Wisconsin Approved Peer Specialist Training, Mental Health
Wisconsin Approved Peer Specialist Training Model of Mental Health offers a unique approach to mental healthcare, leveraging the lived experience of individuals with mental health challenges to support others on their journeys. This model, rooted in a strong foundation of peer support principles, provides comprehensive training to equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to become effective peer specialists.
The program’s curriculum, duration, and assessment methods are carefully designed to ensure high-quality training and effective service delivery.
The Wisconsin model emphasizes experiential learning, recognizing the value of shared experiences in fostering empathy and understanding. Trainees learn not only the theoretical underpinnings of mental health but also practical skills in communication, crisis intervention, and advocacy. The program’s commitment to accessibility and inclusivity ensures diverse representation among peer specialists, promoting culturally sensitive and effective care.
Wisconsin’s Peer Specialist Training Model: A Comprehensive Overview: Wisconsin Approved Peer Specialist Training Model Of Mental Health
Wisconsin’s peer specialist training model represents a significant advancement in mental health care, emphasizing the invaluable contributions of individuals with lived experience. This model, built upon a foundation of recovery-oriented principles, provides a structured pathway for individuals to become effective peer specialists, supporting others navigating similar challenges.
Historical Context of Peer Specialist Programs in Wisconsin
The development of peer specialist programs in Wisconsin reflects a growing recognition of the importance of peer support within the mental health system. Early initiatives focused on establishing support groups and informal peer-to-peer interactions. Over time, these evolved into more formalized training programs, designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to provide effective peer support within a professional context.
The current model represents a culmination of years of experience and refinement, guided by best practices and continuous evaluation.
Core Principles and Philosophy of the Wisconsin Model
The Wisconsin model is firmly grounded in the principles of recovery, empowerment, and self-determination. It recognizes the unique expertise and perspective that individuals with lived experience bring to the support process. The philosophy emphasizes building trusting relationships, fostering hope, and promoting self-advocacy. The model prioritizes the strengths and resilience of individuals, working collaboratively to achieve their personal recovery goals.
Key Components of the Training Curriculum
The Wisconsin peer specialist training curriculum is a comprehensive program designed to equip trainees with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes necessary to provide effective peer support. The curriculum typically includes a defined number of training hours, covering topics such as trauma-informed care, motivational interviewing, crisis intervention, and cultural competency. Learning objectives are clearly defined and aligned with professional standards, ensuring trainees are prepared to meet the demands of the role.
Thinking about a career in pediatrics? The Woodhull Medical and Mental Health Center pediatrics residency program is a great option. It’s crucial to understand the complexities of child development, especially when dealing with working with children with social and mental health issues , and this program provides excellent training in that area. A strong foundation in both medical and mental health aspects is essential for providing holistic care to young patients.
Curriculum Content and Structure
The training program incorporates a variety of teaching methodologies to cater to diverse learning styles. Didactic instruction, such as lectures and presentations, provides foundational knowledge. Experiential learning activities, including role-playing and simulations, offer opportunities to practice skills in a safe and supportive environment. The curriculum is structured to build upon foundational concepts, progressively introducing more complex topics and advanced skills.
Teaching Methodologies and Assessment Methods, Wisconsin approved peer specialist training model of mental health

The program utilizes a blended learning approach, combining online modules with in-person workshops and practical experiences. Assessment methods are designed to evaluate trainee competency across various domains, including knowledge, skills, and attitudes. Evaluations may include written examinations, practical demonstrations, and peer feedback, ensuring a holistic assessment of readiness for practice.
Role and Responsibilities of Peer Specialists
Wisconsin-trained peer specialists play a vital role in supporting individuals receiving mental health services. Their responsibilities include providing emotional support, assisting with navigating the mental health system, and promoting self-management skills. They act as mentors and advocates, helping individuals to identify their strengths and develop personalized recovery plans.
Scope of Practice and Comparison with Other Professionals
The scope of practice for peer specialists is clearly defined, outlining their roles and responsibilities within the context of a multidisciplinary team. While peer specialists provide valuable support, they are not licensed mental health professionals and do not provide therapy or medical interventions. Their role is complementary to that of other mental health professionals, such as psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers, creating a collaborative approach to care.
Impact and Effectiveness of the Model
The Wisconsin peer specialist training model has demonstrated positive impacts on individuals receiving mental health services. Peer support has been shown to improve engagement in treatment, reduce hospitalizations, and enhance overall quality of life. The model’s effectiveness is supported by ongoing evaluation and data collection efforts.
Challenges and Limitations and Comparative Outcomes

Despite its successes, the implementation of the peer specialist model faces challenges, including securing adequate funding, recruiting and retaining qualified peer specialists, and ensuring consistent access to services across diverse communities. Comparisons with other peer support training models reveal that the Wisconsin model’s strengths lie in its focus on recovery-oriented principles and its emphasis on experiential learning. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term impacts and comparative effectiveness across various models.
Thinking about a career in pediatrics? The Woodhull Medical and Mental Health Center Pediatrics Residency Program is a great option, offering valuable experience. It’s especially relevant if you’re interested in working with children with social and mental health issues , as the program integrates mental health into its curriculum. This prepares residents for the complex needs of today’s young patients, making it a truly comprehensive training opportunity.
Check out their websites for more details!
Training Program Accessibility and Inclusivity
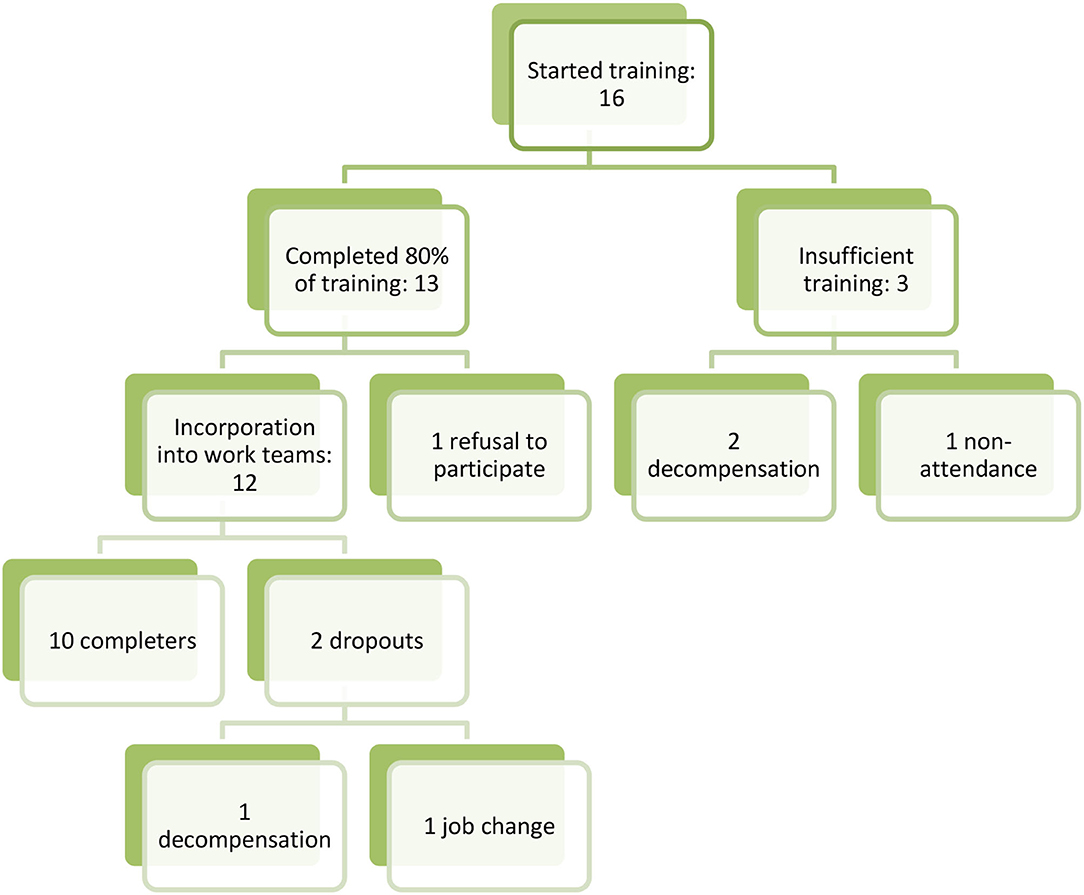
The Wisconsin training program is committed to ensuring accessibility and inclusivity for diverse populations. Efforts are made to remove barriers to participation, including offering flexible training formats, providing language assistance, and accommodating individuals with disabilities. The program prioritizes cultural competency training to ensure that peer specialists are equipped to work effectively with individuals from diverse backgrounds.
Barriers to Access and Strategies to Overcome Them
Potential barriers to access include financial constraints, transportation challenges, and scheduling conflicts. Strategies to overcome these barriers include offering scholarships, providing transportation assistance, and offering training sessions at various times and locations. The program actively seeks to recruit and train peer specialists from diverse backgrounds to better reflect the communities they serve.
Future Directions and Potential Improvements
Ongoing efforts focus on refining the training curriculum to incorporate emerging best practices and address evolving needs in mental health care. This includes exploring innovative teaching methods, incorporating new technologies, and expanding training opportunities to reach underserved populations.
Ongoing Professional Development and Adaptability
Continuous professional development and continuing education opportunities are crucial for maintaining the competence and effectiveness of peer specialists. The model will continue to evolve, adapting to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the mental health landscape. The focus will remain on providing high-quality training and support to ensure peer specialists are well-equipped to meet the needs of the individuals they serve.
The Wisconsin Approved Peer Specialist Training Model represents a significant advancement in mental health care, demonstrating the power of peer support to improve outcomes for individuals struggling with mental illness. By focusing on comprehensive training, ongoing professional development, and a commitment to inclusivity, the model ensures that peer specialists are well-equipped to provide high-quality support and contribute significantly to the mental health landscape.
The model’s continued evolution, adapting to emerging needs and incorporating feedback, positions it as a leader in peer support training and a model for other states to emulate.
Share this content:
