US Work-Life Balance, Anxiety, and Mental Health
Work-life balance and anxiety united states mental health ameria – Work-life balance and anxiety in the United States are inextricably linked, impacting American mental health significantly. This pervasive issue affects various demographics and industries, stemming from factors like long working hours and a lack of employer support. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial to developing effective strategies for improvement.
The current state of work-life balance in the US reveals a concerning trend: many workers struggle to maintain a healthy equilibrium between their professional and personal lives. This imbalance frequently leads to increased anxiety and stress, negatively affecting mental wellbeing and impacting productivity. The consequences extend beyond the individual, affecting families and the overall economy.
The Prevalence of Work-Life Imbalance in the United States
Work-life balance, or the lack thereof, is a significant concern for many Americans. The current state reflects a complex interplay of societal expectations, economic pressures, and individual circumstances. This section will explore the extent of this imbalance, identifying contributing factors and highlighting variations across demographics and industries.
Work-Life Imbalance Across Demographics
Studies consistently show a significant portion of the American workforce struggles with achieving a healthy work-life balance. This issue disproportionately affects certain demographics. For example, women often bear a heavier burden of household responsibilities, leading to longer working hours and increased stress. Similarly, lower-income workers may have less flexibility in their schedules and fewer resources to manage competing demands.
Younger workers may face pressure to prove themselves, leading to overwork, while older workers might grapple with caregiving responsibilities for aging parents.
Factors Contributing to Poor Work-Life Balance

Several key factors contribute to the widespread problem of work-life imbalance. Long working hours are a major culprit, often exceeding 40 hours per week, leaving little time for personal pursuits and rest. Inflexible work arrangements, such as rigid schedules and limited remote work options, further restrict individuals’ ability to manage personal commitments. A lack of employer support, including insufficient paid time off, inadequate childcare assistance, and a culture that discourages taking breaks, exacerbates the problem.
Work-Life Imbalance Across Industries
The prevalence of work-life imbalance varies significantly across different industries and professions. High-pressure jobs in fields like finance, healthcare, and technology often demand long hours and intense workloads, leading to higher rates of burnout and anxiety. Conversely, some industries offer more flexible schedules and better work-life balance support. However, even within seemingly balanced sectors, individual experiences can differ widely depending on factors such as job role, company culture, and management style.
The Link Between Work-Life Imbalance and Anxiety in the US
The relationship between work-life imbalance and anxiety is strong and well-documented. Excessive work demands directly impact mental health, increasing the risk of developing anxiety disorders. This section will examine this causal link and explore the manifestations of work-related stress as anxiety symptoms.
The Causal Relationship Between Work Demands and Anxiety
Chronic stress resulting from long working hours, demanding workloads, and lack of control over one’s work schedule can trigger or worsen anxiety. The constant pressure to perform, meet deadlines, and manage competing priorities leads to a state of hyperarousal, characterized by heightened alertness, irritability, and difficulty relaxing. This constant state of activation significantly increases the likelihood of developing anxiety disorders.
Manifestations of Work-Related Stress as Anxiety Symptoms
Work-related stress manifests in various ways. Individuals may experience physical symptoms like muscle tension, headaches, and digestive problems. Emotionally, they may feel overwhelmed, irritable, and constantly worried. Behaviorally, they might withdraw socially, struggle to sleep, or turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms like excessive alcohol consumption or substance abuse. These symptoms can significantly impair daily functioning and overall well-being.
Impact of Work-Life Imbalance on Mental Health Seeking Behaviors
Work-life imbalance often discourages individuals from seeking mental health help. The stigma associated with mental illness, coupled with the fear of job insecurity or perceived lack of support from employers, prevents many from accessing necessary care. Furthermore, the demanding nature of work often leaves little time or energy for seeking professional help. This reluctance to seek help contributes to the undertreatment of anxiety and other mental health conditions.
Mental Health Resources and Support Systems in the US
The United States offers a range of mental health resources and support systems. However, accessibility and effectiveness vary considerably depending on socioeconomic factors and geographical location. This section will explore these resources and their limitations.
Available Mental Health Resources
Resources include therapy, medication, support groups, and online platforms providing mental health information and tools. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline offers confidential support and referrals. Many employers offer Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) providing access to counseling and other resources. However, the quality and comprehensiveness of these programs vary greatly.
Accessibility and Effectiveness Across Socioeconomic Groups
Access to mental health care is significantly influenced by socioeconomic status. Individuals with limited financial resources may struggle to afford therapy or medication, while those lacking health insurance may face significant barriers to accessing care. Geographical location also plays a role, with rural areas often lacking adequate mental health professionals. Consequently, disparities in access and quality of care exist across different socioeconomic groups.
Workplace Initiatives Promoting Mental Wellbeing
Progressive employers are increasingly recognizing the importance of employee mental health and implementing initiatives to promote wellbeing. These include flexible work arrangements, mental health awareness training, stress management programs, and confidential counseling services. Such initiatives not only benefit employees but also contribute to a more productive and engaged workforce. However, widespread adoption of these practices remains a challenge.
Government Policies and Initiatives Related to Mental Health: Work-life Balance And Anxiety United States Mental Health Ameria
The US government has implemented various policies and initiatives to address mental health concerns and promote work-life balance. This section will examine their effectiveness and potential improvements.
It’s heartbreaking to consider how mental health struggles can impact family life; the question “can my mental health make me lose my child?” is unfortunately very real. Reading resources like this one, xan my mental health make me lose my child , can help shed light on this difficult topic. Understanding the challenges is crucial, and thankfully, progress has been made.
The World Health Organization’s 2001 report, world health organisation 2001 mental health new understanding new hope , offered a renewed perspective, highlighting the importance of seeking help and fostering understanding. Early intervention and support are key to navigating these complex issues and strengthening family bonds.
Current Government Policies and Initiatives
The Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) mandates equal coverage for mental health and substance use disorder treatment under health insurance plans. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) expanded access to health insurance, including mental health services. However, significant challenges remain, including access to affordable care, particularly for those in low-income brackets or in underserved areas.
Effectiveness of Current Policies
While these policies have made progress, significant gaps remain. The effectiveness of MHPAEA is hampered by variations in plan designs and the lack of consistent enforcement. The ACA, while expanding coverage, has not fully addressed the affordability issue for many. Moreover, policies specifically targeting work-life balance and workplace mental health are still relatively limited.
Potential Improvements to Government Policies
Improvements could include stronger enforcement of MHPAEA, increased funding for mental health services, and the development of targeted policies promoting workplace wellbeing and work-life balance. Incentivizing employers to implement supportive programs, promoting mental health literacy, and addressing the stigma associated with mental illness are crucial steps.
Strategies for Improving Work-Life Balance and Reducing Anxiety
Individuals can actively take steps to improve their work-life balance and manage anxiety. This section provides practical strategies categorized for easier implementation.
Practical Strategies for Improving Work-Life Balance
- Time Management: Prioritize tasks, use time-blocking techniques, and learn to delegate effectively.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practice mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation.
- Boundary Setting: Establish clear boundaries between work and personal life, and communicate these boundaries effectively.
- Seeking Support: Connect with friends, family, or a therapist for emotional support.
- Prioritizing Self-Care: Engage in activities that promote physical and mental wellbeing, such as exercise, healthy eating, and sufficient sleep.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing Strategies
- Assessment: Identify current work-life balance challenges and sources of stress.
- Goal Setting: Set realistic goals for improving work-life balance and reducing anxiety.
- Strategy Selection: Choose strategies aligned with personal needs and preferences.
- Implementation: Gradually incorporate chosen strategies into daily routine.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly assess progress and make adjustments as needed.
The Role of Employers in Promoting Employee Well-being
Employers play a critical role in fostering a supportive work environment that prioritizes employee mental health. This section explores their responsibilities and effective initiatives.
Employer Responsibilities in Fostering a Supportive Work Environment
Employers have a moral and often legal obligation to provide a safe and healthy workplace. This includes actively promoting employee mental health and wellbeing. This involves creating a culture of open communication, providing access to mental health resources, and implementing policies that support work-life balance.
Effective Employer-Led Initiatives
Examples of effective initiatives include flexible work arrangements, generous paid time off policies, on-site wellness programs, and mental health awareness training. Providing access to EAPs and creating a culture where employees feel comfortable seeking help are also crucial.
Different Approaches to Support Employee Mental Wellbeing
Employers can adopt various approaches, ranging from offering basic resources like EAPs to implementing comprehensive wellbeing programs that integrate physical and mental health support. Some companies create dedicated wellbeing committees, while others partner with external organizations to provide specialized services. The most effective approach depends on the size and resources of the organization, as well as the specific needs of its employees.
Cultural and Societal Factors Influencing Work-Life Balance
Societal expectations and cultural norms significantly influence attitudes towards work and leisure, impacting work-life balance and mental health. This section explores these influences.
Societal Expectations and Cultural Norms
The “always-on” culture prevalent in many sectors creates an expectation of constant availability and responsiveness, blurring the lines between work and personal life. The societal emphasis on productivity and achievement can lead to individuals feeling pressured to prioritize work over other aspects of their lives, contributing to stress and anxiety.
Cultural Differences in Attitudes Towards Work and Leisure
Cultural norms vary significantly regarding the value placed on work versus leisure. Some cultures prioritize work and view long hours as a sign of dedication, while others emphasize a healthier balance between work and personal life. These differing cultural perspectives influence individual experiences of work-life balance and their overall mental health.
Role of Media Portrayals
Media portrayals often perpetuate unrealistic expectations of work-life balance, often showcasing idealized versions of successful individuals who seemingly effortlessly juggle demanding careers and fulfilling personal lives. This can create pressure on individuals to conform to these unrealistic standards, leading to feelings of inadequacy and stress.
Long-Term Effects of Work-Life Imbalance on Mental and Physical Health
Chronic work-related stress and anxiety have significant long-term consequences for both mental and physical health. This section examines these effects and their economic impact.
It’s incredibly tough to grapple with the fear that mental health struggles might impact your relationship with your child. The question, “can my mental health make me lose my child?”, is a heartbreaking one, and resources like this article offer crucial support. Understanding that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness, is key. This is especially important in light of the WHO’s 2001 report, which highlighted the need for a new understanding and hope in mental health care , emphasizing early intervention and access to quality treatment.
Long-Term Consequences of Chronic Work-Related Stress
Prolonged work-life imbalance can lead to a range of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety disorders, and burnout. Physically, it can manifest as cardiovascular disease, weakened immune system, and gastrointestinal problems. These conditions can significantly impact quality of life and longevity.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Prolonged Work-Life Imbalance, Work-life balance and anxiety united states mental health ameria
The risks include increased blood pressure, heart disease, obesity, and sleep disorders. The chronic stress associated with work-life imbalance can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illness. Furthermore, neglecting self-care activities due to time constraints can exacerbate these risks.
Economic Impact of Work-Related Mental Health Issues
Work-related mental health issues impose significant economic burdens on individuals, employers, and society. Lost productivity, increased healthcare costs, and disability benefits contribute to substantial financial losses. Addressing work-life imbalance and promoting mental wellbeing is therefore not only a matter of individual health but also an economic imperative.
Addressing Work-Life Imbalance: A Call to Action
Addressing work-life imbalance requires a multi-pronged approach involving individuals, employers, and policymakers. This section provides a call to action and inspiring examples.
Recommendations for Individuals, Employers, and Policymakers
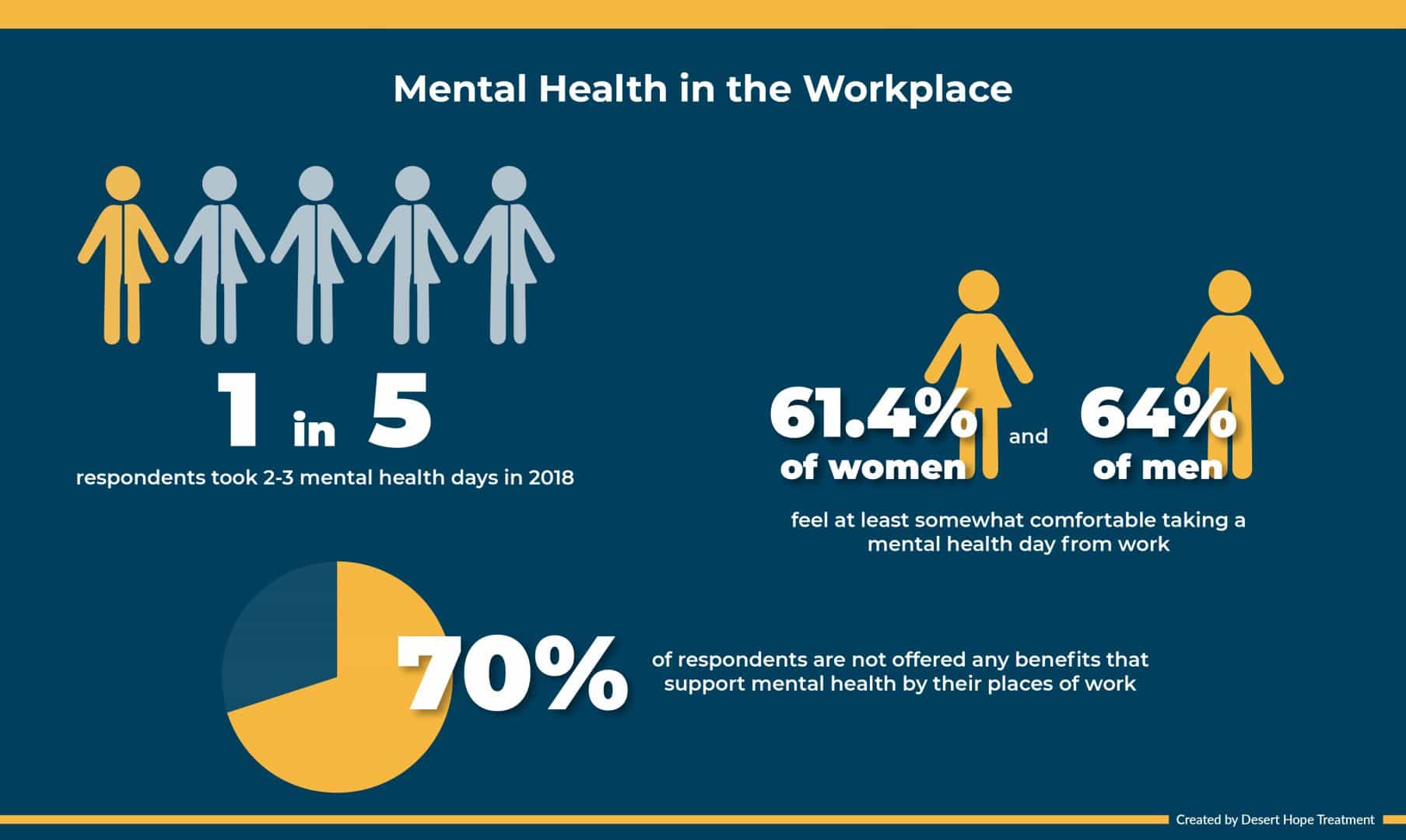
Individuals need to prioritize self-care, set boundaries, and seek support when needed. Employers should create supportive work environments, implement wellbeing initiatives, and foster a culture of open communication regarding mental health. Policymakers should strengthen existing policies, increase funding for mental health services, and implement legislation promoting work-life balance.
Inspiring Stories of Success
Numerous individuals have successfully navigated work-related anxiety and achieved better work-life balance. These stories showcase the power of self-awareness, seeking support, and implementing effective strategies. Sharing these stories can inspire others to take proactive steps towards improving their own wellbeing and advocating for change within their workplaces and communities.
Addressing the intertwined challenges of work-life balance and anxiety requires a multi-pronged approach. Individuals need to prioritize self-care and effective stress management techniques, while employers must foster supportive work environments that prioritize employee well-being. Government policies also play a vital role in creating a societal shift towards valuing mental health and promoting sustainable work practices. Ultimately, a collective effort is needed to create a healthier and more balanced future for American workers.
Share this content:
