Womens Mental Health, A Clinical Guide
Women’s mental health a clinical and evidence-based guide – Women’s Mental Health: A Clinical and Evidence-Based Guide delves into the complexities of mental health challenges specifically affecting women. This guide explores the unique biological, psychological, and social factors contributing to these issues, examining prevalent conditions like anxiety, depression, and postpartum disorders. It also highlights the importance of evidence-based treatments, including psychotherapy and medication, while emphasizing the crucial role of self-care and support systems.
From hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s lifespan to the impact of societal pressures and trauma, this resource provides a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted nature of women’s mental well-being. It aims to empower women with knowledge and resources to navigate their mental health journeys effectively, fostering a path towards improved well-being and resilience.
Introduction to Women’s Mental Health
Women experience a disproportionate burden of mental health conditions compared to men. This section will explore the prevalence and impact of these conditions, highlighting the unique biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to women’s mental well-being, and addressing disparities in access to care.
Prevalence and Impact of Mental Health Conditions in Women
Studies consistently show higher rates of anxiety and depression among women compared to men. These conditions significantly impact various aspects of life, including work productivity, relationships, and overall quality of life. The economic burden associated with untreated mental illness in women is also substantial.
Unique Factors Influencing Women’s Mental Well-being
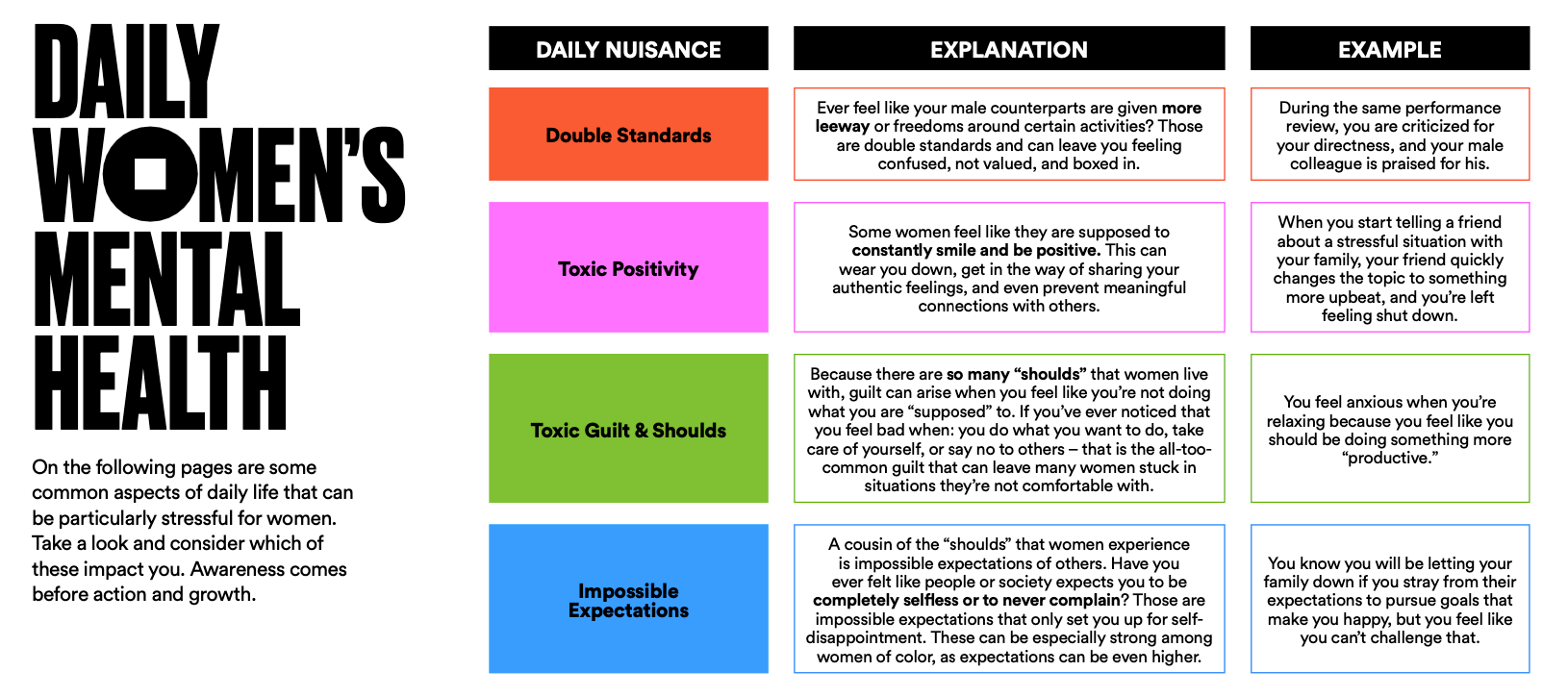
Several factors contribute to the unique mental health experiences of women. These include hormonal fluctuations throughout the lifespan, societal pressures and gender roles, and experiences of gender-based violence.
- Biological Factors: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can significantly impact mood and mental state.
- Psychological Factors: Societal expectations and gender roles can place immense pressure on women, contributing to stress and anxiety. Internalized societal standards of beauty and success can also negatively affect self-esteem.
- Social Factors: Lack of social support, discrimination, and experiences of violence (domestic violence, sexual assault) are significant risk factors for mental health problems in women.
Disparities in Access to Mental Healthcare
Access to quality mental healthcare varies significantly across different demographics of women. Factors such as socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, geographic location, and insurance coverage all play a role in determining access to treatment. Women from marginalized communities often face additional barriers, including cultural stigma and language barriers.
Common Mental Health Conditions in Women
This section will delve into specific mental health conditions frequently diagnosed in women, outlining their symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches. The unique challenges associated with each condition in women will also be addressed.
Anxiety Disorders in Women
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, are significantly more prevalent in women than in men. Symptoms can range from excessive worry and nervousness to physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath. Diagnosis is typically based on clinical interviews and symptom assessment. Treatment often involves a combination of therapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and medication.
Depression in Women
Depression in women often presents with a unique set of symptoms, which can include persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, changes in sleep and appetite, and feelings of worthlessness. Diagnostic criteria are similar to those for men, but the presentation can be influenced by hormonal and social factors. Treatment approaches include psychotherapy (CBT, interpersonal therapy), medication (antidepressants), and lifestyle changes.
Postpartum Depression and Anxiety
Postpartum depression (PPD) and anxiety are common conditions affecting women after childbirth. Symptoms can include mood swings, irritability, anxiety, difficulty bonding with the baby, and thoughts of self-harm or harming the baby. Early identification and intervention are crucial. Treatment options include therapy, medication, and support groups.
Eating Disorders in Women
Eating disorders, such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder, disproportionately affect women. These disorders are characterized by disturbed eating patterns and body image issues. Treatment typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including therapy, nutritional counseling, and medical monitoring.
Trauma and PTSD in Women

Women are at a higher risk of experiencing trauma, including sexual assault, domestic violence, and childhood abuse. Trauma can lead to significant mental health consequences, including Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Symptoms can include flashbacks, nightmares, avoidance of reminders of the trauma, and hyperarousal. Treatment focuses on trauma-informed therapy, such as trauma-focused CBT and EMDR.
Biological Factors and Women’s Mental Health
This section will examine the impact of biological factors, such as hormonal changes and genetics, on women’s mental health across their lifespan.
Hormonal Fluctuations and Mental Health
Hormonal fluctuations throughout a woman’s life, from puberty to menopause, can significantly influence mood and mental well-being. These fluctuations can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or trigger new ones. For example, premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a severe form of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) linked to hormonal changes.
Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a significant role in the predisposition to mental illness. A family history of mental health conditions increases the risk for women developing similar conditions. However, genetics are not deterministic; environmental and social factors also play a crucial role.
Chronic Medical Conditions and Mental Well-being
Chronic medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, thyroid disorders, and chronic pain, can significantly impact women’s mental health. The physical symptoms and emotional burden associated with these conditions can contribute to anxiety, depression, and other mental health challenges.
Social and Environmental Factors
This section explores the significant influence of social and environmental factors on women’s mental health. These factors often interact with biological and psychological factors to create complex and multifaceted challenges.
Societal Pressures, Gender Roles, and Discrimination
Societal pressures related to gender roles, body image, and career expectations can contribute to stress, anxiety, and depression in women. Discrimination based on gender, race, or other factors can further exacerbate these challenges.
Relationships, Family Dynamics, and Social Support
The quality of relationships, family dynamics, and social support networks significantly impact women’s mental well-being. Strong social support systems can buffer against stress and promote resilience, while strained relationships or lack of support can increase vulnerability to mental health problems.
Socioeconomic Status, Education, and Access to Resources
Socioeconomic status, education level, and access to resources are crucial determinants of mental health outcomes. Women with lower socioeconomic status often face greater challenges in accessing mental healthcare and support services.
Violence and Trauma
Exposure to violence and trauma, including domestic violence, sexual assault, and childhood abuse, has profound and long-lasting effects on women’s mental health. These experiences can increase the risk of developing PTSD, depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
Evidence-Based Treatments and Interventions
This section will provide an overview of effective treatments and interventions for women’s mental health conditions, emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach.
Psychotherapy and Medication
Psychotherapy, such as CBT and DBT, are effective in addressing various mental health conditions. Medication, including antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, and mood stabilizers, can also be helpful in managing symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on individual needs and preferences.
Types of Psychotherapy
CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. DBT is particularly effective for individuals with borderline personality disorder and helps manage intense emotions and improve interpersonal skills. Other therapies, such as interpersonal therapy and psychodynamic therapy, may also be beneficial.
Role of Medication
Medication can be a valuable tool in managing symptoms of mental health conditions. However, it’s essential to consider potential side effects and work closely with a healthcare professional to find the right medication and dosage.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies, such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture, can be helpful in managing stress and improving mental well-being. However, these therapies should not replace evidence-based treatments for serious mental health conditions.
Thinking about a career in pediatrics? The Woodhull Medical and Mental Health Center offers a fantastic pediatric residency program; you can check out the application process here: woodhull medical and mental health center program pediatric residency apply. This is a great option if you’re passionate about children’s health. And if you’re interested in mental health counseling specifically, it’s worth considering how many years of college are required.
You can find that information easily by checking out this resource: years of college needed to be a mental health counselor to help you plan your educational path.
Lifestyle Factors and Mental Well-being
Lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and sleep hygiene, play a crucial role in supporting mental health. A healthy lifestyle can help reduce stress, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.
Seeking Help and Support
This section provides practical guidance on recognizing warning signs, accessing mental healthcare services, and building a strong support system.
Identifying Warning Signs and Symptoms, Women’s mental health a clinical and evidence-based guide
Recognizing the warning signs of mental health conditions is crucial for early intervention. These signs can vary depending on the condition but may include persistent sadness, anxiety, changes in sleep or appetite, withdrawal from social activities, and thoughts of self-harm.
Accessing Mental Healthcare Services
Accessing mental healthcare services can involve finding a qualified therapist, psychiatrist, or other mental health professional. Various resources are available to help individuals find appropriate care, including online directories, insurance provider networks, and community mental health centers.
Building a Strong Support System
Building a strong support system is essential for navigating the challenges of mental illness. This may involve connecting with family, friends, support groups, or online communities.
Self-Care and Stress Management Techniques
Practicing self-care and stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and spending time in nature, can significantly improve mental well-being.
Future Directions in Research: Women’s Mental Health A Clinical And Evidence-based Guide
Continued research is crucial to advance our understanding of women’s mental health and improve treatment outcomes. This section highlights key areas requiring further investigation.
Key Areas Requiring Further Research
Further research is needed to better understand the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors contributing to women’s mental health. This includes investigating the effectiveness of different treatments for specific populations of women and exploring the long-term effects of trauma and violence.
Culturally Sensitive and Inclusive Approaches
Research and treatment approaches must be culturally sensitive and inclusive to address the unique needs of women from diverse backgrounds. This requires considering factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and sexual orientation.
Thinking about a career in pediatric care? The Woodhull Medical and Mental Health Center offers a fantastic pediatric residency program; check out their application process here: woodhull medical and mental health center program pediatric residency apply. It’s a demanding but rewarding field, and understanding the educational requirements is key. For those interested in mental health counseling specifically, you might wonder, “How much schooling is involved?” Well, you can find the answer to that question by visiting this page: years of college needed to be a mental health counselor.
Both paths require significant dedication, but the impact you can have on people’s lives makes it all worthwhile.
Technological Advancements in Mental Healthcare
Technological advancements, such as telehealth and mobile apps, hold great potential for improving access to and effectiveness of mental healthcare for women, particularly those in underserved areas.
Ultimately, Women’s Mental Health: A Clinical and Evidence-Based Guide underscores the critical need for a nuanced understanding of women’s mental health. By acknowledging the unique challenges faced by women and emphasizing the efficacy of evidence-based interventions, this guide serves as a valuable resource for both individuals seeking support and healthcare professionals striving to provide effective and compassionate care. It’s a call to action, promoting awareness, encouraging help-seeking behaviors, and advocating for continued research to improve the lives of women struggling with mental health conditions.
Share this content:
