ADHD medication is a crucial part of managing ADHD for many individuals. It can help improve focus, concentration, and overall functioning. Understanding the different types of medication available, their benefits, and potential side effects is essential for making informed decisions about treatment.
This article delves into the world of ADHD medication, exploring the various types, their mechanisms of action, and their impact on individuals with ADHD. We’ll also discuss the importance of lifestyle changes and the role of healthcare professionals in managing medication effectively.
Understanding ADHD Medication
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. While ADHD is often associated with childhood, it can persist into adulthood. ADHD medication is a common treatment option for individuals with ADHD, and it can play a significant role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
This article will delve into the various aspects of ADHD medication, covering its types, benefits, side effects, and management strategies.
Types of ADHD Medications
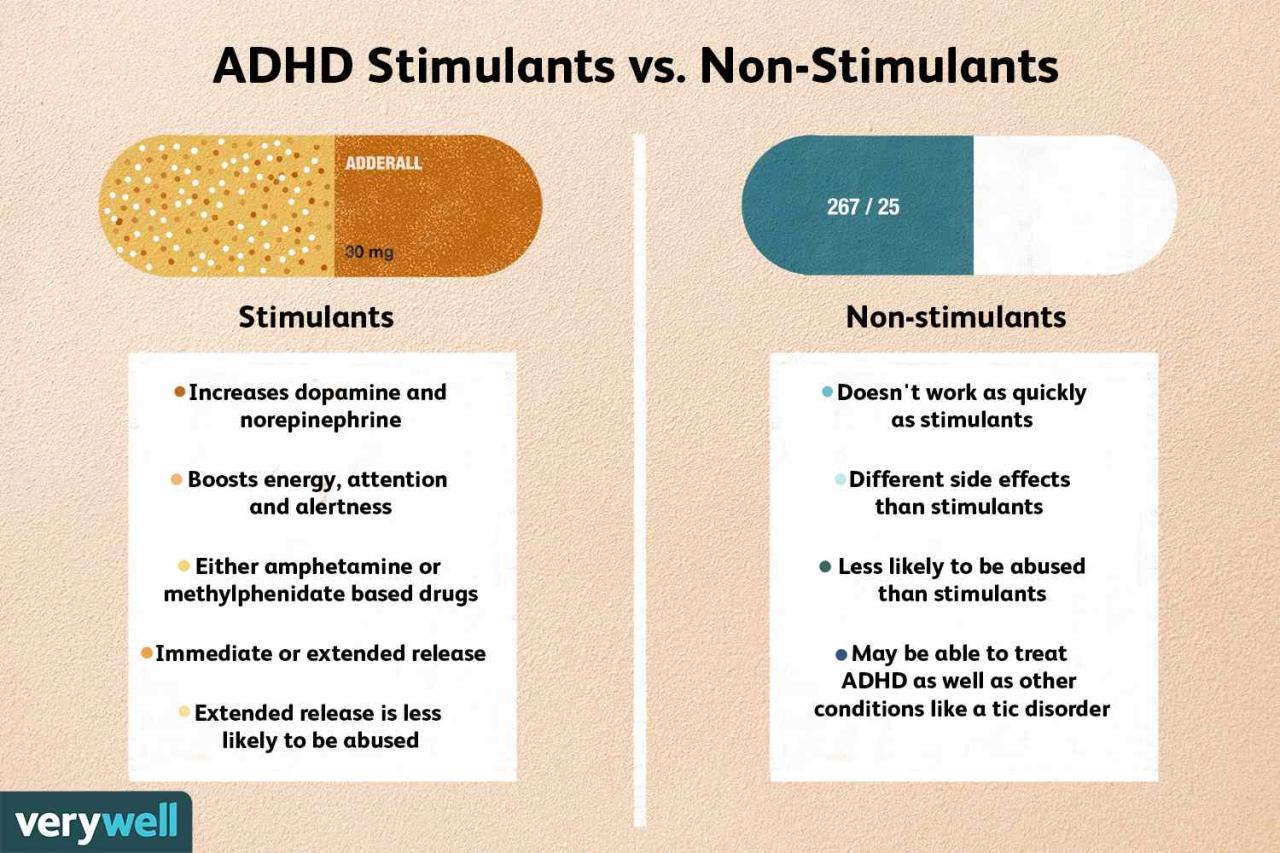
There are two main categories of ADHD medications: stimulants and non-stimulants.
- Stimulants:Stimulants are the most commonly prescribed type of ADHD medication. They work by increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which are neurotransmitters that play a role in attention, focus, and behavior. Examples of stimulant medications include:
- Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta)
- Amphetamine (Adderall, Vyvanse)
- Non-stimulants:Non-stimulant medications work differently than stimulants, targeting different neurotransmitters in the brain. They may take longer to take effect than stimulants but can provide longer-lasting benefits. Examples of non-stimulant medications include:
- Atomoxetine (Strattera)
- Guanfacine (Intuniv)
- Clonidine (Kapvay)
Benefits of ADHD Medication
ADHD medication can have a range of positive effects for individuals with ADHD, including:
- Improved Focus and Concentration:Medication can help individuals with ADHD pay better attention, focus on tasks, and complete them more efficiently. This can have a significant impact on academic performance, work productivity, and overall functioning.
- Reduced Hyperactivity and Impulsivity:ADHD medication can help to reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity, making it easier for individuals to control their behavior and manage their energy levels. This can lead to better social interactions, fewer behavioral problems, and improved relationships.
- Enhanced Emotional Regulation:ADHD medication can help individuals with ADHD regulate their emotions more effectively. This can reduce feelings of frustration, anger, and sadness, leading to a more stable and positive mood.
- Improved Self-Esteem and Confidence:When individuals with ADHD experience positive outcomes from medication, such as improved focus and reduced impulsivity, it can boost their self-esteem and confidence. This can have a positive impact on their overall well-being and sense of self-worth.
Side Effects of ADHD Medication

While ADHD medication can be very beneficial, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects. Some common side effects include:
- Loss of Appetite:Some individuals may experience a decrease in appetite, especially when starting medication. This is usually temporary and can be managed by adjusting meal times or eating more frequent, smaller meals.
- Insomnia:ADHD medication can sometimes interfere with sleep, especially if taken too late in the day. It’s important to take medication as prescribed and avoid taking it close to bedtime.
- Headaches:Headaches are a relatively common side effect of ADHD medication, particularly in the early stages of treatment. They usually subside over time.
- Stomach Upset:Some individuals may experience nausea, vomiting, or stomach cramps, especially when starting medication. These side effects are usually mild and can be managed by taking medication with food.
- Mood Swings:Some individuals may experience mood swings or irritability, especially when starting medication. It’s important to discuss these side effects with a healthcare professional.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to discuss any concerns about side effects and to ensure that the medication is safe and effective for you. They can help manage side effects and adjust medication dosages as needed.
ADHD Medication and Lifestyle
While medication can play a significant role in managing ADHD symptoms, lifestyle changes can also be beneficial. Here are some examples of lifestyle modifications that can complement ADHD medication:
- Healthy Diet:Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients that support brain health and cognitive function.
- Regular Exercise:Regular physical activity can help improve focus, attention, and mood. It can also reduce stress and anxiety, which can exacerbate ADHD symptoms.
- Adequate Sleep:Getting enough sleep is essential for optimal brain function. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to improve focus, concentration, and overall well-being.
- Stress Management Techniques:Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can improve focus and concentration.
- Organizational Strategies:Implementing organizational strategies, such as using calendars, to-do lists, and reminders, can help individuals with ADHD stay on track and manage their time effectively.
Medication Management and Patient Education
Managing ADHD medication effectively requires ongoing communication and collaboration with a healthcare professional. Here are some important aspects of medication management:
- Regular Follow-Up Appointments:It’s essential to schedule regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional to monitor the effectiveness of medication, adjust dosages as needed, and address any side effects.
- Medication Adjustments:Based on your individual needs and response to medication, your healthcare professional may adjust the dosage or type of medication over time. This is a normal part of managing ADHD medication.
- Monitoring for Effectiveness:It’s important to track your progress and communicate with your healthcare professional about how medication is affecting your symptoms. This can help ensure that you’re receiving the most effective treatment.
- Managing Side Effects:If you experience any side effects, it’s crucial to discuss them with your healthcare professional. They can help manage side effects and adjust medication dosages as needed.
- Open Communication with Healthcare Providers:Maintaining open and honest communication with your healthcare provider is essential for effective medication management. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, express concerns, and provide feedback on your experience with medication.
Considerations for Adults with ADHD
Managing ADHD in adulthood presents unique challenges. Adults with ADHD may face difficulties in work, relationships, and personal life. Here are some key considerations for adults with ADHD:
- Medication Adjustments:Medication needs may change as individuals age. It’s important to discuss medication adjustments with a healthcare professional to ensure that it remains effective and appropriate.
- Comorbid Conditions:Adults with ADHD may have co-occurring conditions, such as anxiety or depression, which may require additional treatment. It’s essential to discuss all conditions with a healthcare professional to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Support Groups and Resources:There are numerous support groups and resources available for adults with ADHD. These groups can provide valuable information, support, and connection with others who understand the challenges of living with ADHD.
Medication and Children with ADHD, Adhd medication
Prescribing ADHD medication to children requires careful consideration and a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Parental Involvement:Parental involvement is crucial in medication management for children with ADHD. Parents should be actively involved in discussions with the healthcare professional, understanding the medication’s effects, and monitoring their child’s response.
- Long-Term Effects:While ADHD medication is generally safe for children, it’s important to consider potential long-term effects on developing brains. The healthcare professional will carefully monitor the child’s progress and adjust medication as needed.
- Non-Medication Options:Before considering medication, healthcare professionals may explore non-medication options, such as behavioral therapy, cognitive training, and lifestyle changes. These options may be sufficient for some children with ADHD.
Alternative Treatments for ADHD
In addition to medication, alternative therapies and treatments for ADHD can be considered. These approaches may complement medication or be used as standalone options.
- Behavioral Therapy:Behavioral therapy can teach individuals with ADHD strategies for managing their symptoms, such as improving attention, reducing impulsivity, and enhancing organizational skills.
- Cognitive Training:Cognitive training exercises can help improve cognitive skills, such as working memory, attention, and executive function. This can enhance the ability to focus, plan, and organize.
- Lifestyle Modifications:Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and getting enough sleep, can support brain health and cognitive function, potentially improving ADHD symptoms.
It’s important to note that alternative treatments may not be effective for everyone with ADHD, and it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before pursuing any alternative approaches.
Myths and Misconceptions about ADHD Medication
There are many myths and misconceptions surrounding ADHD medication. It’s important to rely on accurate information and evidence-based practices. Here are some common myths and misconceptions:
- Myth:ADHD medication is addictive. Fact:When taken as prescribed, ADHD medication is not addictive. However, misuse or abuse can lead to dependence.
- Myth:ADHD medication turns children into “zombies.” Fact:ADHD medication does not make children “zombies.” It can help them focus and control their behavior, allowing them to participate more fully in activities.
- Myth:ADHD medication is a “quick fix” for all ADHD symptoms. Fact:ADHD medication is not a cure for ADHD, but it can be a valuable tool for managing symptoms. It’s often most effective when combined with other interventions, such as therapy and lifestyle changes.
It’s essential to seek reliable information from credible sources, such as healthcare professionals, reputable organizations, and evidence-based research.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision to use ADHD medication is a personal one, and it’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks. Working closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and other therapies can lead to significant improvements in managing ADHD and achieving a better quality of life.