Workplace Violence in Healthcare Settings
Workplace violence in mental and general health care settings is a pervasive and critical issue impacting the well-being of healthcare workers and the quality of patient care. Far beyond the occasional outburst, it encompasses a range of aggressive behaviors, from verbal abuse and threats to physical assault, creating a climate of fear and undermining the very foundation of compassionate care.
This exploration delves into the prevalence, contributing factors, consequences, and crucial strategies for prevention and intervention, aiming to shed light on this complex challenge and advocate for safer working environments for all healthcare professionals.
The unique challenges faced by healthcare workers, particularly those in mental health settings, are significant. Factors like understaffing, inadequate security measures, and the inherent risks associated with working with individuals experiencing mental health crises contribute to a higher incidence of violence. Understanding these contributing factors is paramount to developing effective prevention strategies and creating a safer and more supportive workplace.
Prevalence and Types of Workplace Violence in Healthcare
Workplace violence in healthcare settings, encompassing both mental and general healthcare, is a significant concern globally. While precise figures vary due to underreporting and differing definitions, studies consistently demonstrate a high prevalence of incidents, impacting the well-being of healthcare professionals and the quality of patient care. This section details the prevalence, categorizes the types of violence encountered, and highlights the unique risk factors in different healthcare environments.
Statistics on Workplace Violence in Healthcare Settings
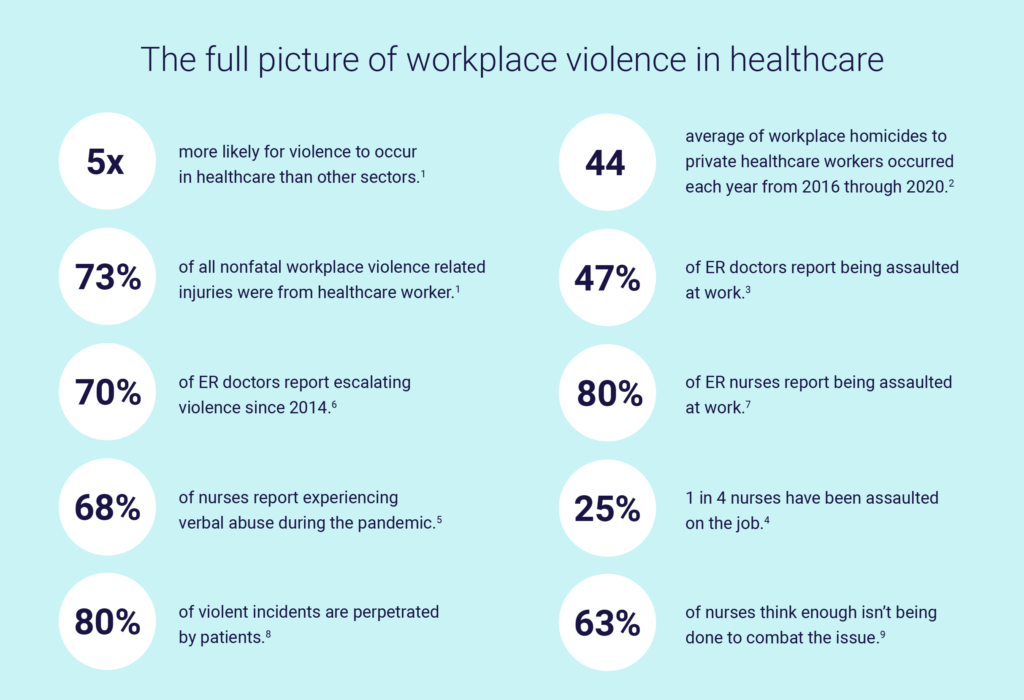
Globally, healthcare workers experience significantly higher rates of workplace violence than professionals in other sectors. Regional variations exist, with some areas exhibiting higher incident rates than others, often linked to factors like socioeconomic conditions and healthcare system infrastructure. While precise global statistics are challenging to obtain due to inconsistent reporting methodologies, numerous studies suggest that a substantial portion of healthcare workers experience at least one incident of violence annually.
For example, studies in certain regions have reported rates exceeding 75% of nurses experiencing verbal abuse and a significant percentage reporting physical assault or threats.
Types of Workplace Violence in Healthcare
Workplace violence in healthcare manifests in various forms, ranging from subtle yet damaging verbal abuse to overt physical assault. Understanding these different forms is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies.
- Physical Assault: This involves physical contact intended to harm, including hitting, kicking, biting, or using weapons. A scenario might involve a patient experiencing a psychotic episode physically attacking a nurse.
- Verbal Abuse: This includes yelling, threats, insults, and intimidation. An example could be a frustrated family member verbally abusing a doctor regarding a loved one’s diagnosis.
- Threats: These range from implied threats of violence to explicit statements of intent to harm. A situation could involve a patient making direct threats to kill a healthcare worker if their demands are not met.
- Harassment: This involves persistent, unwanted behavior that creates a hostile work environment, including stalking, bullying, and discrimination. This might manifest as a colleague consistently undermining another’s work, creating a toxic environment.
Unique Risk Factors in Mental Healthcare Settings
Mental healthcare settings present unique challenges compared to general healthcare. The inherent nature of patient populations, often involving individuals with severe mental illness or substance abuse issues, increases the likelihood of aggressive behavior. Inadequate staffing levels, a lack of appropriate security measures, and insufficient training in de-escalation techniques further exacerbate the risk.
Contributing Factors to Workplace Violence: Workplace Violence In Mental And General Health Care Settings
Workplace violence in healthcare is a multifaceted issue stemming from a complex interplay of systemic, patient-related, and individual factors. Addressing this requires a holistic approach that considers all contributing elements.
Systemic Factors Contributing to Workplace Violence
Healthcare organizations bear a significant responsibility in mitigating workplace violence. Inadequate resources and poor management practices significantly increase risk.
- Staffing Shortages: Overworked and understaffed teams are more vulnerable to violence due to increased stress and reduced ability to manage challenging situations.
- Inadequate Security Measures: Lack of security personnel, poor lighting, insufficient alarm systems, and inadequate physical design contribute to a less secure environment.
- Poor Management Practices: Inadequate training, lack of support for staff, and failure to address previous incidents can create a culture that tolerates or even encourages violence.
Patient Factors and Violence Escalation
Patient characteristics, especially those with pre-existing conditions, can contribute to violent incidents. Understanding these factors is vital for developing targeted interventions.
- Mental Illness: Certain mental illnesses, particularly those involving psychosis or mood disorders, can increase the risk of aggression.
- Substance Abuse: Substance intoxication or withdrawal can significantly impair judgment and increase impulsivity, leading to violent outbursts.
- Aggression: Pre-existing aggressive tendencies or a history of violence can heighten the risk of incidents in healthcare settings.
Impact of Workplace Stress and Burnout
The demanding nature of healthcare work contributes to high levels of stress and burnout. This can make healthcare workers more susceptible to the effects of workplace violence, both physically and psychologically.
Effectiveness of Violence Prevention Strategies
Different prevention strategies demonstrate varying degrees of effectiveness depending on the specific context. A multi-pronged approach is usually required, combining organizational changes with individual-level training and support.
Impact on Healthcare Workers’ Mental and Physical Health
Workplace violence exacts a heavy toll on the mental and physical well-being of healthcare workers, impacting their lives both professionally and personally. The consequences can be severe and long-lasting.
Psychological Consequences of Workplace Violence
The psychological impact of workplace violence can be profound and far-reaching. Many healthcare workers experience various mental health challenges following violent incidents.
- PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder is a common consequence, characterized by intrusive memories, nightmares, and avoidance behaviors.
- Anxiety: Generalized anxiety disorder and panic attacks can develop, leading to persistent fear and worry.
- Depression: Workplace violence can trigger or worsen depressive symptoms, leading to decreased motivation and feelings of hopelessness.
Physical Health Effects of Workplace Violence
Beyond psychological trauma, workplace violence can result in various physical injuries and long-term health problems.
- Injuries: Physical assaults can cause bruises, fractures, lacerations, and other injuries requiring medical attention.
- Chronic Pain: Musculoskeletal injuries and persistent pain are common long-term effects of physical assault or repetitive strain from stressful situations.
Impact on Employee Morale, Job Satisfaction, and Retention
Workplace violence significantly impacts employee morale, job satisfaction, and retention rates. A climate of fear and insecurity can lead to high turnover and difficulty in recruiting and retaining qualified staff.
Impact on Quality of Patient Care
The ripple effect of workplace violence extends to the quality of patient care. Stressed and traumatized healthcare workers are less likely to provide optimal care, potentially leading to errors and decreased patient safety.
Prevention and Intervention Strategies
Implementing a comprehensive violence prevention program is crucial for creating a safe and supportive work environment. This requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing various strategies.
It’s incredibly tough when family dynamics are strained, especially when a child’s well-being is at stake. If you’re dealing with the impact of an ex-partner’s manipulative behavior on your child’s mental health, resources are available. Check out this helpful page: x partners manipulation is affecting my childs mental health for guidance and support. Similarly, if you’re concerned about a veteran struggling with their mental health, remember you’re not alone.
Knowing where to find help is crucial; this resource, worried about a veteran who needs mental health services , offers valuable information and pathways to care.
Comprehensive Violence Prevention Program
A hypothetical violence prevention program would incorporate several key components:
- Risk Assessment: Regular assessments to identify high-risk areas and patient populations.
- Staff Training: Comprehensive training in de-escalation techniques, self-protection strategies, and reporting procedures.
- Security Enhancements: Improved lighting, security personnel, alarm systems, and secure design features.
- Supportive Culture: Promoting a culture of safety, respect, and open communication.
- Incident Reporting and Investigation: Clear protocols for reporting and investigating incidents, with appropriate follow-up and support for victims.
Effective Training Programs for Healthcare Workers
Training should focus on practical skills and strategies to manage potentially violent situations.
- De-escalation Techniques: Training in communication and conflict resolution skills to de-escalate tense situations.
- Self-Protection Strategies: Training in basic self-defense techniques and awareness of personal safety.
- Reporting Procedures: Clear guidelines on how to report incidents and access support services.
Security Measures to Enhance Safety
Implementing robust security measures is essential for creating a safer environment.
- Improved Lighting: Well-lit areas deter violence and increase visibility.
- Security Personnel: Trained security personnel can provide immediate response and support.
- Alarm Systems: Easily accessible alarm systems allow for rapid response to emergencies.
- Controlled Access: Restricting access to certain areas and implementing visitor management systems.
Supportive Organizational Culture
Creating a supportive organizational culture is paramount. This includes prioritizing worker safety, providing adequate resources, and fostering open communication.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Healthcare organizations have both legal and ethical responsibilities to ensure the safety of their employees. Balancing patient rights with the need for a safe working environment is a critical ethical challenge.
Legal Responsibilities of Healthcare Organizations
Organizations are legally obligated to provide a safe working environment for their employees. This includes implementing appropriate safety measures, providing adequate training, and investigating incidents of violence.
Ethical Obligations of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals face ethical dilemmas in balancing patient autonomy with the need to maintain a safe working environment. This requires careful consideration of individual patient needs and the safety of staff.
Policies and Procedures for Compliance
Organizations should develop and implement clear policies and procedures to comply with relevant legislation and ethical guidelines. These policies should address incident reporting, investigation, and disciplinary actions.
Legal Frameworks Addressing Workplace Violence
Many jurisdictions have laws and regulations addressing workplace violence in healthcare settings. These laws often mandate reporting requirements, safety standards, and employer responsibilities.
It’s incredibly tough when family issues impact a child’s well-being. If you’re dealing with a situation where an ex-partner’s manipulative behavior is negatively affecting your child’s mental health, check out this resource: x partners manipulation is affecting my childs mental health. They offer support and guidance. Knowing where to turn for help is crucial, especially when considering the long-term effects on a child.
This is also true for veterans struggling with their mental health; if you’re worried about a veteran who needs mental health services , remember that seeking professional help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
The Role of Technology in Violence Prevention

Technology plays an increasingly important role in preventing and responding to workplace violence in healthcare. Various technological solutions can enhance safety and improve response times.
Technology for Violence Prevention, Workplace violence in mental and general health care settings
Several technologies can contribute to a safer environment:
- Security Cameras: Provide visual surveillance and act as a deterrent.
- Panic Buttons: Allow for immediate alerts to security personnel in emergencies.
- Electronic Monitoring Systems: Track staff location and provide real-time alerts.
Benefits and Limitations of Technology
While technology offers significant benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations. Over-reliance on technology can create a false sense of security, and privacy concerns must be addressed.
Successful Implementation of Technology
Examples of successful technology implementation include the use of panic buttons linked directly to security personnel, resulting in faster response times and improved staff safety. Integration of security camera footage with incident reporting systems allows for more thorough investigations.
Hypothetical Technological Solution
A hypothetical technological solution could involve a mobile application integrating panic buttons, real-time location tracking, and direct communication with security and emergency services. This app could also facilitate streamlined incident reporting and data analysis to identify trends and improve prevention strategies.
Ultimately, addressing workplace violence in healthcare requires a multifaceted approach. It necessitates a commitment from healthcare organizations to invest in robust prevention programs, provide comprehensive training for staff, and foster a culture of safety and respect. By prioritizing the well-being of healthcare workers, we not only protect individuals but also safeguard the quality and accessibility of essential healthcare services for everyone.
The path forward demands collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, and technology developers to create safer, more supportive environments where healthcare professionals can deliver care without fear of violence.
Share this content:
