Anxiety medication plays a crucial role in helping millions manage anxiety disorders, offering a path towards a calmer and more fulfilling life. These medications, often prescribed by mental health professionals, work by targeting specific brain chemicals and pathways associated with anxiety, ultimately aiming to reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
From the historical development of early anxiolytics to the emergence of newer, more targeted medications, the field of anxiety medication has undergone significant advancements. Understanding the different types of medications available, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is essential for making informed decisions about treatment.
Introduction to Anxiety Medication
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can manifest in various ways, from occasional feelings of worry and nervousness to debilitating panic attacks and phobias. While lifestyle changes, therapy, and relaxation techniques can be helpful in managing anxiety, medication can be a valuable tool for some individuals.
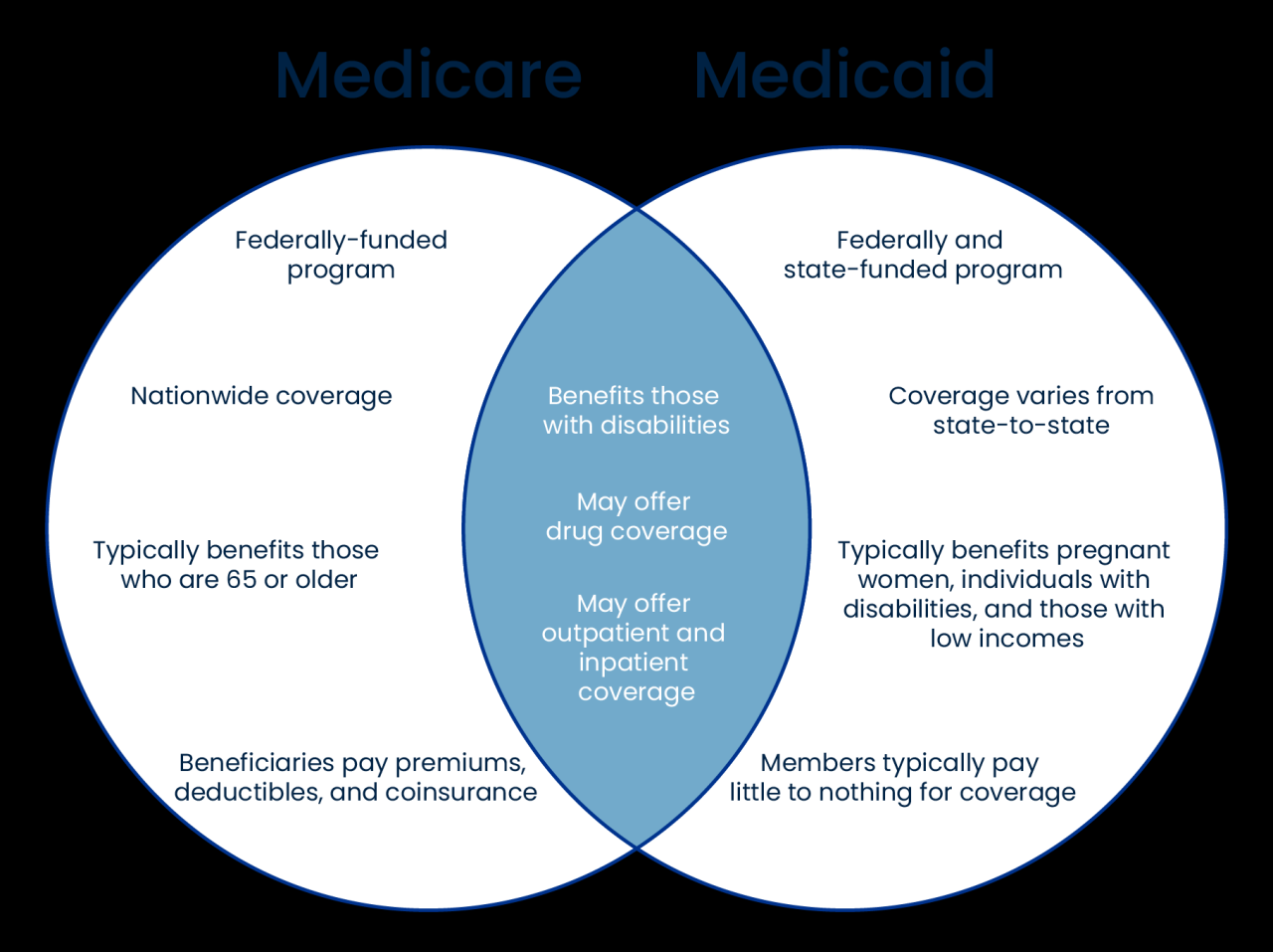
Anxiety medication, also known as anxiolytics, are a class of drugs that are used to treat anxiety disorders by reducing anxiety symptoms and improving mood.
History and Evolution of Anxiety Medication
The use of medication for anxiety dates back centuries, with ancient civilizations employing natural remedies like herbs and plants. In the early 20th century, the discovery of barbiturates marked a significant advancement in the treatment of anxiety. However, these medications were highly addictive and had a narrow therapeutic window.
In the 1950s, the introduction of benzodiazepines revolutionized anxiety treatment, offering a safer and more effective option. However, the potential for dependence and side effects led to the development of newer classes of medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), which target specific neurotransmitters in the brain.
These newer medications have a lower risk of dependence and offer a broader range of therapeutic benefits.
Types of Anxiety Disorders and Medication Use
Anxiety disorders are a diverse group of conditions, each with its own unique characteristics and treatment approaches. Some common types of anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life.
- Panic Disorder: Marked by recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear or discomfort accompanied by physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Characterized by intense fear and anxiety in social situations.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Involves intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors that individuals feel compelled to perform.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): A condition that develops after a traumatic event, causing flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance behaviors.
Medication is often used in conjunction with therapy to treat anxiety disorders. The specific type of medication and dosage will vary depending on the individual’s diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and other factors. For example, SSRIs and SNRIs are commonly used for GAD and social anxiety disorder, while benzodiazepines are often prescribed for panic disorder and acute anxiety episodes.
Types of Anxiety Medication
Anxiety medications are broadly categorized into different classes, each with its unique mechanism of action, side effects, and effectiveness. Understanding these classes can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)

SSRIs are a class of antidepressants that work by increasing the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. By increasing serotonin levels, SSRIs can help reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall mood.
- Mechanism of Action:SSRIs block the reuptake of serotonin in the synapse, allowing serotonin to remain in the synaptic cleft for a longer duration, increasing its availability to bind to serotonin receptors.
- Common Medications:Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), Paroxetine (Paxil), Escitalopram (Lexapro), Citalopram (Celexa)
- Potential Side Effects:Nausea, headache, dizziness, sexual dysfunction, weight gain, insomnia, and withdrawal symptoms.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
SNRIs are a class of antidepressants that work by increasing the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Norepinephrine is another neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, attention, and energy levels. By increasing both serotonin and norepinephrine levels, SNRIs can provide broader benefits for anxiety and depression.
- Mechanism of Action:SNRIs block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the synapse, increasing their availability in the brain.
- Common Medications:Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Potential Side Effects:Similar to SSRIs, SNRIs can cause nausea, headache, dizziness, sexual dysfunction, and increased blood pressure.
Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that work by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) in the brain. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps calm the nervous system. By increasing GABA activity, benzodiazepines can reduce anxiety, promote relaxation, and induce sleep.
- Mechanism of Action:Benzodiazepines bind to GABA receptors in the brain, enhancing the effects of GABA and reducing neuronal activity.
- Common Medications:Alprazolam (Xanax), Lorazepam (Ativan), Diazepam (Valium), Clonazepam (Klonopin)
- Potential Side Effects:Drowsiness, dizziness, impaired coordination, memory problems, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms.
Other Classes of Anxiety Medication
In addition to SSRIs, SNRIs, and benzodiazepines, other classes of medication are used to treat anxiety, including:
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs):TCAs, such as imipramine (Tofranil) and amitriptyline (Elavil), are older antidepressants that can be effective for anxiety, but they have a higher risk of side effects than newer medications.
- Buspirone (Buspar):Buspirone is a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic that works by targeting serotonin receptors in the brain. It is often used for GAD and can take several weeks to reach full effectiveness.
- Beta-Blockers:Beta-blockers, such as propranolol (Inderal), are primarily used to treat high blood pressure but can also help manage physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat and trembling.
Prescription and Usage of Anxiety Medication
Getting a prescription for anxiety medication involves a comprehensive assessment by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a psychiatrist or primary care physician. The process typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:The doctor will review your medical history, including any previous diagnoses, medications, and allergies. They will also conduct a physical examination to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your anxiety.
- Mental Health Assessment:The doctor will assess your mental health symptoms, including the severity, duration, and impact of your anxiety. They may use standardized questionnaires or interviews to gather information about your symptoms.
- Diagnosis:Based on the information gathered, the doctor will make a diagnosis and determine if anxiety medication is appropriate for your condition.
- Medication Selection and Dosage:If medication is recommended, the doctor will choose the most suitable type and dosage based on your individual needs and preferences. They will consider factors such as your age, medical history, and other medications you are taking.
Importance of Proper Dosage and Administration
It is crucial to take anxiety medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Taking too much medication can increase the risk of side effects, while taking too little may not provide adequate relief. The doctor will monitor your response to medication and adjust the dosage as needed.
It is also important to take medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels in your bloodstream.
Risks of Misuse and Abuse
Misuse and abuse of anxiety medication can lead to serious health consequences. Taking medication without a prescription, exceeding the recommended dosage, or mixing medication with alcohol or other drugs can increase the risk of dependence, overdose, and other adverse effects.
It is essential to use anxiety medication responsibly and only as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Managing Side Effects and Potential Drug Interactions
Anxiety medication can cause various side effects, some of which may be mild and temporary, while others may be more severe. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and sexual dysfunction. It is important to discuss any side effects you experience with your doctor, as they may be able to adjust your medication or recommend strategies for managing them.
Additionally, it is crucial to inform your doctor about any other medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you are taking, as these can interact with anxiety medication and potentially increase the risk of side effects.
Alternative Treatment Options
While medication can be an effective treatment for anxiety, it is not always the only or best option. Non-pharmacological approaches, such as therapy, lifestyle changes, and relaxation techniques, can also play a significant role in managing anxiety.
Therapy
Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. CBT focuses on teaching coping skills and strategies for managing anxiety in challenging situations. Other types of therapy, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), can also be beneficial for anxiety.
Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle changes can significantly impact anxiety levels. These changes may include:
- Regular Exercise:Physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Healthy Diet:Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve mood and energy levels. Avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
- Adequate Sleep:Getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining mental and physical health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stress Management:Identify and manage stressors in your life. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can be helpful for reducing stress.
Relaxation Techniques, Anxiety medication
Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery, can help calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety symptoms. These techniques can be practiced independently or with the guidance of a therapist.
The Impact of Anxiety Medication
Anxiety medication can have both positive and negative impacts on individuals. It is essential to weigh these potential benefits and drawbacks carefully before making a decision about medication use.
Benefits of Anxiety Medication
Anxiety medication can provide significant benefits for individuals with anxiety disorders, including:
- Symptom Relief:Medication can help reduce anxiety symptoms, such as worry, nervousness, panic attacks, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat and trembling.
- Improved Quality of Life:By reducing anxiety symptoms, medication can improve overall quality of life, allowing individuals to participate more fully in social activities, work, and relationships.
- Enhanced Functioning:Medication can help individuals focus better, make decisions more effectively, and cope with daily stressors more easily.
Drawbacks of Anxiety Medication
Anxiety medication can also have drawbacks, including:
- Side Effects:Medication can cause various side effects, some of which may be mild and temporary, while others may be more severe. It is important to discuss any side effects with your doctor.
- Dependence:Some anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, can be habit-forming and lead to dependence. It is essential to use these medications responsibly and only as prescribed by a doctor.
- Withdrawal Symptoms:Abruptly stopping some anxiety medications can cause withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. It is important to taper off medication gradually under the supervision of a doctor.
- Cost:Anxiety medication can be expensive, especially for individuals without health insurance. It is important to discuss cost concerns with your doctor and explore options for affordable medication.
Long-Term Effects of Anxiety Medication
The long-term effects of anxiety medication vary depending on the type of medication and individual factors. Some medications, such as SSRIs and SNRIs, are generally considered safe for long-term use. However, benzodiazepines should be used for short periods only due to the risk of dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
It is essential to discuss any concerns about long-term effects with your doctor.
Ethical Considerations
The use of anxiety medication raises ethical considerations, particularly regarding the potential for over-prescription and the over-reliance on medication as a primary treatment approach. It is important to balance the benefits of medication with the potential risks and to consider alternative treatment options, such as therapy and lifestyle changes.
Open communication between patients and healthcare professionals is crucial for making informed decisions about medication use.
Future Directions in Anxiety Medication
Research and development in anxiety medication are ongoing, with a focus on developing safer, more effective, and more targeted treatments. Future directions include:
New Medications

Researchers are developing new classes of medications that target specific brain circuits involved in anxiety. These medications may have fewer side effects and provide more personalized treatment options.
Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the treatment of anxiety disorders include:
- Personalized Medicine:Tailoring treatment to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and other factors.
- Digital Therapeutics:Using technology-based interventions, such as apps and wearable devices, to manage anxiety.
- Combination Therapies:Combining medication with therapy and lifestyle changes to achieve optimal outcomes.
Challenges and Opportunities
The future of anxiety medication presents both challenges and opportunities. Challenges include:
- Developing effective and safe medications:It is challenging to develop medications that target specific brain circuits without causing significant side effects.
- Addressing the stigma of mental illness:Stigma can prevent individuals from seeking treatment for anxiety disorders, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Ensuring equitable access to treatment:Access to mental healthcare services and medication can vary widely based on socioeconomic factors and geographic location.
Opportunities include:
- Advancements in neuroscience research:Continued research into the brain mechanisms of anxiety can lead to the development of more targeted and effective treatments.
- Increased awareness and acceptance of mental illness:Raising awareness about anxiety disorders can help reduce stigma and encourage individuals to seek help.
- Development of innovative technologies:Technology can play a role in improving access to mental healthcare and providing personalized treatment options.
Final Thoughts
The journey towards managing anxiety is multifaceted, and while anxiety medication can be a valuable tool, it’s crucial to remember that it’s often most effective when combined with other approaches. Therapy, lifestyle modifications, and relaxation techniques can complement medication, creating a comprehensive strategy for tackling anxiety.
Ultimately, finding the right balance of treatment options empowers individuals to regain control and navigate life’s challenges with greater confidence and resilience.