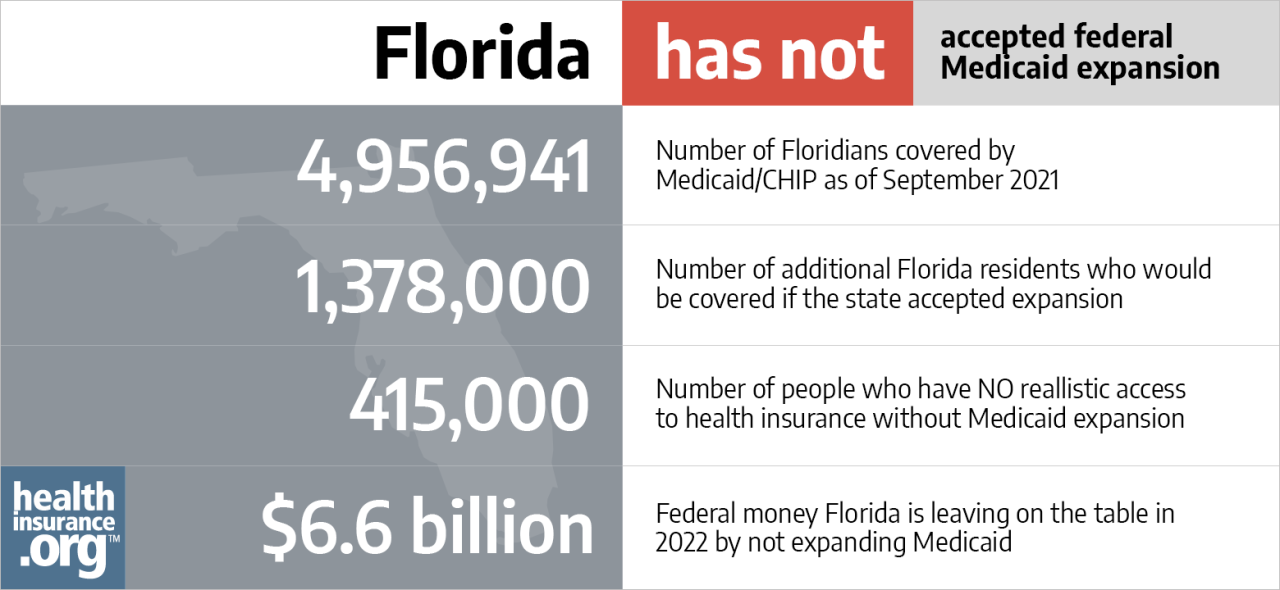
Medical coding is the language of healthcare, translating complex medical information into standardized codes used for billing, research, and data analysis. These codes, like ICD-10 and CPT, provide a universal system for understanding and communicating patient diagnoses, procedures, and treatments.
Ever wondered what “bid” means in a medical prescription? It’s actually a common abbreviation for “twice a day,” indicating the frequency of medication intake. If you’re ever unsure about a medical abbreviation, it’s always best to ask your doctor or pharmacist for clarification.
You can also find a comprehensive list of medical abbreviations, including “bid,” on the MDBP website , which provides valuable information for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
From its origins in the early 20th century, medical coding has evolved significantly, adapting to technological advancements and the growing complexity of healthcare. Accurate medical coding is crucial for ensuring proper reimbursement, tracking health trends, and improving patient care.
Introduction to Medical Coding
Medical coding is a crucial process in healthcare that involves translating medical documentation into standardized codes. These codes are used for a variety of purposes, including billing and reimbursement, tracking patient health data, and conducting research. Medical coders play a vital role in ensuring that healthcare providers receive appropriate compensation for their services, and that patients receive the care they need.
History of Medical Coding
The history of medical coding dates back to the early 20th century, when the American Medical Association (AMA) developed the first standardized coding system, known as the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code set. The goal was to create a uniform language for describing medical procedures and services, which would facilitate communication and billing between healthcare providers and insurance companies.
Over the years, medical coding has evolved significantly, with the development of new coding systems and the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs). Today, medical coding is a complex and ever-changing field, requiring specialized knowledge and skills.
You might see “BID” on a prescription and wonder what it means. It’s a common medical abbreviation that stands for “twice a day.” This means you would take the medication two times, usually at 12-hour intervals. If you’re unsure about the dosage or frequency of your medication, it’s always best to ask your doctor or pharmacist for clarification.
You can learn more about this abbreviation and others at bid medical abbreviation.
Importance of Accurate Medical Coding
Accurate medical coding is essential for the smooth functioning of the healthcare system. It ensures that healthcare providers are paid appropriately for the services they provide, that patients receive the correct care, and that healthcare data is collected and analyzed effectively.
Inaccurate coding can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Underpayment or non-payment for services
- Delays in patient care
- Inaccurate data for research and quality improvement
- Audits and penalties from government agencies
Types of Medical Coding
There are several different types of medical coding systems used in healthcare, each with its own purpose and application. Some of the most common types of medical coding include:
ICD-10-CM
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) is used to code diagnoses, symptoms, and other health conditions. It is a comprehensive coding system that includes over 14,000 codes, covering a wide range of medical conditions. The ICD-10-CM is used for billing, tracking patient health data, and conducting research.
CPT
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code set is used to code medical procedures and services. It includes over 10,000 codes, covering a wide range of medical procedures, from simple office visits to complex surgeries. The CPT is used for billing, tracking patient care, and conducting research.
HCPCS
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is a coding system that includes both CPT codes and Level II codes. Level II codes are used to code medical supplies, equipment, and services that are not covered by the CPT code set.
The HCPCS is used for billing and tracking patient care.
Comparison of Coding Systems
The different coding systems are used in conjunction with each other to provide a comprehensive picture of patient care. The ICD-10-CM codes are used to describe the patient’s diagnosis, while the CPT and HCPCS codes are used to describe the procedures and services provided.
The use of multiple coding systems can be complex, but it is essential for ensuring accurate billing and data collection.
The Medical Coding Process
The medical coding process involves a series of steps, from reviewing medical documentation to submitting claims to insurance companies. Here are the key steps in the medical coding process:
Reviewing Medical Documentation

The first step in the medical coding process is to review the medical documentation, such as patient charts, lab reports, and radiology reports. The coder must carefully review the documentation to identify the diagnosis, procedures, and services provided to the patient.
This step is crucial for ensuring accurate coding.
Assigning Codes
Once the coder has reviewed the medical documentation, they must assign the appropriate codes to the diagnosis, procedures, and services. This involves using the ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS code sets to select the most appropriate codes for the patient’s care.
Coding Accuracy
Coders must ensure that the codes they assign are accurate and reflect the patient’s care. They must be familiar with the coding guidelines and regulations to ensure that they are using the correct codes.
Submitting Claims, Medical coding
After the codes have been assigned, the coder must submit the claims to the insurance company. This involves using electronic health records (EHRs) or other software to generate the claims and submit them to the insurance company. The insurance company will then review the claims and determine the amount of reimbursement.
Role of Medical Coders
Medical coders play a vital role in the medical coding process. They are responsible for reviewing medical documentation, assigning codes, and submitting claims. They must be knowledgeable about the coding guidelines and regulations, as well as the different coding systems used in healthcare.
Use of EHRs
Electronic health records (EHRs) have revolutionized the medical coding process. EHRs allow coders to access patient data electronically, which makes the coding process more efficient and accurate. EHRs also help to reduce errors by providing automated coding tools and alerts.
Medical Coding Standards and Regulations
Medical coding is subject to a number of regulations and standards, which are designed to ensure accuracy, consistency, and compliance. These regulations and standards are enforced by government agencies and private organizations.
Key Regulations and Standards
- HIPAA:The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a federal law that protects patient health information. Medical coders must comply with HIPAA regulations when handling patient data.
- Medicare and Medicaid:The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has a number of regulations that govern medical coding for Medicare and Medicaid claims. These regulations ensure that providers are paid appropriately for the services they provide to Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries.
- ICD-10-CM and CPT Guidelines:The ICD-10-CM and CPT code sets are accompanied by guidelines that explain how to use the codes correctly. Medical coders must be familiar with these guidelines to ensure that they are using the codes appropriately.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with medical coding standards and regulations is essential for several reasons. It helps to ensure that:
- Patients receive the care they need.
- Healthcare providers are paid appropriately for the services they provide.
- Healthcare data is collected and analyzed accurately.
- The healthcare system is protected from fraud and abuse.
Consequences of Coding Errors
Coding errors can have serious consequences, including:
- Underpayment or non-payment for services.
- Delays in patient care.
- Audits and penalties from government agencies.
- Legal liability.
Challenges and Trends in Medical Coding
The field of medical coding is constantly evolving, with new challenges and trends emerging regularly. Medical coders must stay up-to-date on these changes to ensure that they are using the correct codes and complying with regulations.
Challenges Faced by Medical Coders
- Increasing Complexity:The medical coding system is becoming increasingly complex, with new codes and guidelines being introduced regularly. This makes it challenging for coders to keep up with the changes.
- Data Security:Medical coders must be aware of data security regulations, such as HIPAA, and take steps to protect patient health information. This can be a challenge, as healthcare data is often sensitive and valuable.
- High Demand:The demand for medical coders is high, which can lead to long hours and high levels of stress.
Emerging Trends in Medical Coding
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI is being used to automate some of the tasks involved in medical coding, such as code assignment and claim processing. This is expected to increase efficiency and reduce errors.
- Big Data:The increasing volume of healthcare data is creating new opportunities for data analysis and research. Medical coders will need to be able to work with large datasets and use data analytics tools.
- Telehealth:The growth of telehealth is creating new challenges and opportunities for medical coders. Coders will need to be familiar with the coding guidelines for telehealth services.
Future of Medical Coding
The future of medical coding is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, such as AI and big data. Medical coders will need to be adaptable and willing to learn new skills to stay ahead of the curve. The demand for medical coders is expected to remain high in the coming years, as the healthcare system continues to grow and evolve.
Education and Training for Medical Coders
To become a medical coder, you need to have the right education and training. This involves obtaining a formal education and certification to demonstrate your skills and knowledge.
Educational Requirements
While a college degree is not always required for medical coding, it can be beneficial to have an associate’s degree in health information management or a related field. Some employers may prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree, particularly for management or leadership roles.
Training Programs and Certifications
There are a number of training programs available for aspiring medical coders. These programs can be found at community colleges, technical schools, and online. Training programs typically cover the following topics:
- Medical terminology
- Anatomy and physiology
- ICD-10-CM, CPT, and HCPCS coding systems
- Medical coding guidelines and regulations
- EHR systems
After completing a training program, you can take a certification exam to demonstrate your competency as a medical coder. Some of the most common certifications include:
- Certified Professional Coder (CPC) from the American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC)
- Registered Health Information Technician (RHIT) from the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA)
Tips for Aspiring Medical Coders
- Develop Strong Medical Terminology Skills:Medical coding requires a strong understanding of medical terminology. You can improve your skills by taking courses or studying medical dictionaries.
- Stay Up-to-Date on Coding Guidelines:The coding guidelines are constantly changing. You need to stay up-to-date on these changes to ensure that you are using the correct codes.
- Network with Other Medical Coders:Networking with other medical coders can help you stay informed about industry trends and job opportunities.
Careers in Medical Coding
Medical coding offers a variety of career paths, from entry-level positions to management roles. The job outlook for medical coders is positive, as the demand for qualified professionals is expected to grow in the coming years.
Career Paths
- Entry-Level Medical Coder:This role typically involves reviewing medical documentation, assigning codes, and submitting claims.
- Senior Medical Coder:Senior medical coders often have more experience and may be responsible for training new coders or overseeing coding projects.
- Coding Manager:Coding managers are responsible for overseeing the coding department and ensuring that coding is accurate and compliant.
- Coding Auditor:Coding auditors review medical records and claims to ensure that coding is accurate and compliant.
Job Outlook
The job outlook for medical coders is positive. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment of medical coders will grow by 10% from 2020 to 2030, which is faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the aging population, the increasing use of electronic health records, and the growing demand for healthcare services.
Finding Employment
- Network:Networking with other medical coders can help you learn about job openings and get your foot in the door.
- Job Boards:Online job boards, such as Indeed and Monster, are good resources for finding medical coding jobs.
- Professional Organizations:Professional organizations, such as the AAPC and AHIMA, offer job boards and networking opportunities.
Last Point
As healthcare continues to evolve, medical coding will remain essential for navigating the complexities of the system. From understanding the intricacies of coding systems to navigating regulatory landscapes, medical coders play a vital role in ensuring efficient and effective healthcare delivery.