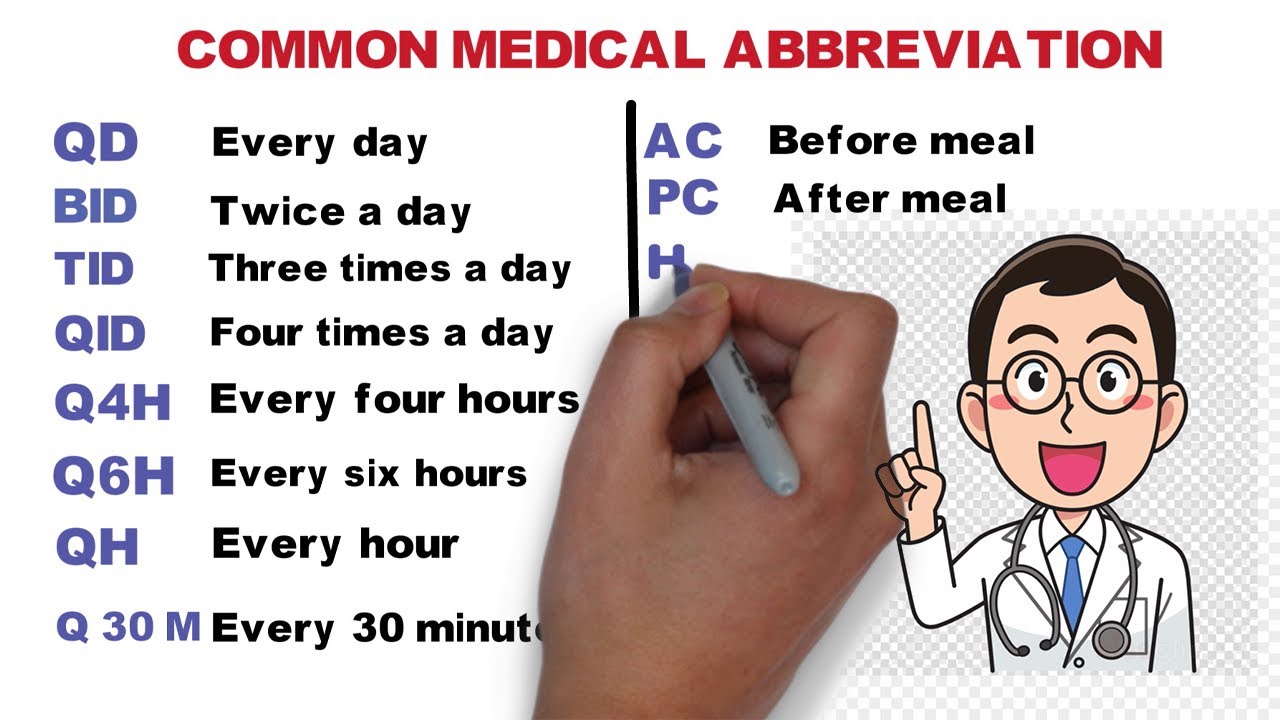
Blood pressure medication plays a crucial role in managing high blood pressure, a condition that affects millions worldwide. These medications work by targeting various mechanisms within the body to lower blood pressure, reducing the strain on your heart and blood vessels.
While they offer significant benefits, understanding the different types of medication, their potential side effects, and the importance of lifestyle modifications is essential for effective management.
This guide explores the different types of blood pressure medication, their uses, and factors that influence their selection. We’ll delve into the role of lifestyle changes in managing blood pressure and discuss the potential risks associated with long-term medication use.
Blood Pressure Medication: An Overview
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. Untreated hypertension can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Blood pressure medication, also known as antihypertensive drugs, plays a crucial role in managing and preventing these complications.
Definition of Blood Pressure Medication
Blood pressure medication refers to a diverse group of drugs designed to lower blood pressure by acting on different mechanisms within the body. These medications work by relaxing blood vessels, reducing the heart’s workload, or decreasing the amount of fluid in the body.
Types of Blood Pressure Medication and Their Mechanisms of Action
There are various types of blood pressure medications, each working through different mechanisms. Here’s a breakdown of some common types:
- Diuretics:These medications work by increasing urine production, reducing the amount of fluid in the body, and thereby lowering blood pressure. Examples include hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide.
- Beta-blockers:These drugs block the effects of adrenaline on the heart, slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of contractions. Examples include metoprolol and atenolol.
- ACE inhibitors:These medications block the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that constricts blood vessels. This results in relaxation of blood vessels and lower blood pressure. Examples include lisinopril and ramipril.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs):Similar to ACE inhibitors, ARBs block the effects of angiotensin II by preventing it from binding to its receptors. Examples include losartan and valsartan.
- Calcium channel blockers:These drugs relax blood vessels by blocking the flow of calcium into the muscle cells that control blood vessel contraction. Examples include amlodipine and diltiazem.
- Alpha-blockers:These medications relax blood vessels by blocking the effects of adrenaline on blood vessel walls. Examples include doxazosin and terazosin.
Common Side Effects Associated with Blood Pressure Medication
While blood pressure medication is generally safe and effective, some side effects can occur. These side effects vary depending on the type of medication and individual sensitivity. Common side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Cough
- Swelling in the ankles and feet
- Low blood pressure
It’s important to discuss any side effects you experience with your healthcare provider. They can help determine if the side effects are manageable or if a change in medication is necessary.
Common Blood Pressure Medications
A wide range of blood pressure medications are available, and your healthcare provider will choose the best option based on your individual needs and medical history. Here’s a look at some of the most frequently prescribed medications:
Specific Uses and Benefits of Common Medications

- Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ):This diuretic is often used as a first-line treatment for hypertension. It is effective in lowering blood pressure and is generally well-tolerated.
- Lisinopril:An ACE inhibitor, lisinopril is effective in lowering blood pressure and is often used for patients with high blood pressure and other conditions like heart failure or diabetes.
- Metoprolol:A beta-blocker, metoprolol is used to lower blood pressure and is also effective in treating heart conditions like angina and arrhythmias.
- Amlodipine:A calcium channel blocker, amlodipine is used to lower blood pressure and is also effective in treating chest pain (angina).
- Losartan:An ARB, losartan is effective in lowering blood pressure and is often used for patients with high blood pressure and diabetes.
Comparison of Medication Effectiveness
The effectiveness of different blood pressure medications can vary depending on individual factors such as age, health history, and the severity of hypertension. Some medications may be more effective for certain conditions than others. For example, ACE inhibitors are often preferred for patients with diabetes, while beta-blockers may be more effective for patients with heart failure.
Your healthcare provider will carefully consider your individual needs and medical history to determine the most appropriate medication for you.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure Medication Choice
Choosing the right blood pressure medication for an individual requires careful consideration of several factors. Healthcare professionals use a comprehensive approach to ensure the best possible outcome for each patient.
Importance of Individual Patient Factors
Several factors influence the choice of blood pressure medication, including:
- Age:Older adults may require different medications or lower dosages than younger individuals.
- Health History:Existing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease can influence medication choice.
- Lifestyle:Factors like diet, exercise, and smoking habits can impact the effectiveness of blood pressure medication.
- Drug Interactions:Other medications a patient is taking can interact with blood pressure medication, necessitating adjustments or alternative choices.
- Cost and Availability:The cost and availability of different medications can also play a role in the decision-making process.
Considerations for Different Patient Profiles, Blood pressure medication
| Patient Profile | Medication Considerations |
|---|---|
| Older Adults | Diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs may be appropriate, depending on individual health conditions. |
| Patients with Diabetes | ACE inhibitors or ARBs are often preferred due to their benefits in protecting the kidneys. |
| Patients with Heart Failure | Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or ARBs may be recommended to improve heart function and reduce the risk of complications. |
| Patients with Kidney Disease | ACE inhibitors or ARBs are often used to slow the progression of kidney disease. |
Blood Pressure Medication and Lifestyle Modifications
While blood pressure medication is essential for many individuals, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing blood pressure and enhancing the effectiveness of medication.
Role of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications can help lower blood pressure naturally and improve overall health. These changes can also enhance the effectiveness of blood pressure medication.
Recommended Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet:Eating a balanced diet low in sodium, saturated fat, and cholesterol can help lower blood pressure. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Regular Exercise:Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Exercise helps lower blood pressure, improve heart health, and manage weight.
- Weight Management:Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce blood pressure. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can make a difference.
- Stress Management:Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Limit Alcohol Intake:Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Quit Smoking:Smoking significantly increases the risk of high blood pressure and other health problems. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your health.
Interaction of Medication and Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes work in synergy with blood pressure medication to achieve optimal blood pressure control. By adopting healthy habits, you can enhance the effectiveness of your medication and reduce the need for higher dosages.
Blood Pressure Medication and Potential Risks
While blood pressure medication is generally safe and effective, long-term use can be associated with potential risks and complications. It’s essential to be aware of these risks and discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Potential Risks and Complications
- Low Blood Pressure:Some blood pressure medications can cause a drop in blood pressure, especially when taken in combination with other medications or when standing up quickly.
- Side Effects:As mentioned earlier, blood pressure medications can cause various side effects, ranging from mild to severe. Some common side effects include dizziness, headache, fatigue, and cough.
- Drug Interactions:Blood pressure medication can interact with other medications, leading to potential complications. It’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Dependence:Long-term use of blood pressure medication can lead to dependence, meaning that your body may become reliant on the medication to maintain normal blood pressure levels.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and overall health is crucial when taking blood pressure medication. Your healthcare provider will schedule regular check-ups to monitor your blood pressure, assess the effectiveness of your medication, and identify any potential side effects or complications.
It’s essential to attend these appointments and discuss any concerns you may have.
By working closely with your healthcare provider and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of developing serious health complications.
Final Review
Managing high blood pressure requires a holistic approach that combines medication with lifestyle modifications. By understanding the different types of blood pressure medication, their benefits, and potential risks, individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that optimizes their health and well-being.
Remember, regular monitoring, adherence to medication, and proactive lifestyle changes are key to achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.