schools and trauma-informed care hinges on collaboration, communication, and a shared commitment to student well-being. By prioritizing preventative measures, fostering a supportive school culture, and providing accessible mental health services, schools can empower students to thrive academically and emotionally. The ongoing evaluation and adaptation of this framework ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness in supporting the evolving needs of students and the school community.
Share this content:
