Medicaid eligibility is a complex topic that affects millions of Americans, providing crucial access to healthcare for those with limited financial resources. Understanding the intricate rules and requirements can be challenging, but navigating this system is essential for securing necessary medical care.
If you’re struggling with depression, you’re not alone. It’s a common condition that can be effectively treated with therapy and medication. There are a variety of depression medication options available, and your doctor can help you find the right one for you.
It’s important to remember that everyone is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s also important to be patient, as it may take some time to find the right medication and dosage.
This
Depression is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on your life. If you’re struggling, it’s important to seek professional help. There are a variety of treatment options available, including depression medication. These medications can help to balance your brain chemistry and improve your mood.
It’s important to work with a doctor to find the right medication and dosage for you.
guide explores the key aspects of Medicaid eligibility, from the basics of program structure to the practical steps involved in applying and maintaining coverage.
Medicaid, a government-funded health insurance program, is designed to ensure that low-income individuals and families have access to essential medical services. The program’s structure and eligibility criteria vary across states, creating a patchwork of coverage options that can be difficult to understand.
This guide aims to shed light on the complexities of Medicaid eligibility, providing a comprehensive overview of the program’s history, requirements, application process, and the benefits it provides.
Medicaid Eligibility Overview
Medicaid is a government-funded health insurance program in the United States that provides coverage for low-income individuals and families. It is a vital component of the nation’s healthcare system, ensuring access to essential medical services for millions of Americans who might otherwise be unable to afford them.
Purpose and Scope of Medicaid
Medicaid’s primary purpose is to provide financial assistance for healthcare services to eligible individuals and families. Its scope encompasses a wide range of medical services, including but not limited to:
- Hospitalization
- Outpatient care
- Prescription drugs
- Dental care
- Mental health services
- Long-term care
Medicaid is administered jointly by the federal and state governments, with the federal government providing matching funds to states based on their Medicaid expenditures. This collaborative approach allows states to tailor their Medicaid programs to meet the specific needs of their populations.
Eligibility Categories for Medicaid
Medicaid eligibility is determined based on a variety of factors, including income, assets, and family size. The program encompasses several eligibility categories, each with its own set of specific requirements:
- Low-income families: This category includes families with children who meet certain income thresholds.
- Pregnant women: Pregnant women with limited income are eligible for Medicaid, regardless of their family size.
- Children: Children under the age of 19 who meet specific income and asset requirements are eligible for Medicaid.
- Individuals with disabilities: Individuals with disabilities who meet certain income and asset criteria are eligible for Medicaid.
- Seniors: Individuals aged 65 and older who meet specific income and asset requirements are eligible for Medicaid.
History of Medicaid
Medicaid was established in 1965 as part of President Lyndon B. Johnson’s “Great Society” programs. Its initial purpose was to provide healthcare coverage to low-income families, children, and individuals with disabilities. Over the years, Medicaid has undergone significant evolution, expanding its scope and eligibility criteria to include additional populations, such as pregnant women and seniors.
Eligibility Requirements: Medicaid Eligibility
Medicaid eligibility is determined by a combination of factors, including income, assets, and residency. These requirements can vary slightly from state to state, but generally include:
General Eligibility Criteria
- Income Limits: Medicaid programs have income limits that individuals and families must meet to be eligible. These limits are based on the Federal Poverty Level (FPL), which is adjusted annually to account for inflation. For example, a family of four with an annual income below 138% of the FPL would typically qualify for Medicaid.
- Asset Limits: In addition to income, Medicaid programs often have asset limits, which restrict the amount of assets an individual or family can own to be eligible. These limits can vary by state and may exclude certain assets, such as a primary residence or retirement savings.
- Residency Requirements: Medicaid programs generally require applicants to be residents of the state in which they are applying for coverage. This requirement ensures that state resources are used to provide healthcare for its own residents.
Specific Eligibility Requirements for Different Groups
- Children: Children are typically eligible for Medicaid if their family income is below a certain threshold. Some states have expanded Medicaid coverage for children to include families with incomes above the FPL.
- Pregnant Women: Pregnant women are eligible for Medicaid regardless of their family income if they meet certain residency requirements. This expanded coverage is designed to ensure that pregnant women have access to prenatal care and other essential healthcare services.
- Individuals with Disabilities: Individuals with disabilities who meet certain income and asset requirements are eligible for Medicaid. These requirements can vary by state, but generally include a determination of disability by the Social Security Administration or a state agency.
State-Specific Eligibility Requirements
Eligibility requirements for Medicaid can vary significantly from state to state. Some states have expanded Medicaid coverage to include more individuals and families, while others have maintained more restrictive eligibility criteria. It is essential to contact your state’s Medicaid agency to determine the specific eligibility requirements in your area.
Application Process
Applying for Medicaid involves several steps, including:
Steps Involved in Applying
- Gather Required Documentation: Applicants must gather documentation to support their application, such as proof of income, residency, and identity. This documentation may include pay stubs, tax returns, utility bills, and identification cards.
- Submit Application: Applications for Medicaid can be submitted online, by mail, or in person at a local office. Some states offer online portals where applicants can complete and submit their applications electronically.
- Eligibility Verification: Once an application is submitted, state officials will verify the applicant’s eligibility based on the provided documentation. This process may involve contacting employers, banks, or other relevant parties to confirm income and asset information.
- Eligibility Determination: After verifying eligibility, state officials will make a determination regarding the applicant’s eligibility for Medicaid. If the applicant is deemed eligible, they will receive a notice of approval and a Medicaid card.
Documentation Required
The specific documentation required for a Medicaid application can vary by state. However, common documents include:
- Proof of income
- Proof of residency
- Proof of identity
- Proof of citizenship or immigration status
- Social Security numbers for all household members
- Medical documentation for individuals with disabilities
Verification and Determination Process
State Medicaid agencies have processes in place to verify eligibility and make determinations. These processes may involve:
- Income Verification: Verifying income information through pay stubs, tax returns, or other documentation.
- Asset Verification: Verifying asset information through bank statements, property records, or other documentation.
- Residency Verification: Verifying residency information through utility bills, driver’s licenses, or other documentation.
- Disability Determination: Assessing disability status through medical documentation or a state disability determination process.
Medicaid Benefits
Medicaid covers a wide range of medical services, including:
Types of Medical Services Covered
- Inpatient and Outpatient Hospital Services: Coverage for hospitalization, emergency room visits, and other outpatient services.
- Physician Services: Coverage for doctor visits, consultations, and other medical services provided by physicians.
- Prescription Drugs: Coverage for prescription medications, including generic and brand-name drugs.
- Mental Health Services: Coverage for mental health counseling, therapy, and other mental health services.
- Dental Services: Coverage for dental checkups, cleanings, fillings, and other dental services.
- Vision Services: Coverage for eye exams, eyeglasses, and other vision services.
- Long-Term Care: Coverage for nursing home care, assisted living, and other long-term care services for individuals who meet specific eligibility criteria.
Specific Benefits for Different Populations
Medicaid provides specific benefits for different populations, such as:
- Children: Coverage for well-child checkups, immunizations, and other preventive care services.
- Pregnant Women: Coverage for prenatal care, labor and delivery, and postpartum care.
- Individuals with Disabilities: Coverage for specialized medical services, rehabilitation services, and other supports to address their unique needs.
- Seniors: Coverage for long-term care services, including nursing home care and assisted living.
Limitations and Exclusions
While Medicaid covers a wide range of medical services, there are some limitations and exclusions:
- Cosmetic Procedures: Medicaid typically does not cover cosmetic procedures that are not medically necessary.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Medicaid generally does not cover over-the-counter medications.
- Non-Essential Services: Medicaid may not cover certain non-essential services, such as elective surgeries or alternative therapies.
Maintaining Eligibility
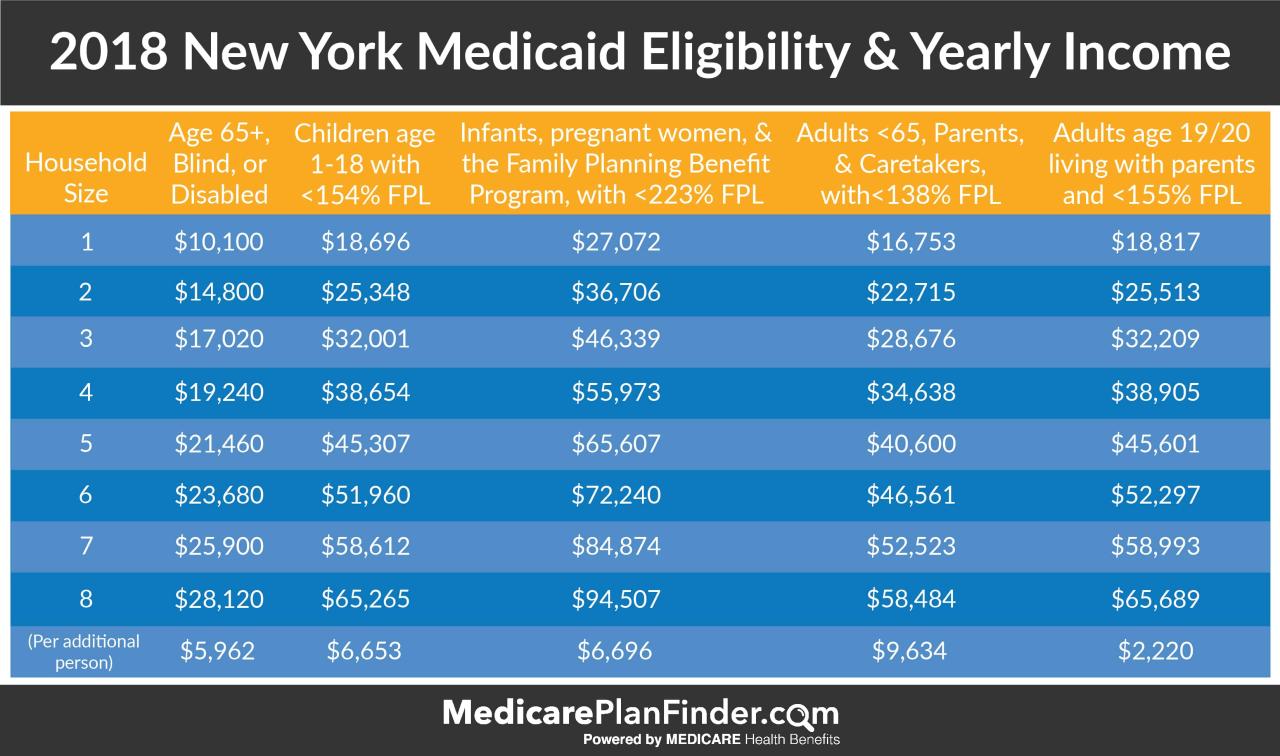
Medicaid eligibility is not permanent and can be affected by changes in circumstances:
Factors Affecting Eligibility
Several factors can affect Medicaid eligibility, including:
- Changes in Income: Increases or decreases in income can impact eligibility. Individuals must report any changes in income to their state Medicaid agency.
- Changes in Family Size: Changes in family size, such as the birth of a child or the addition of a new household member, can affect eligibility.
- Changes in Residency: Moving to a new state can affect Medicaid eligibility, as each state has its own eligibility requirements.
- Changes in Assets: Significant changes in assets, such as the sale of a property or inheritance, can impact eligibility.
Reporting Changes in Eligibility Factors
Individuals must report any changes in their eligibility factors to their state Medicaid agency. Failure to report changes can result in the loss of coverage or penalties.
Consequences of Failing to Maintain Eligibility, Medicaid eligibility
Individuals who fail to maintain Medicaid eligibility may face the following consequences:
- Loss of Coverage: Individuals may lose their Medicaid coverage if they no longer meet the eligibility requirements.
- Financial Penalties: Some states may impose financial penalties on individuals who fail to report changes in their eligibility factors.
- Debt for Unpaid Medical Bills: Individuals who receive medical services while ineligible for Medicaid may be responsible for paying for those services.
Challenges and Issues
Access to Medicaid can be challenging for some individuals and families:
Challenges Faced by Individuals and Families
Individuals and families may face several challenges in accessing Medicaid, including:
- Navigating Complex Eligibility Requirements: The eligibility requirements for Medicaid can be complex and confusing, making it difficult for individuals to determine their eligibility.
- Lack of Awareness of Medicaid Benefits: Some individuals may not be aware of the benefits available through Medicaid or how to apply for coverage.
- Limited Access to Application Assistance: Individuals may have difficulty accessing assistance with completing Medicaid applications, particularly those who are unfamiliar with the process or who lack access to technology.
- Discrimination and Bias: Some individuals may face discrimination or bias based on their race, ethnicity, or other factors, which can make it more difficult to access Medicaid.
Impact of Medicaid Eligibility on Healthcare Access and Outcomes
Medicaid eligibility has a significant impact on healthcare access and outcomes:
- Improved Access to Healthcare: Medicaid provides coverage for essential medical services, allowing individuals to access healthcare they might otherwise be unable to afford.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Studies have shown that Medicaid coverage can lead to improved health outcomes, such as lower mortality rates and improved access to preventive care.
- Reduced Unmet Healthcare Needs: Medicaid helps reduce unmet healthcare needs, allowing individuals to receive timely and appropriate medical care.
Potential Solutions to Improve Medicaid Eligibility and Access
Several potential solutions can improve Medicaid eligibility and access:
- Simplify Eligibility Requirements: Streamlining eligibility requirements and making them easier to understand can improve access to Medicaid.
- Expand Outreach and Education: Increasing awareness of Medicaid benefits and eligibility requirements can help individuals access the coverage they need.
- Increase Access to Application Assistance: Providing more resources and support for individuals completing Medicaid applications can help overcome barriers to access.
- Address Discrimination and Bias: Taking steps to address discrimination and bias in the Medicaid system can ensure equitable access to coverage for all individuals.
Ending Remarks
Navigating the world of Medicaid eligibility can be a daunting task, but understanding the program’s intricacies is crucial for those seeking affordable healthcare. By familiarizing yourself with the eligibility requirements, application process, and benefits available, you can empower yourself to access the healthcare you need.
Remember, resources are available to assist you throughout this process, and seeking guidance from qualified professionals can make the journey smoother.