Hypertension medication plays a crucial role in managing high blood pressure, a condition affecting millions worldwide. These medications work by targeting various mechanisms within the body, helping to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of serious health complications like heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease.
Understanding the different types of medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is essential for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
This guide delves into the world of hypertension medication, exploring the various options available, the factors influencing medication selection, and the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment plans. We’ll also discuss the role of lifestyle modifications in managing hypertension and provide insights into managing medication during pregnancy.
Understanding Hypertension Medication
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. If left untreated, hypertension can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
Fortunately, there are many effective medications available to help manage hypertension.
Types of Hypertension Medication
Hypertension medication is typically categorized by the way it works to lower blood pressure. Each type of medication works on a different part of the body’s system to reduce the pressure in your arteries. Here are some of the most common types of hypertension medications:
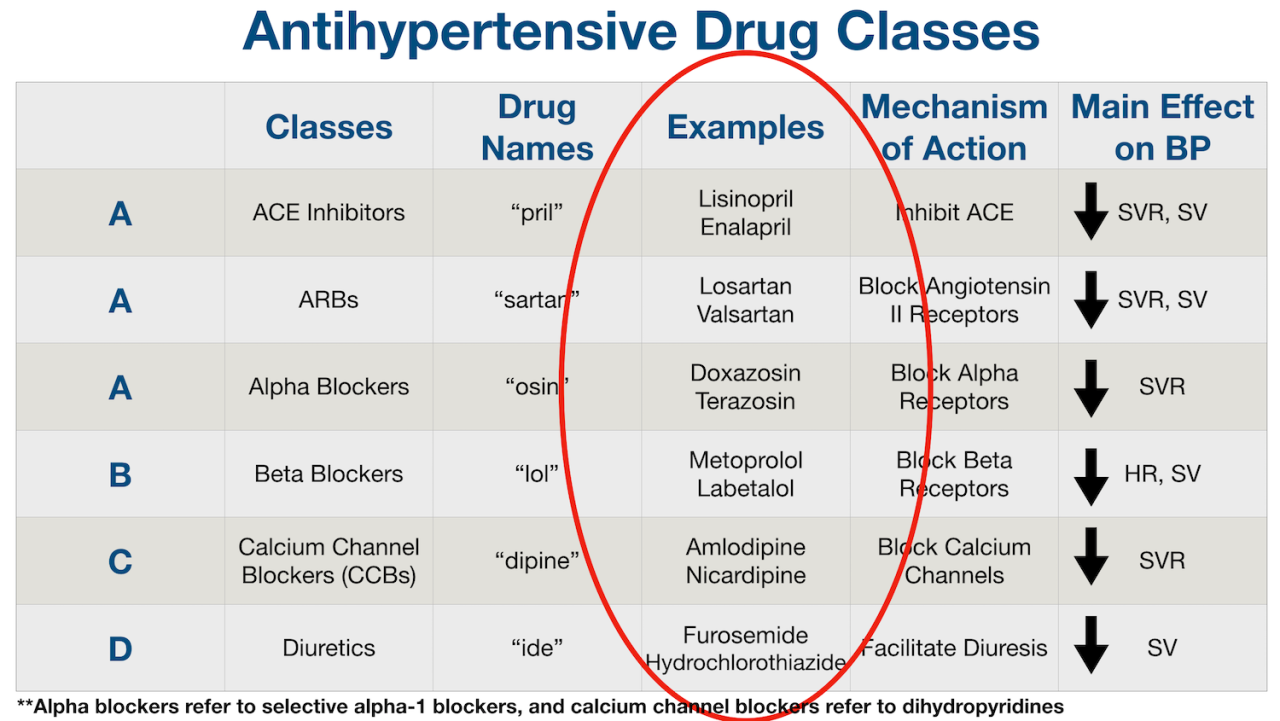
- Diuretics: These medications help your body remove excess salt and water through urine. This helps to lower blood volume, which in turn reduces blood pressure. Common examples include hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide.
- Beta-blockers: These medications block the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are hormones that can cause your heart to beat faster and your blood vessels to constrict. This helps to lower blood pressure by slowing your heart rate and relaxing your blood vessels.
Common examples include metoprolol and atenolol.
- ACE inhibitors: These medications block the production of angiotensin II, a hormone that constricts blood vessels. This helps to lower blood pressure by relaxing and widening blood vessels. Common examples include lisinopril and ramipril.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): These medications block the action of angiotensin II by preventing it from binding to receptors in your blood vessels. This helps to lower blood pressure by relaxing and widening blood vessels. Common examples include losartan and valsartan.
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications block the flow of calcium into the muscle cells of your heart and blood vessels. This helps to lower blood pressure by relaxing your blood vessels and slowing your heart rate. Common examples include amlodipine and diltiazem.
- Alpha-blockers: These medications block the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline on blood vessels, causing them to relax and widen. This helps to lower blood pressure by reducing the resistance to blood flow. Common examples include doxazosin and terazosin.
Common Side Effects of Hypertension Medication
Like all medications, hypertension medications can cause side effects. The severity of these side effects varies from person to person. Some common side effects include:
- Dizziness: This is a common side effect of many hypertension medications, especially when you first start taking them. It’s important to get up slowly from a sitting or lying position to avoid dizziness.
- Fatigue: Some medications can cause fatigue or tiredness. If you experience fatigue, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
- Headache: Headaches can be a side effect of some hypertension medications. If you experience headaches, talk to your doctor.
- Cough: ACE inhibitors can cause a dry cough in some people. If you experience a cough, talk to your doctor.
- Swelling: Some medications can cause swelling in the ankles, feet, or hands. If you experience swelling, talk to your doctor.
- Gastrointestinal problems: Some medications can cause nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. If you experience gastrointestinal problems, talk to your doctor.
It’s important to note that these are just some of the most common side effects. Other side effects may occur, and the severity of side effects can vary from person to person. If you experience any side effects, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Choosing the Right Medication
Choosing the right hypertension medication for you depends on a number of factors. Your doctor will consider your individual medical history, current health conditions, and lifestyle factors to determine the best medication for you.
Factors Healthcare Professionals Consider
When choosing hypertension medication, healthcare professionals consider several factors, including:
- Severity of hypertension: The higher your blood pressure, the more likely you are to need medication. Your doctor will determine the appropriate medication based on your blood pressure readings.
- Other health conditions: Your doctor will need to consider any other health conditions you have, such as diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease. Certain medications may be contraindicated or require careful monitoring if you have other health conditions.
- Medications you are currently taking: Your doctor will need to consider any other medications you are currently taking to avoid drug interactions.
- Lifestyle factors: Your doctor will consider your lifestyle factors, such as diet, exercise, and smoking habits. These factors can influence the effectiveness of certain medications.
- Personal preferences: Your doctor will also consider your personal preferences for medication, such as whether you prefer a pill or a liquid.
Key Considerations for Patients, Hypertension medication
When discussing medication options with your doctor, there are several key considerations for patients:
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor any questions you have about your medication. It’s important to understand how the medication works, its potential side effects, and how to take it properly.
- Discuss potential side effects: Talk to your doctor about the potential side effects of each medication. This will help you to make an informed decision about which medication is right for you.
- Be honest about your lifestyle: Be honest with your doctor about your lifestyle habits, such as diet, exercise, and smoking. This information will help your doctor to choose the most effective medication for you.
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring and Follow-up Appointments
Once you start taking hypertension medication, it’s important to monitor your blood pressure regularly. This will help your doctor to determine if your medication is working effectively and to adjust your dosage if necessary. Your doctor will also schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your blood pressure and discuss any concerns you may have.
Managing Hypertension Medication
Taking hypertension medication as prescribed is crucial for managing your blood pressure and preventing serious health complications. Understanding how to manage your medication effectively can help you achieve the best possible outcomes.
Importance of Taking Medication as Prescribed
It’s essential to take your hypertension medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. This means taking the correct dosage at the right time and not skipping doses. Even missing a single dose can temporarily increase your blood pressure.
“Taking your medication as prescribed is the most important step in managing your hypertension. Consistency is key.”
Potential Consequences of Missing Doses or Stopping Medication Prematurely
Missing doses or stopping medication prematurely can have serious consequences for your health. It can lead to an increase in blood pressure, which can put you at risk for stroke, heart attack, or other cardiovascular problems. Stopping medication abruptly can also cause rebound hypertension, a sudden spike in blood pressure that can be dangerous.
Managing Potential Side Effects and Communicating with Healthcare Providers
While hypertension medications are generally safe and effective, they can sometimes cause side effects. If you experience any side effects, it’s important to talk to your doctor. They may be able to adjust your dosage or recommend a different medication.
It’s also important to communicate openly and honestly with your healthcare providers about any concerns you have about your medication. They are there to help you manage your hypertension and achieve the best possible outcomes.
Lifestyle Modifications: Hypertension Medication
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing hypertension. Making healthy choices can help lower your blood pressure, reduce your risk of complications, and improve your overall health.
Role of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can help manage hypertension by:
- Lowering blood pressure: Healthy lifestyle choices can help lower your blood pressure naturally, reducing the need for medication or lowering your dosage.
- Reducing risk of complications: Lifestyle changes can reduce your risk of developing complications associated with hypertension, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure.
- Improving overall health: Healthy lifestyle choices can improve your overall health and well-being.
Recommended Dietary Changes and Exercise Routines
Here are some recommended dietary changes and exercise routines for individuals with hypertension:
| Dietary Changes | Exercise Routines |
|---|---|
|
|
Tips on Stress Management and Smoking Cessation
Stress and smoking can also contribute to hypertension. Here are some tips on stress management and smoking cessation:
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation. Engage in activities you enjoy, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones. Seek professional help if you are struggling to manage stress.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your health. Talk to your doctor about smoking cessation programs and resources available to help you quit.
Hypertension Medication and Pregnancy
Hypertension during pregnancy can pose risks to both the mother and the baby. Managing hypertension during pregnancy requires careful consideration and close monitoring.
Potential Risks Associated with Hypertension Medication During Pregnancy
Some hypertension medications can pose risks to the developing fetus. Therefore, it’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of each medication with your doctor. Your doctor will carefully consider your individual situation and choose the safest medication for you and your baby.
Alternative Treatment Options for Pregnant Women with Hypertension
In some cases, lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications and regular exercise, may be sufficient to manage hypertension during pregnancy. However, if medication is necessary, your doctor may recommend alternative medications that are considered safe for pregnancy, such as:
- Methyldopa: This medication is often used as a first-line treatment for hypertension during pregnancy.
- Labetalol: This medication is a beta-blocker that is also considered safe for pregnancy.
- Hydralazine: This medication is a vasodilator that helps to relax blood vessels.
Managing Hypertension During Pregnancy and Postpartum
Managing hypertension during pregnancy requires close monitoring by your doctor. You will need to have regular blood pressure checks and prenatal appointments. Your doctor may also recommend additional tests, such as fetal monitoring, to ensure the health of your baby.
After you give birth, your doctor will continue to monitor your blood pressure. It’s important to continue taking your medication as prescribed and to follow your doctor’s recommendations for managing your hypertension postpartum.
Closing Summary
Living with hypertension requires a proactive approach that involves medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. By understanding the different types of hypertension medication, their potential benefits and side effects, and the importance of adhering to prescribed treatment plans, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to effectively manage their condition and improve their overall health.
Remember, consistent blood pressure management is key to reducing the risk of complications and living a healthier, longer life.