Youngchildren’s mental health statistics 2019 since 1999 in america – Young children’s mental health statistics 2019 since 1999 in america: From 1999 to 2019, the prevalence of mental health disorders among young children in America has been a growing concern. This article takes a comprehensive look at the data, analyzing trends, demographic factors, risk and protective factors, treatment and services, and policy and prevention efforts.
The data shows a significant increase in the rates of anxiety, depression, and ADHD among young children over the past two decades. This increase is particularly concerning given the long-term impact that mental health disorders can have on a child’s development and well-being.
Mental health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and cultural influences play a significant role in shaping it. As highlighted by the Mental Health Association of Maryland, your culture influences your mental and emotional health apex . Culture can influence our beliefs, values, and behaviors, which in turn impact our mental and emotional states.
Recognizing and understanding these cultural influences can empower individuals to make informed decisions that support their mental health.
Mental Health Trends Over Time
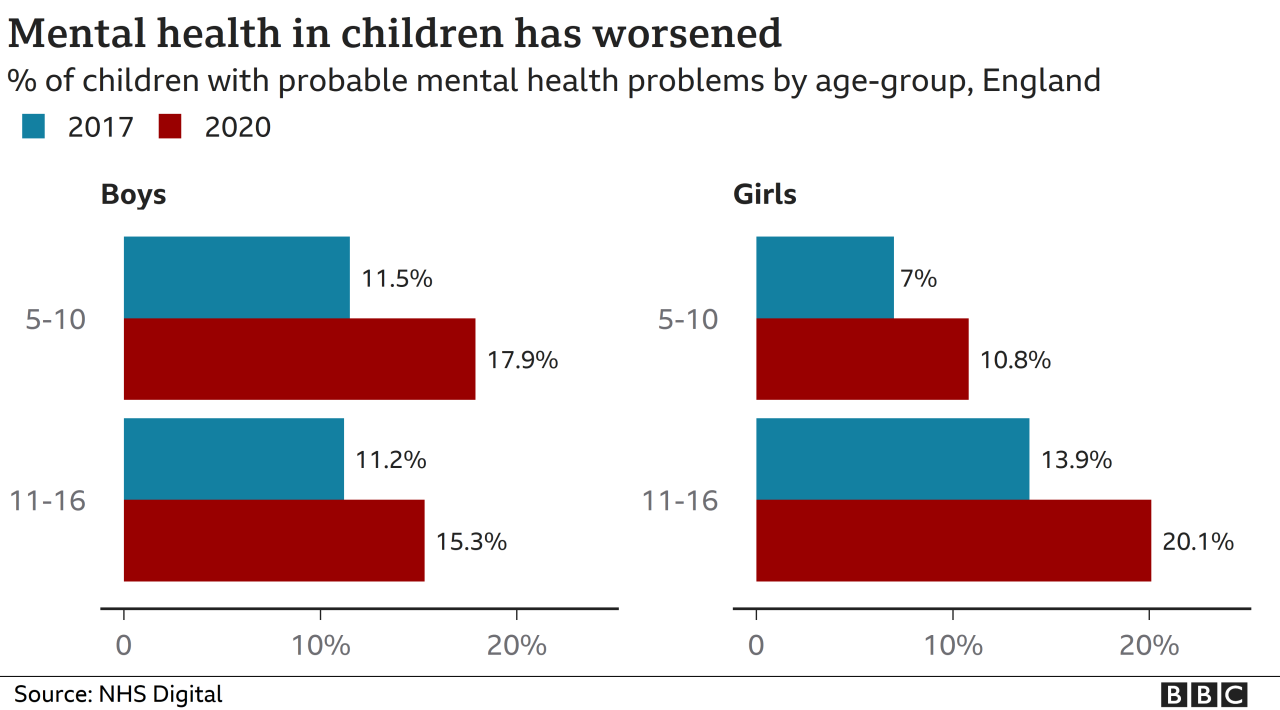
Mental health disorders among young children in America have been on the rise since 1999. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the prevalence of anxiety disorders among children aged 3-17 increased from 5.4% in 1999 to 8.3% in 2019. The prevalence of depression increased from 2.5% to 4.4% during the same period, while the prevalence of ADHD increased from 5.6% to 9.4%.
Comparison of Disorder Rates
- Anxiety disorders are the most common mental health disorder among young children, affecting 8.3% of children aged 3-17 in 2019.
- Depression is the second most common disorder, affecting 4.4% of children aged 3-17 in 2019.
- ADHD is the third most common disorder, affecting 9.4% of children aged 3-17 in 2019.
Significant Changes and Patterns
The increase in the prevalence of mental health disorders among young children is a significant public health concern. The CDC reports that the increase in anxiety disorders has been particularly pronounced among girls, with the prevalence increasing from 4.5% in 1999 to 10.1% in 2019. The increase in depression has also been more pronounced among girls, with the prevalence increasing from 1.9% in 1999 to 5.8% in 2019.
Demographic Factors
Impact of Age, Gender, Race, and Socioeconomic Status
Demographic factors such as age, gender, race, and socioeconomic status can all impact a young child’s mental health. Younger children are more likely to experience anxiety disorders, while older children are more likely to experience depression and ADHD. Girls are more likely to experience anxiety and depression than boys, while boys are more likely to experience ADHD.
In the context of children, mental health takes precedence over academic performance. As the Mental Health Association of Maryland emphasizes, your child’s mental health is more important than their grades . Children’s mental health directly affects their overall well-being, development, and academic success.
Parents and educators should prioritize fostering a supportive environment that encourages children to express their emotions, develop healthy coping mechanisms, and seek help when needed.
Children from racial and ethnic minority groups are more likely to experience mental health disorders than white children. Children from low-income families are also more likely to experience mental health disorders than children from high-income families.
Disparities in Access to Care and Treatment
There are significant disparities in access to mental health care and treatment for young children based on demographic factors. Children from racial and ethnic minority groups are less likely to receive mental health care than white children. Children from low-income families are also less likely to receive mental health care than children from high-income families.
These disparities in access to care can lead to worse mental health outcomes for children from marginalized communities.
Role of Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health, such as poverty, housing instability, and food insecurity, can all contribute to mental health problems in young children. Children who live in poverty are more likely to experience mental health disorders than children who do not live in poverty.
Children who live in unstable housing are also more likely to experience mental health disorders than children who live in stable housing. Children who are food insecure are also more likely to experience mental health disorders than children who are food secure.
Risk and Protective Factors: Youngchildren’s Mental Health Statistics 2019 Since 1999 In America
Risk Factors for Mental Health Problems
There are a number of risk factors that can contribute to mental health problems in young children. These risk factors include:
- Family history of mental illness
- Exposure to trauma or abuse
- Poverty
- Housing instability
- Food insecurity
- Parental mental illness
- Parental substance abuse
Protective Factors for Mental Health
There are also a number of protective factors that can promote resilience and prevent mental health disorders in young children. These protective factors include:
- Strong family relationships
- Supportive school environment
- Access to mental health care
- Positive coping skills
- Healthy lifestyle
Effective Interventions
There are a number of effective interventions that can target risk and protective factors and promote mental health in young children. These interventions include:
- Family-based therapy
- School-based mental health services
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Medication
Treatment and Services
Types of Mental Health Treatments and Services
There are a variety of mental health treatments and services available for young children in America. These treatments and services include:
- Individual therapy
- Group therapy
- Family therapy
- Medication
- Hospitalization
Effectiveness of Different Treatments and Interventions
The effectiveness of different mental health treatments and interventions varies depending on the individual child and the specific disorder being treated. However, research has shown that family-based therapy, school-based mental health services, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and medication can all be effective in treating mental health disorders in young children.
Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Care
There are a number of barriers that can prevent young children from accessing mental health care. These barriers include:
- Stigma associated with mental illness
- Lack of insurance
- Transportation difficulties
- Long wait times for appointments
Policy and Prevention
Role of Public Policy
Public policy can play a significant role in promoting young children’s mental health. Policies that support families, schools, and communities can help to create environments that are conducive to good mental health. These policies include:
- Expanding access to mental health care
- Providing funding for mental health research
- Promoting mental health literacy
- Reducing stigma associated with mental illness
Effectiveness of Prevention Programs and Initiatives
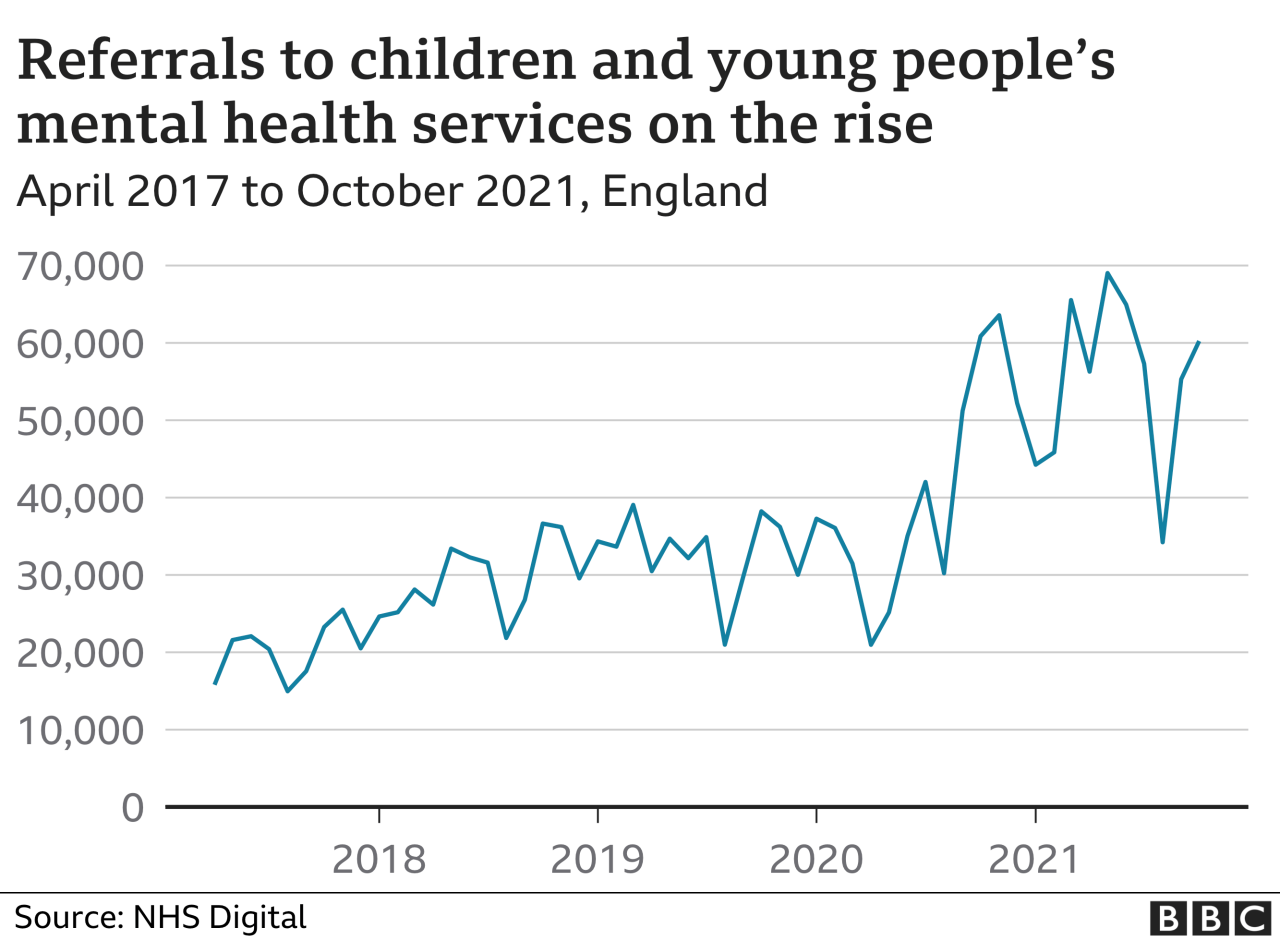
Prevention programs and initiatives can be effective in reducing the risk of mental health disorders in young children. These programs and initiatives typically focus on teaching children coping skills, promoting resilience, and creating supportive environments. Research has shown that prevention programs can be effective in reducing the risk of anxiety, depression, and ADHD.
Recommendations for Improving Mental Health Policies and Services, Youngchildren’s mental health statistics 2019 since 1999 in america
There are a number of recommendations that can be made for improving mental health policies and services for young children. These recommendations include:
- Increasing funding for mental health care
- Expanding access to mental health care in schools
- Training more mental health professionals to work with young children
- Reducing stigma associated with mental illness
- Promoting mental health literacy
Summary
In conclusion, the mental health of young children in America is a critical issue that requires attention and action. By understanding the trends, risk factors, and protective factors, we can develop more effective interventions and policies to promote the mental health of our youngest citizens.
